Abstract
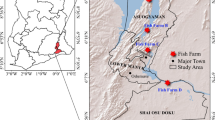
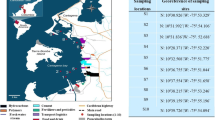
The presented results include decade of monitoring of the Vistula Lagoon waters and have been supplemented by the determination of chlorinated compounds, as well as on concentrations of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) in the sedimentation zone. Monitoring of river waters entering the Polish part of the lagoon and the lagoon waters confirmed the presence of plant protection chemical; the largest contributors has lindane (34%) and DDTtotal (21%); the same as for sediments were dominate lindane (19%) and DDTtotal (14%) within pp-DDT isomer dominate (13%). In the lagoon water, PCDD/Fs were determined within a range of 1.5–5.6 ng dm−3, leading to average toxicity of 0.18 ± 0.13 ng TEQ·dm−3. In sediments, their concentrations fell within a range of 22.7–405.7 ng kg−1 dw and the average toxicity of the lagoon sediments was set at 5.00 ± 1.98 ng TEQ·kg−1 dw. Both in water and sediments, the greatest share among PCDD/Fs has octa-chlorodibenzodioxin. Due to the hydromorphological conditions of the lagoon, the waters are mixed to the bottom causing the surface layer of sediment to become remobilized—this is suggested as the key factor when it comes to water recontamination and increased access of POPs to marine organisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Durante, C. A., Santos-Neto, E. B., Azevedo, A., Crespo, E. A., & Lailson-Brito, J. (2016). POPs in the South Latin America: Bioaccumulation of DDT, PCB, HCB, HCH and Mirex in blubber of common dolphin (Delphinus delphis) and Fraser’s dolphin (Lagenodelphis hosei) from Argentina. Science of the Total Environment, 572, 352–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.176.
Elmquist, M., Gustafsson, Ö., & Andersson, P. (2004). Quantification of sedimentary black carbon using the chemothermal oxidation method: an evaluation of ex situ pretreatments and standard additions approaches. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 2(12), 417–427.
Gerber, R., Smit, N. J., Van Vuren, J. H., Nakayama, S. M., Yohannes, Y. B., Ikenaka, Y., Ishizuka, M., & Wepener, V. (2016). Bioaccumulation and human health risk assessment of DDT and other organochlorine pesticides in an apex aquatic predator from a premier conservation area. Science of the Total Environment, 550, 522–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.129.
Kosior, M., Barska, I., & Domagala-Wieloszewska, M. (2002). Heavy metals, sigma DDT and sigma PCB in the gonads of pikeperch females spawning in southern Baltic Sea lagoons. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 11(2), 127–134.
Lassen, C., Hansen, E., Jensen, A. A., Olendrzyński, K., Kolsut, W., Żurek, J., Kargulewicz, I., Debski, B., Skośkiewicz, J., Holtzer, M., Grochowalski, A., Brante, E., Poltimae, H., Kallaste, T., & Kapturauskas, J. (2003). Survey of dioxin sources in the Baltic Region (extended summary). Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 10(1), 49–56.
Lee, S. Y., Dunn, R. J. K., Young, R. A., Connolly, R. M., Dale, P. E. R., Dehayr, R., & Welsh, D. T. (2006). Impact of urbanization on coastal wetland structure and function. Austral Ecology, 31(2), 149–163.
Nieczaj IJ, Silicz MW, Jabłońska T (1975) Hydrografia zlewiska zalewu. In: Łazarienko NN, Majewski A (ed) Hydrometeorologiczny ustrój Zalewu Wiślanego. IMGW, Wydawnictwa Komunikacji i Łączności, Warszawa, pp 21–28.
Onuska, F. I., & Terry, K. A. (1993). Extraction of pesticides from sediments using a microwave technique. Chromatographia, 36(1), 191–194.
Pegoraro, C. N., Harner, T., Su, K., & Chiappero, M. S. (2016). Assessing levels of POPs in air over the South Atlantic Ocean off the coast of South America. Science of the Total Environment, 571, 172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.149.
Rappe, C. (1994). Dioxin, patterns and source identification. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 348(1), 63–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00321606.
Reindl, A., Falkowska, L., Szumiło, E., & Staniszewska, M. (2013). Residue of chlorinated pesticides in fish caught in the Southern Baltic. Oceanol Hydrobiol, 42(3), 251–259. https://doi.org/10.2478/s13545-013-0081-z.
Sapota, G. (2006). Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in bottom sediments from the Baltic Sea. Oceanol Hydrobiol, 35(4), 295–306.
Staniszewska, M., Boniecka, H., & Gajecka, A. (2013). Organochlorine, organophosphoric and organotin contaminants, aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals in sediments of the ports from the Polish part of the Vistula Lagoon (Baltic Sea). Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 22(2), 151–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2013.722137.
Sun, J., Pan, L., Zhan, Y., Lu, H., Tsang, D. C., Liu, W., Wang, X., Li, X., & Zhu, L. (2016). Contamination of phthalate esters, organochlorine pesticides and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in agricultural soils from the Yangtze River Delta of China. Science of the Total Environment, 544, 670–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.012.
Sundqvist, K. L., Tysklind, M., Geladi, P., Cato, I., & Wiberg, K. (2009). Congener fingerprints of tetra-through octa-chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in Baltic surface sediments and their relations to potential sources. Chemosphere, 77(5), 612–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.08.057.
Szlinder-Richert, J., Usydus, Z., & Drgas, A. (2012). Persistent organic pollutants in sediment from the southern Baltic: risk assessment. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 14(8), 2100–2107. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2em30221g.
Van den Berg, M., Birnbaum, L. S., Denison, M., De Vito, M., Farland, W., Feeley, M., Fiedler, H., Hakansson, H., Hanberg, A., Haws, L., Rose, M., Safe, S., Schrenk, D., Tohyama, C., Tritscher, A., Tuomisto, J., Tysklind, M., Walker, N., & Peterson, R. E. (2006). The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicological Sciences, 93(2), 223–241. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfl055.
Verta, M., Salo, S., Korhonen, M., Assmuth, T., Kiviranta, H., Koistinen, J., Ruokojärvi, P., Isosaari, P., Bergqvist, P. A., Tysklind, M., Cato, I., Vikelsøe, J., & Larsen, M. M. (2007). Dioxin concentrations in sediments of the Baltic Sea—a survey of existing data. Chemosphere, 67(9), 1762–1775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.125.
Wypych K, Nieczaj IJ, Sołowiew II, Jaworska M (1975) Ukształtowanie dna i osady denne zalewu. In Łazarienko NN, Majewski A (ed), Hydrometeorologiczny ustrój Zalewu Wiślanego. IMGW, Wydawnictwa Komunikacji i Łączności, Warszawa, pp. 41–57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reindl, A.R., Bolałek, J. Organochlorine contaminants in the Vistula Lagoon sedimentation zone as possible source of lagoon recontamination. Environ Monit Assess 190, 442 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6804-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6804-2