Abstract
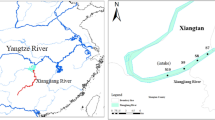
Yongding River is a vital socioeconomic zone in China in providing daily usage for humans, animals, and running of industries and agriculture. This study first provides a comparative assessment for the heavy metal pollution in the surface water from 82 estuarine locations along the basin, including the Guanting Reservoir and seven wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). The occurrence, distribution, potential sources, and water quality relating to the detected heavy metals were addressed. Eleven typical elements (Pb, Cr, As, Cd, Sb, Ba, V, Ti, Zn, Ni, and Be) were investigated, and the results showed that all the measured concentrations were below the WHO guideline limits. Most heavy metals exhibited higher levels in the middle of Yongding River basin due to the discharge of WWTPs. Pb, Ti, Zn, and Cd in the surface water mainly originated from anthropogenic discharge, while Sb and V were mostly contributed to geogenic sources according to the principal component analysis. Three documented methods, water quality index (WQI), heavy metal pollution (HPI), and Nemerow pollution index (Pn) values, were used to evaluate the contamination monitoring of surface water. All the locations were classified as low and moderate risk except Y12, B2, and Y13 for their Pn values were higher than 1.0. The present study highlights the status of heavy metals in Yongding River basin which is helpful in providing fundamental data for assessment of water quality and the effective protection for Yongding River basin in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves RIS, Sampaio CF, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL, Segura-muñoz SI (2014) Metal concentrations in surface water and sediments from Pardo River, Brazil: Human health risks. Environ Res 133:149–155
Audry S, Schäfer J, Blanc G, Jouanneau JM (2004) Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) in the Lot River reservoirs (France). Environ Pollut 132(3):413–426
Bengraïne K, Marhaba TF (2003) Using principal component analysis to monitor spatial and temporal changes in water quality. J Hazard Mater 100:179–195
Bilgin A, Konanç MU (2016) Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal pollution of Coruh River Basin (Turkey) by multivariate statistical methods. Environ Earth Sci 75(12):1029
Cheng KC, Poon BHT, Lan CY, Wong MH (2003) Assessment of metal and nutrient concentrations in river water and sediment collected from the cities in the Pearl River delta, South China. Chemosphere 52:1431–1440
Dai D, Sun MD, Lv XB, Lei K (2020) Evaluating water resource sustainability from the perspective of water resource carrying capacity, a case study of the Yongding River watershed in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. China Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:21590–21603
Duncan AE, de Vries NK, Nyarko B (2018) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the main Pra River and its tributaries in the Pra Basin of Ghana. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 10:264–271
Gaillardet, J., Viers, J., Dupré, B., 2005. Trace elements in river waters. In Drever, J.I.(Ed.), H.DHolland, K.K. Turekian (executive Ed.), Surface and groundwater, weathering, and soils, vol5, Treatise on geochemistry (pp.225–272). Netherlands: Elsevier.
Giri S, Singh AK (2014) Assessment of surface water quality using heavy metal pollution index in Subarnarekha River, India. Exp Health 5:173–182
Giri S, Singh AK (2019) Assessment of metal pollution in groundwater using a novel multivariate metal pollution index in the mining areas of the Singhbhum copper belt. Environ Earth Sci 78:192
Gozzard E, Mayes WM, Potter HAB, Jarvis AP (2011) Seasonal and spatial variation of diffuse (non-point) source zinc pollution in a historically metal mined river catchment. UK Environ Pollut 159:3113–3122
Huang SB, Wang ZJ, Xu YP, Mei M (2005) Distribution, sources and potential toxicological significance of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Guanting Reservoir sediments. China J Environ Sci 17(1):48–53
Jiang DY, Wang YY, Zhou SY, Long Z, Liao Q, Yang JQ, Fan J (2019) Multivariate analyses and human health assessments of heavy metals for surface water quality in the Xiangjiang River Basin, China. Environ Toxicol Chem 38(8):1645–1657
Jiang B, Wong CP, Lu F, Ouyang Z, Wang Y (2014) Drivers of drying on the Yongding River in Beijing. J Hydrol 519:69–79
Kaiser HF (1960) The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas 20:141–151
Kennedy, P., Gadd, J. 2000. Preliminary examination of inorganiccom pounds present in tyres, brake pads and road bitumen in New Zealand. Prepared by Kingett Mitchell Ltd for Ministry of Transport, November 2000. Revised October 2003.
Li S, Zhang Q (2010) Spatial characterization of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the upper Han River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 176:579–588
Luo W, Wang T, Lu Y, Giesy JP, Shi Y, Zheng Y, Xing Y, Wu G (2007) Land scape ecology of the Guanting Reservoir, Beijing, China: multivariate and geostatistical analyses of metals in soils. Environ Pollut 146(2):567–576
Liu J, Xu Y, Cheng Y, Zhao Y, Pan Y (2017) Occurrence and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Xiangjiang River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:2711–2723
Lohani MB, Singh A, Rupainwar DC, Dhar DN (2008) Seasonal variations of heavy metal contamination in River Gomti of Lucknow City region. Environ Monit Assess 147:253–263
Meng, J., Zhou, Y.Q., Liu, S.F., Chen, S.Q., Wang, T.Y. 2019. Increasing perfluoroalkyl lsubstances and ecological process from the Yongding Watershed to the Guanting Reservoir in the Olympic host cities, China. 2019, Environ. Int., 133, 105224.
Nan ZR, Li JJ, Zhang JM, Cheng GD (2002) Cadmium and zinc interactions and their transfer in soil–crop system under actual field conditions. Sci Total Environ 285:187–195
Nriagu JO, Pacyna JM (1988) Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature 333:134–139
Peters K, Bundschuh M, Schäfer RB (2013) Review on the effects of toxicants on freshwater ecosystem functions. Environ Pollut 180:324–329
Prasad B, Bose JM (2001) Evaluation of heavy metal pollution index for surface and spring water near a limestone mining area of the lower Himalayas. Environ Geol 41:183–188
Prasad S, Saluja R, Joshi V, Grag JK (2020) Heavy metal pollution in surface water of the Upper Ganga River, India: human health risk assessment. Environ Monit Assess 192:742
Razak NHA, Praveena SM, Aris AZ, Hashim Z (2015) Drinking water studies: a review on heavy metal, application of biomarker and health risk assessment (a special focus in Malaysia). J Epidemiol Glob Health 5(4):297–310
Resongles E, Casiot C, Freydier R, Dezileau L, Viers J, Elbazpoulichet F (2014) Persisting impact of historical mining activity to metal (Pb, Zn, Cd, Ti, Hg) and metal loid (As, Sb) enrichment in sediments of the Gardon River Southern France. Sci Total Environ 481(1):509–521
Shah MT, Ara J, Muhammad S, Khan S, Tariq S (2012) Health risk assessment via surface water and sub-surface water consumption in the mafic and ultramafic terrain, Mohmand agency, northern Pakistan. J Geochem Explor 118:60–67
Sharma S (1996) Applied multi-variate techniques. Wiley, New York.
Simeonov V, Stratis JA, Samara C, Zachariadis G, Voutsa D, Anthemidis A (2003) Assessment of the surface water quality in northern Greece. Water Res 37:4119–4124
Singh KP, Malik A, Mohan D, Sinha S (2004) Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)-a case study. Water Res 38:3980–3992
Tang W, Shan B, Zhang W, Zhang H, Wang L, Ding Y (2014) Heavy metal pollution characteristics of surface sediments in different aquatic ecosystems in Eastern China: a comprehensive understanding. PLoS One 9(9):e108996
Tepe Y (2014) Toxic metals: trace metals - chromium, nickel, copper, and aluminum, Encycl. Food Safe 2:356–362
Tepe, Y., Acrylamide in Surface and Drinking Water, V. Gokmen, Ed., Acrylamide Food Analysis, Content Potential Health Effects, Elsevier, Amsterdam 2015, 275–293.
Ustaoğlu F, Aydin H (2020) Health risk assessment of dissolved heavy metals in surface water in a subtropical rivers basin system of Giresun (north-eastern Turkey). Desalin Water Treat 194:222–234
Vega M, Pardo R, Barrado E, Deban L (1998) Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Res 32:3581–3592
Wang L, Wang Y, Xu C, An Z, Wang S (2011) Analysis and evaluation of the source of heavy metals in water of the River Changjiang. Environ Monit Assess 173:301–313
Waseem A, Arshad J, Iqbal F, Sajjad A, Mehmood Z, Murtaza G (2014) Pollution status of Pakistan: a retrospective review on heavy metal contamination of water, soil, and vegetables. Biomed Res Int 4(2):813206
WHO (2017) Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 1–564
Xiao J, Wang L, Deng L, Jin Z (2019) Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci Total Environ 650:2004–2012
Xu L, Wang TY, Luo W, Ni K, Liu SJ, Wang L, Li QS, Lu YL (2013) Factors influencing the contents of metals and As in soils around the watershed of Guanting Reservoir. China J Environ Sci 25:561–568
Xue ND, Zhang D, Xu XB (2006) Organo chlorinated pesticide multiresidues in surface sediments from Beijing Guanting reservoir. Water Res 40(2):183–194
Yuan ZH, Li QH, Ma XY, Han MS (2020) Assessment of heavy metals contamination and water quality characterization in the Nanming River, Guizhou Province. Environ Geochem Heath 43:1273–1286
Zhang Z, Lu Y, Li H, Tu Y, Liu B, Yang Z (2018) Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Sci Total Environ 645:235–243
Zhang WY, Ma L, Abuduwaili J, Ge YX, Issanova G (2020) Distribution characteristics and assessment of heavy metals in the surface water of the Syr Darya River, Kazakhstan. Pol J Environ Stud 29(1):979–988
Zhang Z, Sun Y, li L, Sun Y, Yu D, Song W (2013) The causes of water pollution of Yongdingxin River in Tianjin and suggestions for comprehensive treatment (in Chinese). Haihe Water Resour. 5:6–7
Zhai X, Xia J, Zhang Y (2014) Water quality variation in the highly disturbed Huai River basin, China from 1994 to 2005 by multi-statistical analyses. Sci Total Environ 496:594–606
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2018ZX07111-002) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JJ: data curation, formal analysis and writing—original draft preparation, conceptualization; GZ: supervision, project administration, writing—reviewing, editing and validation; YX: data curation and methodology, writing—reviewing and editing; JZ: investigation and data curation; LL: sampling and formal analysis; CL: investigation, sampling, and data curation; DW: methodology and visualization; YL: investigation, supervision, and project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Xianliang Yi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, J., Zhao, G., Xu, Y. et al. Occurrence and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in the surface water of Yongding River Basin, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 17821–17831 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16932-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16932-6