Abstract
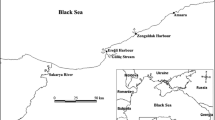
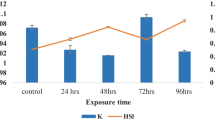
The health of a marine ecosystem can effectively be monitored by studying the levels of biomarkers in a representative species. A change in background level of a biomarker indicates exposure to a specific type of pollutants. It also identifies bioavailability and the organism response to the causative agent among the compounds present in the surrounding water body. Yellowfin seabream (Acanthopagrus latus), a local variety of fish, was examined for parent PAHs in the liver, its metabolites in bile by the GC-MS method as exposure biomarkers and cytochrome P4501A1 by assay of ethoxyresorufin-o-deethylase (EROD) in the liver as an effect biomarker. A comparison was made between fish collected in 2015 with the fish collected in 2005–2006 and stored at − 80 °C in the fish bank. The objective was to examine the extent of changes in the environmental quality of the Kuwait marine area and the status of fish health concerning oil-related pollutants since Arabian Gulf is surrounded by oil-producing countries. Interestingly, insignificant differences between the liver PAH content and EROD activity were observed in fish over the sampling periods. The fish efficiently metabolized PAHs and excreted hydroxy-metabolites in bile. The study suggested that environmental quality of the Kuwait marine area was not deteriorated to any serious extent in the last decade and biomarkers can be used effectively in assessing the thrust of sub-optimal levels of various contaminants present in the marine area on the resident biota.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas, E., Beyer, J., & Goksøyer, A. (1998). PAH in fish bile detected by fixed wavelength fluorescence. Marine Environmental Research 48, 225–228.
Aas, E., Beyer, J., & Goksøyer, A. (2000). Fixed wavelength fluorescence (FF) of bile as a monitoring tool for polyaromatic hydrocarbon exposure in fish: evaluation of compound specificity, inner filters effect, and signal interpretation. Biomarkers, 5, 9–23.
Al-Sarawi, H. A., Jha, A. N., Al-Sarawi, M. A., & Lyons, B. P. (2015). Historic and contemporary contamination in the marine environment of Kuwait: an overview. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100, 621–628.
Al-Yakoob, S., Saeed, T., & Al-Hashash, H. (1993). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in edible tissue of fish from the Gulf after the 1991 oil spill. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 27, 297–301.
Al-Yamani, F. Y., Bishop, J., Ramadhan, E., Al-Husaini, M., & Al-Ghadban, A. N. (2004). Oceanographic atlas of Kuwait’s waters. Kuwait: EPA and KISR Publications.
Al-Zaidan, A. S., Al-Sarawi, H. A., Massoud, M. S., Al-Enezi, M., Smith, A. J., Bignell, J. P., Green, M. J., Askem, C., Bolamb, T. P. C., Barber, J. L., Bersuder, P., & Lyons, B. P. (2015). Histopathology and contaminant concentrations in fish from Kuwait’s marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100, 637–645.
Baumard, P., Budzinski, H., Michon, Q., Garrigues, P., Burgeot, T., & Bellocq, J. (1998). Origin and bioavailability of PAHs in the Mediterranean Sea from mussel and sediment records. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 47, 77–90.
Beg, M. U., Al-Bahloul, M., Jacob, P. G., Beg, K. R., Al-Matrouk, K., & Abdel-Elah, K. (2001). Biomarker response in sheim (Acanthopagrus latus) exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicity, 67, 210–216.
Beg, M. U., Gevao, B., Al-Jandal, N., Beg, K. R., Butt, S. A., Ali, L. N., & Al-Hussaini, M. (2009). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in three varieties of fish from Kuwait Bay. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 29, 75–89.
Beg, M. U., Al-Subiai, S. N., Al-Jandal, N., Butt, S. A., Beg, K. R., & Al-Hussaini, M. (2015). Seasonal effect on biomarkers of exposure to petroleum hydrocarbons in fish from Kuwait’s marine area. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100, 673–680.
De Silva, D., Buzitis, J., Krahn, M. M., Bicego, M. C., & Pires-Vanin, A. M. S. (2006). Metabolites in bile of fish from Sao Sebastiano Channel, Sao Paulo, Brazil as biomarker of petrogenic polycyclic aromatic compounds. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, 175–180.
Fowler, S. W., Readman, J. W., Oregion, B., Villeneuve, J. P., & McCay, K. (1993). Petroleum hydrocarbon, trace metals in nearshore gulf sediments, biota, before and after the 1991 war: an assessment or temporal and spatial trends. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 27, 171–182.
ICES. (2001). The International Council for the Exploration of the Sea: Report of the ICES Advisory Committee on the Marine Environment, No. 248, Helsingør, 5.9 June 2001, Palægade 2.4 DK-1261 Copenhagen K Denmark, pp. 257.
Jhonson-Restrepo, B., Olivero-Verbel, J., Lu, S., Guette-Fernandez, J., Baldiris-Avila, R., O’Byrne-Hoyos, I., Aldous, K. M., Addink, R., & Kannan, K. (2008). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their hydroxylated metabolites in fish bile and sediments from coastal waters of Columbia. Environmental Pollution, 151, 452–459.
Kannan, K., & Perrotta, E. (2008). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in livers of California sea otters. Chemosphere, 71, 649–655.
Krahn, M. M., Rhodes, L. D., Myers, M. S., Moore, L. K., MacLeod Jr., W. D., & Malins, D. C. (1986). Associations between metabolites of aromatic compounds in bile and the occurrence of hepatic lesions in English sole (Parophrys vetutus) from Puget Sound, Washington. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 15, 61–67.
Krahn, M. M., Ylitalo, G. M., Buzitis, J., Botton, J. N., Wigren, C. A., Chan, S. L., & Varanasi, U. (1993). Analyses for petroleum-related contaminants in marine fish and sediments following the Gulf oil spill. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 27, 285–292.
Lin, E., Cormier, M., & Racine, R. N. (1996). Fish biliary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites estimated by fixed-wavelength fluorescence comparison with HPLC-fluorescent detection. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 35, 16–23.
Literathy, P., Morel, G., Zarba, M., Samhan, M., Al-Bloushi, A., Al-Hashash, H., Al-Matrouk, K., Jacob, P. G., & Saeed, T. (1992). Petroleum compounds in the marine environment of Kuwait. Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Report No. KISR 4054, Kuwait.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19, 18–97.
Lowry, O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Lyons, B. P., Barber, J. L., Rumney, H. S., Bolam, T. P. C., Bersuder, P., Law, R. J., Mason, C., Smith, A. J., Morris, S., Devlin, M. J., Al-Enezi, M., Massoud, M. S., Al-Zaidan, A. S., & Al-Sarawi, H. A. (2015). Baseline survey of marine sediments collected from the State of Kuwait: PAHs, PCBs, brominated flame retardants and metal contamination. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100, 629–636.
Notar, M., Leskov-Sek, H., & Faganel, J. (2001). Composition, distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Gulf of Trieste, northern Adriatic Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42, 36–44.
OSPAR Commission. (1999). The joint assessment and monitoring program, Guidelines for Monitoring Contaminants in Biota, no. 1999-2. Oslo and Paris Commision.
ROPME. (1999). Regional report of the state of the marine environment. The regional Organization for the Protection of marine environment, Kuwait, ROPME/GC-9/002.
Ruddock, P. J., Bird, D. J., McEvoy, J., & Peters, L. D. (2003). Bile metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in European eels Anguilla Anguilla from United Kingdom estuaries. The Science of the Total Environment, 301, 105–117.
Sadiq, M., Saeed, T., & Fowler, S. W. (2002). Seafood contamination. In N. Y. Khan, M. Munawar, & A. R. G. Price (Eds.), The Gulf ecosystem: health and sustainability (pp. 327–351). Leiden: Backhuys Publisher.
Saeed, T., Al-Yakoob, S., Al-Hashash, H., & Al-Bahloul, M. (1995). Preliminary exposure assessment for Kuwaiti consumers to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sea food. Environment International, 21, 255–263.
Salvo, L. M., Severino, D., deAssis, H. C. S., & DaSilva, J. R. M. C. (2016). Photochemical degradation increases polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) toxicity to the grouper Epinephelus marginatus as assessed by multiple biomarkers. Chemosphere, 144, 540–547.
Sole, M., Anto, M., Baena, M., Carrasson, M., & Cartes, J. E. (2010). Hepatic biomarkers of xenobiotic metabolism in eighteen marine fish from NW Mediterranean shelf and slope waters in relation to some of their biological and ecological variables. Marine Environmental Research, 70, 181–188.
Stagg, R. M., McIntosh, A., & Mackie, P. (1995). Elevation of hepatic monooxygenase activity in the das Limanda limanda L. in relation to environmental contamination with petroleum hydrocarbons in the northern North Sea. Aquatic Toxicology, 33, 245–264.
Stegeman, J. J., & Lech, J. J. (1991). Cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase systems in aquatic species: carcinogens metabolism and biomarkers for carcinogen and pollutant exposure. Environmental Health Perspectives, 90, 101–109.
Stroomberg, G. J., de Knecht, J. A., Ariese, F., van Gestel, C. A. M., & Velthorst, N. H. (1999). Pyrene metabolites in the hepatopancreas and gut of the isopod Porcellio scaber, a new biomarker for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure in terrestrial ecosystems. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 2217–2224.
Torre, C. D., Tornambe, A., Cappello, S., Mariottini, M., Perra, G., Giuliani, S., Amato, E., Falugi, C., Crisari, A., Yakimov, M. M., & Magaletti, E. (2012). Modulation of CYP1A and genotoxic effects in European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) exposed to weathered oil: a mesocosm study. Marine Environmental Research, 76, 48–55.
Van Schanke, A., Holtz, F., van der Meer, J., Boon, J. P., Ariese, F., Stroomberg, G., van der Berg, M., & Everaarts, J. M. (2001). Dose- and time-dependent formation of biliary benzo (a) pyrene metabolites in in the marine flatfish dab (Limanda limanda). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 1641–1647.
Varanasi, U., Chan, S. L., MacLeod, W. D., Brown, D. W., Burrows, D. G., Tilbury, K. L., Landahl, J. T., Wigren, C. A., Hom, T., & Pierce, S. M. (1990). Survey of subsistence fish and shellfish for exposure to oil spilled from Exxon Valdez. First year: 1989. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Marine Fisheries Service, Seattle, WA NOAA Tech. Mem.NMFS F/NWC-191.
Whyte, J. J., Jung, R. E., Schmitt, C. J., & Tillitt, D. E. (2000). Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activity in fish as a biomarker of chemical exposure. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 30, 347–570.
Yang, X. A., Peterson, D. S., Baumann, P. C., & Lin, E. L. C. (2003). Fish biliary PAH metabolites estimated by fixed-wavelength fluorescence as an indicator of environmental exposure and effects. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 29, 116–123.
Zhu, I. Z., Cai, X. F., & Wang, J. (2005). PAHs in aquatic sediment in Hangzhou, China: analytical method, pollution pattern, risk assessment and sources. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 17, 748–755.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Samira A. S. Omar, Director General, Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Kuwait, for the interest and financial support to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beg, M.U., Butt, S.A., Al-Dufaileej, S. et al. Biomarkers in fish as a measure of the state of marine environment of Kuwait. Environ Monit Assess 190, 325 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6704-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6704-5