Abstract
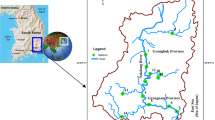
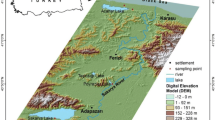
This study was carried out to determine the accumulation levels of heavy metals (Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu, Fe, Cr) in seston to three different freshwater resources poured into the Iskenderun Bay. Seasonal averages of physico-chemical parameters measured at stations, Arsuz Stream, Payas Stream, and Ceyhan River, are classified as Class III—contaminated water according to the temperature parameter in the summer. Payas Stream has been determined to be Class III—polluted water according to pH parameters during the summer season. Ceyhan River was found to be Class III—contaminated water according to the dissolved oxygen parameter in the autumn season. Heavy metal accumulation levels in the seston were determined Fe > Cr > Zn > Cu > Pb > Cd in Arsuz Stream, Fe > Zn > Pb > Cr > Cu > Cd in Payas Stream, and Fe > Zn > Cr > Cu > Pb > Cd in Ceyhan River. The results in this study showed that high accumulation levels in seston were determined for Fe while low accumulation levels for Cd.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ağcasulu, Ö. (2007). Sakarya Nehri Çeltikçe Çayı’nda Yaşayan Capoeta tinca (Heckel, 1843)‘nın Dokularında Ağır Metal Birikiminin İncelenmesi. Gazi Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Yüksek Lisans Tezi, 54s, Ankara.
Anonymous. (1997). Türkiye Kıyılarındaki Lagünlerin Yönetim ve Geliştirilme Stratejileri ve Islahı. 1. Cilt., Tarım ve Köyişleri Bakanlığı Tarımsal Üretim ve Geliştirme Genel Müdürlüğü 578s.
Anonymous. (2000). Aslantas Dam and related aspects of the Ceyhan River Basin, Turkey. A WCD case study prepared as an input to the World Commission on Dams. Agrin Co. Ltd. Cape Town. http://www.dams.org.
Bu-Olayan, A. H., Al-Hassan, R., & Thomas, B. V. (2001). Trace metal toxicity to phytoplankton of Kuwait coastal waters. Ecotoxicology, 10, 185–189.
Campanella, L., Conti, M. E., Cubbada, F., & Sucapane, C. (2001). Trace metals in seagrass, algae and molluscs from an uncontaminated area in the Mediterranean. Environmental Pollution, 111, 117–126.
Dural, M., & Göksu, M. Z. L. (2006). Çamlık Lagünü (Karataş, Adana), Seston, Bentoz ve Sedimentinde Mevsimsel Ağır Metal Değişimi. Ege Üniversitesi Su Ürünleri Dergisi, 23(1), 65–69.
Edwards, J. W., Edyvane, K. S., Boxall, V. A., Hamann, M., & Soole, S. L. (2001). Metal levels in seston and marine fish flesh near industrial and metropolitan centres in South Ausralia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42(5), 389–396.
EEA. (2000). Europe’s environment—the Dobris assessment. Copenhagen.
Fisher, N. S. (1986). On the reactivity of metals for marine phytoplankton. Limnology and Oceanography, 31, 443–449.
Förstner, U., & Wittman, G. T. W. (1983). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Gibbs, R. J. (1986). Segregation of metals by coagulation in estuaries. Marine Chemistry, 18, 149–159.
González-Dávila, M. (1995). The role of phytoplankton cells on thecontrol of heavy metal concentration in seawater. Mar Chem, 48, 215–236 gatıve Implıcatıons. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 114: 145–155.
Koelmans, A. A. (1998). Geochemistry of suspended and settling solids in two freshwater lakes. Hydrobiologia, 364, 15–29.
Özdamar, K. (2001). SPSS ile Biyoistatistik. Kaan Kitapevi, Yayın No: 3, 4. Baskı, ISBN: 975-6787-03-1, Eskişehir.
Saad, M. A. H., & Hassan, E. M. (2002). Heavy metals in the Rosetta estuary of the Nile and the adjoining Mediterranean waters: evidence of removal of dissolved heavy metals from waters as a result of possible binding to suspended matter. Hydrobiologia, 469, 131–147.
Swadis, T., Brown, M. T., Zachariadis, G., & Sratis, I. (2001). Trace metal concentrations in marine macroalgae from different biotopes in the Aegean Sea. Environment International, 27, 43–47.
Tuğrul, S., Yemenicioğlu, S., Sağlamtimur, Doğan, N. (2007). Akdeniz Kıyı Alanları Kirlilik Kaynaklarında Uzun Süreli Eğilim İzleme: Nehirler Ve Atıksular (2003-2006). Ulusal Su Günleri Antalya. s 596–606.
Turner, A., & Millward, G. E. (2002). Suspended particles: their role in estuarine biogeochemical cycles. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 55, 857–883.
UNEP. (1984). Determination of total Cd, Zn, Pb and Cu in selected marine organisms by flameless AAS reference methods for marine pollution studies, vol. 11 (1984).
Yılmazer, D. (1996). Ceyhan Nehri Eskikent-Bebeli Arası Agır Metal Analizleri ve Mevsimsel Hidro-Jeokimyasal Degisimleri, ¨Ç.Ü. Fen Bil. Ens. Yuksek Lisans Tezi, Adana.
Yılmazer, D., Yaman, S., (1997). Heavy metal load and chemical prole of Ceyhan River, Adana, Turkey, Int. Symp. On Geology and Environment (GEOENV’97) abstracts p.175, Istanbul, 61.
Yılmazer, D., & Yaman, S. (1999). Heavy metal pollution and chemical profile of Ceyhan River (Adana-Turkey). Turkish Journal of Engineering and Environmental Science, 23, 59–61.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of Mustafa Kemal University (BAP 2015/11000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dural Eken, M., Akman, B. Assessment of heavy metal pollution of seston from freshwater resources poured into the Northeast Mediterranean region. Environ Monit Assess 190, 308 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6642-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6642-2