Abstract
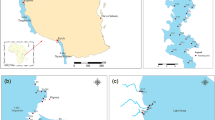
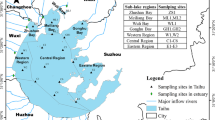
Baiyangdian Lake (BYD), a large shallow lake in North China, has complex water landscape patterns that are underlies spatial variations in water quality. In this study, we collected 61 water samples from three water landscapes (reed littoral zones, fish ponds, and open water) and analyzed them for water quality parameters, such as dissolved organic carbon (DOC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP). Water landscape distribution (determined using remote sensing imagery) was then used to assess correlations between water quality parameters and water landscape proportion in differently scaled buffer zones. There was substantial variation across all subareas, with TN and TP concentrations ranging from 0.90 to 4.10 mg/L and 0.06 to 0.18 mg/L, respectively, in class IV of water quality as a whole. Spatial variations in water quality were mainly caused by water landscape distribution and external nutrient inputs. There were negative correlations between DOC, TN, and TP concentrations and the area proportion of reed littoral zones in the 300 and 500 m buffers. In contrast, DOC, TN, and TP concentrations were significantly positively correlated with the area proportion of fish ponds in the 100 m buffer. Furthermore, compared with reed littoral zones, a lower ratio of nitrogen to phosphorus and a higher proportion of dissolved organic nitrogen and tyrosine-like proteins were found in fish ponds. These effects were mainly attributed to the development of internal sediment loadings due to nutrient exchange across the sediment–water interface. Therefore, dredging-based sediment removal from fish ponds should be considered to suppress internal phosphorus loading and accelerate recovery of the BYD ecosystem.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Chen C, Kong M, Wang YY, Shen QS, Zhong JC, Fan CX (2020) Dredging method effects on sediment resuspension and nutrient release across the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(21):25861–25869
Han Q, Tong R, Sun W, Zhao Y, Yu J, Wang G, Shrestha S, Jin Y (2020) Anthropogenic influences on the water quality of the Baiyangdian Lake in North China over the last decade. Sci Total Environ 701:134929
Herbeck LS, Unger D, Wu Y, Jennerjahn TC (2013) Effluent, nutrient and organic matter export from shrimp and fish ponds causing eutrophication in coastal and back-reef waters of NE Hainan, tropical China. Cont Shelf Res 57:92–104
Horppila J (2019) Sediment nutrients, ecological status and restoration of lakes. Water Res 160:206–208
Hu SS, Liu CM, Zheng HX, Wang ZG, Yu JJ (2012) Assessing the impacts of climate variability and human activities on streamflow in the water source area of Baiyangdian Lake. J Geogr Sci 22(5):895–905
Huisman J, Codd GA, Paerl HW, Ibelings BW, Verspagen JMH, Visser PM (2018) Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat Rev Microbiol 16(8):471–483
Ji Z, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Chen T, Long Z, Li M, Pei Y (2019) Distribution, ecological risk and source identification of heavy metals in sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake, Northern China. Chemosphere 237:124425
Lee SW, Hwang SJ, Lee SB, Hwang HS, Sung HC (2009) Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc Urban Plan 92(2):80–89
Lu D, Kang Z, Yang B, Dan SF, Zhang D, Zhang P, Huang H, Zhong Q (2020) Compositions and spatio-temporal distributions of different nitrogen species and lability of dissolved organic nitrogen from the Dafengjiang River to the Sanniang Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 156:111205
Lurling M, Faassen EJ (2012) Controlling toxic cyanobacteria: effects of dredging and phosphorus-binding clay on cyanobacteria and microcystins. Water Res 46(5):1447–1459
Lusk MG, Toor GS (2016) Biodegradability and molecular composition of dissolved organic nitrogen in urban stormwater runoff and outflow water from a stormwater retention pond. Environ Sci Technol 50(7):3391–3398
Lv SC, Wang F, Yan WJ, Wang YC, Yu QB, Li YQ (2019) DOC fluorescence properties and degradation in the Changjiang River Network, China: implications for estimating in-stream DOC removal. Biogeochemistry 145(3):255–273
Mainali J, Chang H (2018) Landscape and anthropogenic factors affecting spatial patterns of water quality trends in a large river basin, South Korea. J Hydrol 564:26–40
Markovic S, Liang AQ, Watson SB, Guo J, Mugalingam S, Arhonditsis G, Morley A, Dittrich M (2019) Biogeochemical mechanisms controlling phosphorus diagenesis and internal loading in a remediated hard water eutrophic embayment. Chem Geol 514:122–137
Meng F, Huang G, Yang X, Li Z, Li J, Cao J, Wang Z, Sun L (2013) Identifying the sources and fate of anthropogenically impacted dissolved organic matter (DOM) in urbanized rivers. Water Res 47(14):5027–5039
Nobre RLG, Caliman A, Cabral CR, Araujo FC, Guerin J, Dantas F, Quesado LB, Venticinque EM, Guariento RD, Amado AM, Kelly P, Vanni MJ, Carneiro LS (2020) Precipitation, landscape properties and land use interactively affect water quality of tropical freshwaters. Sci Total Environ 716:137044
Parsons CT, Rezanezhad F, O’Connell DW, Van Cappellen P (2017) Sediment phosphorus speciation and mobility under dynamic redox conditions. Biogeosciences 14(14):3585–3602
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (2002) Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis methods, 4th edn. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, pp 210–213
Tu L, Jarosch KA, Schneider T, Grosjean M (2019) Phosphorus fractions in sediments and their relevance for historical lake eutrophication in the Ponte Tresa basin (Lake Lugano, Switzerland) since 1959. Sci Total Environ 685:806–817
Varol M (2020) Spatio-temporal changes in surface water quality and sediment phosphorus content of a large reservoir in Turkey. Environ Pollut 259:113860
Wang F, Wang X, Zhao Y, Yang ZF (2014) Long-term periodic structure and seasonal-trend decomposition of water level in Lake Baiyangdian, Northern China. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(2):327–338
Wang F, Zhao Y, Xie SL, Li JY (2017) Implication of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria for nitrogen removal in a shallow lake. Clean Soil Air Water 45(4):1500319
Welch EB, Cooke GD (2005) Internal phosphorus loading in shallow lakes: importance and control. Lake Reserv Manag 21(2):209–217
Xia LL, Liu RZ, Zao YW (2012) Correlation analysis of landscape pattern and water quality in Baiyangdian watershed. Procedia Environ Sci 13:2188–2196
Xie YJ, Yu XJ, Ng NC, Li K, Fang L (2018) Exploring the dynamic correlation of landscape composition and habitat fragmentation with surface water quality in the Shenzhen river and deep bay cross-border watershed, China. Ecol Indic 90:231–246
Yang C, Yang P, Geng J, Yin H, Chen K (2020) Sediment internal nutrient loading in the most polluted area of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Chaohu, China) and its contribution to lake eutrophication. Environ Pollut 262:114292
Yu J, Fan C, Zhong J, Zhang Y, Wang C, Zhang L (2016) Evaluation of in situ simulated dredging to reduce internal nitrogen flux across the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Pollut 214:866–877
Zhang Y, Song C, Ji L, Liu Y, Xiao J, Cao X, Zhou Y (2018) Cause and effect of N/P ratio decline with eutrophication aggravation in shallow lakes. Sci Total Environ 627:1294–1302
Zhao Y, Song K, Li S, Ma J, Wen Z (2016) Characterization of CDOM from urban waters in Northern-Northeastern China using excitation-emission matrix fluorescence and parallel factor analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(15):15381–15394
Zhu Y, Jin X, Tang W, Meng X, Shan B (2019) Comprehensive analysis of nitrogen distributions and ammonia nitrogen release fluxes in the sediments of Baiyangdian Lake, China. J Environ Sci 76:319–328
Funding
This research was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2018ZX07110004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Liqing Li gave the idea of this research work. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Liqing Li and Xinghong Chen. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Liqing Li and Xinghong Chen. Meiyi Zhang, Weijun Zhang, Dongsheng Wang, and Hongjie Wang helped the work with his ideas and made a critical editing and reviewing of the whole manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Chen, X., Zhang, M. et al. The spatial variations of water quality and effects of water landscape in Baiyangdian Lake, North China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 16716–16726 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16938-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16938-0