Abstract
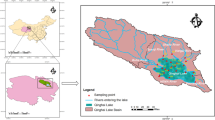
This study sought to analyze heavy metal (Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, Mn, and Fe) pollution status in the waters of Aibi Lake in northwest China through the use of an applied comprehensive pollution index, health risk model, and multivariate statistical analyses in combination with the lake’s land use types. Results showed that (1) the maximum (average) values of the heavy metals Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, Mn, and Fe were 0.0644 (0.0123), 0.0006 (0.0002), 0.0009 (0.0032), 0.1235 (0.0242), 0.0061 (0.0025), and 0.0222 (0.0080) μg/L, respectively. Among these, in all the samples, Pb and Ni exceeded the standard and acceptable values put forth by the World Health Organization by 21.13 and 25.67%, respectively. Ni also exceeded (30.16%) the third grade of the Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water of China. The levels of the six heavy metals were all within the fishery and irrigation water quality standard ranges in China. (2) The average values for single pollution index of heavy metals Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, Mn, and Fe were 1.000, 0.0006, 0.0009, 3.000, 0.060, and 0.070, respectively, among which Ni levels indicated moderate to significant pollution, while others indicated healthy levels. (3) Health risk evaluation showed that the Rn values for Pb, Zn, Cu, Mn, and Fe were 1.8 × 10−4, 5.33 × 10−9, 4.80 × 10−7, 1.08 × 10−6, and 2.51 × 10−7 a−1, respectively, of which, in all samples, Pb and Ni contents all exceeded the maximum acceptable risk levels according to the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) as well as the U.S. Environment Protection Agency. (4) Combining with multivariate statistical analyses along with the land use distribution within the lake basin, Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, and Mn were mainly influenced by the agriculture production and emission from urban lives and traffics, and Fe mainly originated from the natural environment. The results of this research can provide reference values for heavy metal pollution prevention in Aibi Lake as well as for environmental protection of rump lakes in the arid regions of northwest China and Central Asia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuduwaili, J., Yong, Z. Z., & Qing, J. F. (2015). Assessment of the distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the dry surface sediment of Aibi Lake in Northwest China. PLoS One, 10(3), e0120001. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120001.
Batvari, B. P. D., Sivakumar, S., Shanthi, K., Lee, K. J., Oh, B. T., Krishnamoorthy, R. R., & Kamala-Kannan, S. (2016). Heavy metals accumulation in crab and shrimps from Pulicat lake, north Chennai coastal region, southeast coast of India. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 32(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713475500.
Cai, X. Q., & Gao, Q. L. (2016). The characteristics of lake water quality pollution in Kaifeng City were evaluated based on the Nemerow index. Jilin Agriculture, 11, 82–83 (In Chinese).
Du, W., Li, A. M., Lu, M., An, K., Fan, J., & Hubei, E. M. C. (2014). Preliminary health risk assessment of heavy metals in the Yangtze River of Wuhan Area. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(S2), 535–539 (In Chinese).
Dung, T. T. T., Cappuyns, V., Swennen, R., & Phung, N. K. (2013). From geochemical background determination to pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments and soils. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 12(4), 335–353.
Duruibe, J. O., Ogwuegbu, M. O. C., & Egwurugwu, J. N. (2007). Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. International Journal of Physical Sciences, 2(5), 112–118.
Fu, J., Hu, X., Tao, X., Yu, H., & Zhang, X. (2013). Risk and toxicity assessments of heavy metals in sediments and fishes from the Yangtze River and Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere, 93(9), 1887–1895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.061.
Hu, R. J. (2004). China Tianshan natural geography. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press (In Chinese).
Huang, L., & Jiao, F. (2010). Health risk assessment and sources analysis in Yangcheng Lake water resources. Environmental Science and Management, 35(6), 190–194 (In Chinese).
Kampbell, D. H., An, Y. J., Jewell, K. P., & Masoner, J. R. (2003). Groundwater quality surrounding Lake Texoma during short-term drought conditions. Environmental Pollution, 125(2), 183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00072-1.
Karadede, H., & Ünlü, E. (2000). Concentrations of some heavy metals in water, sediment and fish species from the Atatürk Dam Lake (Euphrates), Turkey. Chemosphere, 41(9), 1371–1376. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00563-9.
Li, F., Fan, Z., Xiao, P., Oh, K., Ma, X., & Hou, W. (2009). Contamination, chemical speciation and vertical distribution of heavy metals in soils of an old and large industrial zone in Northeast China. Environmental Geology, 57(8), 1815–1823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1469-8.
Li, T., Shi, L., Ma, Z., Yang, S. J., Wang, H. Y., & Zhou, Y. X. (2014). Health risk assessment on heavy metal pollution in water environment of Hailang river. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 8(12), 5521–5526 (In Chinese).
Li, X. P., Qi, J. Y., & Chen, Y. H. (2011). Preliminary health risk assessment of heavy metals in the main drinking water sources of Guangzhou. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 31(3), 547–553 (In Chinese).
Li, X,H., Zhang, F., Wang, J., Wang, D,F. (2017). Analysis and assessment of water quality of Ebinur Lake basin in autumn. Environmental Pollution & Control, 39(6), 587–593 (In Chinese).
Li, Y. L., & Liu, J. L. (2009). Health risk assessment on heavy metal pollution in the water environment of Luan River. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 28(6), 1177–1184 (In Chinese).
Liao, J., Chen, J., Ru, X., Chen, J., Wu, H., & Wei, C. (2017). Heavy metals in river surface sediments affected with multiple pollution sources, South China: distribution, enrichment and source apportionment. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 176, 9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.08.013.
Liu, F., Li, M., Zhang, R. F., & Cui, Y. (2012). Pollution analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in Lhasa River. Environmental Chemistry- Huanjing Huaxue, 31(5), 580–585 (In Chinese).
Liu, J., He, X. X., Lin, X. R., Chen, W. C., Zhou, Q. X., Shu, W. S., & Huang, L. N. (2015). Ecological effects of combined pollution associated with e-waste recycling on the composition and diversity of soil microbial communities. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(11), 6438–6447. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5049804.
Lu, A., Wang, J., Qin, X., Wang, K., Han, P., & Zhang, S. (2012). Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Science of the Total Environment, 425, 66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.03.003.
Martin, S., & Griswold, W. (2009). Human health effects of heavy metals. Environment Science Technology Brief Cite, 15, 1–6.
Mi, Y., Chang, S.L, Shi, Q,D.,Gao, X., Huang, C. (2009). Aquatic environmental quality assessment in Ebinur Lake Catchment during high flow Period 2008. Journal of Lake Sciences, 21(6), 891–894 (In Chinese).
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China (MEPPRC). (1989). Water quality standard for fisheries (GB 11607–89). (In Chinese).
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China (MEPPRC). (1992). Standards for irrigation water quality (GB 5084–92). (In Chinese).
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China (MEPPRC). (2002). Environmental quality standards for surface water (GB 3838–2002). (In Chinese).
O-Ogoyi, D., Mwita, C. J., Nguu, E. K., & Shiundu, P. M. (2011). Determination of heavy metal content in water, sediment and microalgae from Lake Victoria, East Africa. The Open Environmental Engineering Journal, 4(1), 156–161.
Öztürk, M., Özözen, G., Minareci, O., & Minareci, E. (2008). Determination of heavy metals in of fishes, water and sediment from the Demirköprü Dam Lake (Turkey). Journal of Applied Biological Sciences, 2(3), 99–104.
Prasanna, M. V., Praveena, S. M., Chidambaram, S., Nagarajan, R., & Elayaraja, A. (2012). Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring: a case study from Curtin Lake, Miri City, East Malaysia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 67(7), 1987–2001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1639-6.
Saeed, S. M., & Shaker, I. M. (2008). Assessment of heavy metals pollution in water and sediments and their effect on Oreochromis niloticus in the northern delta lakes, Egypt. In 8th International Symposium on Tilapia in Aquaculture, 475–490.
Shi, J., Wang, H., Xu, J., Wu, J., Liu, X., Zhu, H., & Yu, C. (2007). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils: a case study of Changxing, China. Environmental Geology, 52(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0443-6.
Skordas, K., Kelepertzis, E., Kosmidis, D., Panagiotaki, P., & Vafidis, D. (2015). Assessment of nutrients and heavy metals in the surface sediments of the artificially lake water reservoir Karla, Thessaly, Greece. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(8), 4483–4493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3736-1.
Sun, C., Chen, Z., Zhang, G., Shi, G., & Bi, C. (2009). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in drinking water sources in Shanghai, China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(1), 60–65 (In Chinese).
Xie, X. J., Wang, F. Y., Wang, G. J., Mei, R. W., & Wang, C. Z. (2017). Study on heavy metal pollution in surface water in China. Environmental Science and Management, 42(2), 31–34 (In Chinese).
Wang, L., Lv, A. H., & Wang, Y. Y. (2011). Pollution evaluation of heavy metals in superficial sediment of Chaiwopu Lake Urumqi. Journal of the Environmental Management College of China – EMCC, 21(1), 8–12 (In Chinese).
Wang, L. M., Zhang, S., Zhao, S. N., & Wu, Y. (2014a). Spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in Ulansuhai Lake. Journal of Environmental Health, 31(12), 1088–1089 (In Chinese).
Wang, W., Fan, X. K., Huang, C. G., Zheng, H., Chen, Z. J., Fan, B. H., & Xu, C. W. (2016). Monitoring and comparison analysis of heavy metals in the five great lakes in Jiangsu Province. Journal of Lake Sciences, 28(3), 494–501 (In Chinese).
Wang, Y. H., He, X., & Himit, Y. (2014b). Analysis of soil granularity in Ebinur Lake wetland. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 32(6), 183–187 (In Chinese).
Wang, Z., Yao, L., Liu, G., & Liu, W. (2014c). Heavy metals in water, sediments and submerged macrophytes in ponds around the Dianchi Lake, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 107, 200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.06.002.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2011). Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality. (fourth edition) Geneva.
Zeng, H., Wu, J., & Liu, W. (2014). Two-century sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution from Lake Sayram: a deep mountain lake in central Tianshan, China. Quaternary International, 321, 125–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2013.09.047.
Zhang, G. G., & Huang, B. (2014). Health risk assessment of heavy metals in Dongting Lake water system in Hunan Province, China. Water Resources Protection, 30(1), 14–17,47 (In Chinese).
Zhang, Y. S., Wu, F. C., Zhang, R. Y., Liao, H. Q., & Ling, H. W. (2009). Sediment records of heavy metal pollution in Bosten Lake, Xinjiang. Earth and Environment, 37(1), 50–55 (In Chinese).
Zhang, Z., Abuduwaili, J., & Jiang, F. (2013). Determination of occurrence characteristics of heavy metals in soil and water environments in Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Analytical Letters, 46(13), 2122–2131. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2013.784919.
Zhang, Z., Juying, L., Mamat, Z., & QingFu, Y. (2016). Sources identification and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Bortala River, Northwest China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 126, 94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.025.
Zhang, Z. Y., Abuduwaili, J., & Jiang, F. Q. (2015). Heavy metal contamination, sources, and pollution assessment of surface water in the Tianshan Mountains of China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(2), 1–13.
Zhao, Y., Yang, Z., & Li, Y. (2010). Investigation of water pollution in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2, 737–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.085.
Zheng, H. (2014). The current situation of drinking water standards in China. Journal of Hygiene Research, 43(1), 166–169 (In Chinese).
Zhong, L., Liu, L., & Yang, J. (2012). Characterization of heavy metal pollution in the paddy soils of Xiangyin County, Dongting lake drainage basin, central south China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 67(8), 2261–2268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1671-6.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the joint fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China of the Government of Xinjiang Autonomous Region (No. U1603241), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41501541), the High-level Talent Introduction Program of Xinjiang Autonomous Region (2016), Doctoral startup fund of Xinjiang University (No. 62346), and Scientific research startup project for college teachers of Xinjiang Autonomous Region (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhaoyong, Z., Xiaodong, Y. & Shengtian, Y. Heavy metal pollution assessment, source identification, and health risk evaluation in Aibi Lake of northwest China. Environ Monit Assess 190, 69 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6437-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6437-x