Abstract
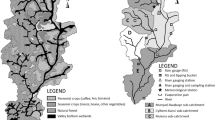
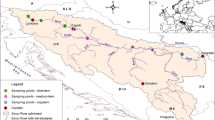
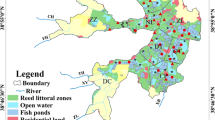
The objective of this study was to identify the spatial and temporal variabilities of selected nutrients in the Setiu Wetlands Lagoon (SWL), Malaysia. Water samples were collected quarterly at ten monitoring sites. This study presents results from a 10-year field investigation (2003 to 2010 and 2014 to 2015) of water quality in the SWL. For the spatial pattern, four clusters were identified with hierarchical cluster analysis. Analysis of the temporal trend shows that the high total suspended solid loading in 2010 was due to large-scale land clearing upstream of the SWL. The enrichment of ammonium after 2010 could plausibly be due to land-based aquaculture diffuse discharges. In 2005–2007, expansion of oil palm plantations within the Setiu catchment had doubled the phosphorus concentration in the SWL. The natural and anthropogenic alterations of the lagoon inlets profoundly influenced the spatial distribution patterns of nutrients in the SWL. These results suggest that intense anthropogenic disturbances close to the SWL accounted for the water quality deterioration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida, C. A., Quintar, S., Gonzalez, P., & Mallea, M. A. (2007). Influence of urbanization and tourist activities on the water quality of the Potrero delos Funes River (San Luis – Argentina). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 133, 459–465.
APHA. (1998). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (20th ed.). New York: American Public Health Association.
Bazilah M. Z. (2008). The effect of monsoon on the distribution of inorganic nitrogen and total nitrogen in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Science. Faculty of Maritime and Marine Science, University Malaysia, Terengganu, Terengganu. 101p.
Brock, D. A. (2001). Nitrogen budget for low and high freshwater inflows, Nueces Estuary. Texas. Estuaries and Coasts, 24(4), 509–521.
Chang, C. C., Kendall, C., Silva, S. R., Battaglin, W. A., & Campbell, D. H. (2002). Nitrate stable isotopes: tools for determining nitrate sources among different land uses in the Mississippi River Basin. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 59(12), 1874–1885.
Chong, V. C. (2007). Mangrove-fishery linkages: the Malaysian perspective. Bulletin of Marine Science, 80, 755–772.
Chung, W. N. (2005). Distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu, South China Sea. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Biology. Faculty of Science and technology, College University Science and Technology Malaysia, Terengganu. 107p.
Cuach, L. F. (2004). Nitrogen and phosphorus in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Science Faculty of Science and technology, College University Science and Technology Malaysia, Terengganu.
Devlin, M. J., Massoudb, M. S., Hamidb, S. A., Al-Zaidan, A., Al-Sarawi, H., Al-Enezi, M., Al-Ghofran, L., Smith, A. J., Barryc, J., Stentiford, G. D. d., Morris, S., da Silva, E. T., & Lyons, B. P. (2015). Changes in the water quality conditions of Kuwait’s marine waters: Long term impacts of nutrient enrichment. Marine Pollution Bulletin., 100(2), 607–620.
Ellis, A. M., Culver, S. J., Mallinson, D. J., Corbett, D. R., Leorri, E., Buzas, M. A., & Shazili, N. A. M. (2014). The influence of aquaculture on modern foraminefera and sediments in the Setiu estuary and lagoon, Terengganu: A spatial investigation. The Journal of Foraminiferal Research, 44(4), 390–415.
Emiliana, V., Federico, F., Alessandra, N. X., Francesco, M. P., & Andrea, T. (2016). Earth observation for maritime spatial planning: measuring, observing and modeling marine environment to assess potential aquaculture sites. Sustainability, 8, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060519.
Forestry Department Peninsula Malaysia (FOR) (2005) Forestry Development. Available at: http://www.forestry.gov.my/eDevelopment.html. Accessed 13/12/05.
Hayati, N. (2013). Distribution and cycling of nitrogen and carbon-based nutrients in Setiu Wetlands, Terengganu. Posgraduate thesis, Master in Science Institue of Ocenanography & Environment, University Malaysia Terengganu.
Jabatan Pengaliran dan Saliran Malaysia (JPS). 2016. Department of Irrigation and Drainage Malaysia. Ministry of natural resources and environment Malaysia. http://infobanjir.water.gov.my/. Accessed Oct 10 2016.
Jamilah, M. S., Nik Fuad, N. K., & Ibrahim, K. (2015). Managing Setiu wetlands for ecosystem services. In F. Mohamad, J. M. Salim, J. M. Jani, & R. Shahrudin (Eds.), Setiu Wetlands: Species, Ecosystems and Livelihoods (pp. 217–228). Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia: Penerbit Universiti Malaysia Terengganu.
Kamaruzaman, J., & Dahlan, H. T. (2008). Managing sustainable mangrove forests in Peninsular Malaysia. Journal of Sustainable Development., 1(1), 88–96.
Karie Ng, K.L. (2006). Distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu, South China Sea. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Biology Faculty of Science and technology, College University Science and Technology Malaysia, Terengganu. 123p.
Kendall, C., & Caldwell, E. A. (1998). Fundamentals of isotope geochemistry. In C. Kendall & J. J. McDonnell (Eds.), Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology (pp. 51–86). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science B.V.
Koh, M. K., Sathiamurthy, E., Suratman, S., & Mohd Tahir, N. (2012). Sandbar-regulated hydrodynamic influences on river hydrochemistry at Mengabang Telipot River, Peninsular Malaysia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(12), 7653–7664.
Lim, S. K. (2005). Primary productivity in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Biology. Faculty of Science and technology, College University Science and Technology Malaysia, Terengganu. 99p.
Lim, S. C. (2007). Distribution of dissolved phosphorus and orthophosphate in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Science Faculty of Maritime and Marine Science, University Malaysia, Terengganu, Terengganu. 94p.
Ling, S. M., Ramchandran, S., Shuib, A., Nair, M., Syamsul Herman, M. A., & Prabhakaran, S. (2013). Rural resources as tourism capital: The case of Setiu Wetlands, Terengganu, Malaysia. The Malaysian Forester, 76(1), 27–39.
Mahmud, A. I., Emiru, K. T., & Viez, E. R. (2015). Aquaculture Activities in Mangroves, Peninsular Malaysia. World Applied Sciences Journal, 33(4), 684–689.
Malaysian Wetland Working Group (MWWG) (1987). Malaysian wetland directory, Vol. 1: Introduction (p. 55). Peninsular Malaysia: Department of Wildlife and National Parks.
Middelburg, J. J., & Nieuwenhuize J. (2000). Nitrogen uptake by heterotrophic bacteria and phytoplankton in the nitrate-rich Thames estuary. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 203, 13–21.
Nur Syahirah, Y. (2008). A study of distribution of orthophosphate and total phosphours in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Science Faculty of Maritime and Marine Science, University Malaysia, Terengganu, Terengganu. 87p.
Nuuru, A. A. R. (2012). Distribution and cycling of phosphorus and silicon- based nutrients in Setiu Wetlands, Terengganu. Posgraduate thesis, Master in Science Institue of Ocenanography & Environment, University Malaysia Terengganu.
O’Donnell, J. (1990). The formation and fate of a river plume: a numerical model. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 20, 551–569.
Olila, O. G., Reddy, K. R., & Stites, D. L. (1997). Influence of draining on soil phosphorus forms and distribution in a constructed wetland. Ecological Engineering, 9, 157–169.
Ortega-Cisneros, K., Scharler, U. M., & Whitfield, A. K. (2014). Inlet mouth phase influences density, variability and standing stocks of plankton assemblages in temporarily open/closed estuaries. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 136, 139–148.
Rosnan, Y., Mohd, L. H., & Noor, A. M. S. (1995). Grain-size distribution of sediment in the vicinity of Setiu lagoon-estuary system. Pertanika Journal of Tropical Agricultural Science, 18(1), 71–76.
Sathiamurthy, E. (2015). Setiu River Basin: a brief account of the hydrologic connections of Setiu Wetlands. In F. Mohamad, J. M. Salim, J. M. Jani, & R. Shahrudin (Eds.), Setiu Wetlands: Species, Ecosystems and Livelihoods (pp. 101–109). Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia: Penerbit Universiti Malaysia Terengganu.
Seah, B. P. (2004). Chlorophyll a and primary productivity in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Science Faculty of Science and technology, College University Science and Technology Malaysia, Terengganu. 91p.
See, H. C. (2006). Primary productivity and chlorophyll-a in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu, South China Sea. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Biology Faculty of Science and technology, College University Science and Technology Malaysia, Terengganu. 134p.
Setiu District Local Plan (RTDS). (2006). Official portal of Setiu District Council. http://mds.terengganu.gov.my/en/citizens/setiu-district-local-plan-rtds/page/0/8. Accessed 20 Dec 2016
Siew, K. S. (2004). Hydrology survey in Setiu Lagoon. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Biology Marine, Faculty of Science and Technology, Kolej Universiti Sains dan Teknologi Malaysia, Terengganu. 136p.
Soetaert, K., Middelburg, J. J., Heip, C., Meire, P., Van Damme, S., & Maris, T. (2006). Long-term change in dissolved inorganic nutrients in the heterotrophic Scheldt estuary (Belgium, the Netherlands). Limnology and Oceanography, 51(1part2), 409–423.
Suratman, S., Mohd Tahir, M., Jusoh, S., & Ariffin, M. (2005). Assessment of anthropogenic effects on water quality in Setiu Wetlands. Terengganu. Sains Malaysiana, 34, 87–92.
Suratman, S., Husein, A., Latif, M. T., & Weston, K. (2014). Reassessment of physico-chemical water quality in Setiu Wetlands. Malaysia. Sains Malaysiana., 43, 1127–1131.
Tan, L. Y. (2007). Distribution of total dissolved nitrogen and organic nitrogen in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Science Faculty of Maritime and Marine Science, University Malaysia, Terengganu, Terengganu. 132p.
Tan, C. L. (2016). Safeguarding the wetlands of Setiu. Star 2. http://www.star2.com/living/livingenvironment/2016/05/03/safeguarding-the-wetlands-of-setiu. Accessed 20 December 2016.
Teoh, B. S. (2007). Primary productivity and chloropyll-a in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Science Faculty of Maritime and Marine Science, University Malaysia, Terengganu, Terengganu.
Wankel, S. D., Kendall, C., Francis, C. A., & Paytan, A. (2006). Nitrogen sources and cycling in the San Francisco Bay Estuary: A nitrate dual isotopic composition approach. Limnology and Oceanography, 51(4), 1654–1664.
Wilkie, M. L. (2007). Mangroves of Asia 1980–2005: COUNTRY REPORTS. Rome: Forestry Department Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Working Paper 137.
Wilson, M. A., Costanza, R., Boumans, R. M. J., & Liu, S. L. (2005). Intergrated assessment and valuation of ecosystem goods and services provided by coastal systems. In J. G. Wilson (Ed.), 1-24 pp The Intertidal Ecosystem. Dublin, Ireland: Royal Irish Academy Press.
WWF-Malaysia. (2014). Setiu Wetlands: The hidden gem of Terengganu. Petaling Jaya, Selangor: WWF-Malaysia.
Yip, L.V. (2008). Monsoon effects on primary productivity, chloropyll-a and total suspended solids (TSS) in Setiu Lagoon, Terengganu. Undergraduate thesis, Bachelor of Science in Marine Science Faculty of Maritime and Marine Science, University Malaysia, Terengganu, Terengganu. 118p.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Wan FA Jusoh, L.C. Yap, P.Z. Loh and K. Saudarasan for assistance with sample collection and processing. Thanks to Dr. Rose Norman for assistance with proof reading of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Ministry of Higher Education of Malaysia through Niche Research Grant Scheme (NRGS-53131) and WWF-Malaysia (53173).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poh, S.C., Ng, N.C.W., Suratman, S. et al. Nutrient availability in the Setiu Wetland Lagoon, Malaysia: trends, possible causes and environmental impacts. Environ Monit Assess 191, 3 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7128-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7128-y