Abstract
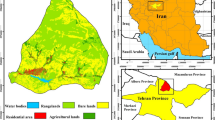
A hierarchical intensity analysis of land-use change is applied to evaluate the dynamics of a coupled urban coastal system in Rasht County, Iran. Temporal land-use layers of 1987, 1999, and 2011 are employed, while spatial accuracy metrics are only available for 2011 data (overall accuracy of 94%). The errors in 1987 and 1999 layers are unknown, which can influence the accuracy of temporal change information. Such data were employed to examine the size and the type of errors that could justify deviations from uniform change intensities. Accordingly, errors comprising 3.31 and 7.47% of 1999 and 2011 maps, respectively, could explain all differences from uniform gains and errors including 5.21 and 1.81% of 1987 and 1999 maps, respectively, could explain all deviations from uniform losses. Additional historical information is also applied for uncertainty assessment and to separate probable map errors from actual land-use changes. In this regard, historical processes in Rasht County can explain different types of transition that are either consistent or inconsistent to known processes. The intensity analysis assisted in identification of systematic transitions and detection of competitive categories, which cannot be investigated through conventional change detection methods. Based on results, built-up area is the most active gaining category in the area and wetland category with less areal extent is more sensitive to intense land-use change processes. Uncertainty assessment results also indicated that there are no considerable classification errors in temporal land-use data and these imprecise layers can reliably provide implications for informed decision making.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afrakhteh, R., Asgarian, A., Sakieh, Y., & Soffianian, A. (2016). Evaluating the strategy of integrated urban-rural planning system and analyzing its effects on land surface temperature in a rapidly developing region. Habitat International, 56, 147–156.
Akinyemi, F. O., Pontius Jr., R. G., & Braimoh, A. K. (2016). Land change dynamics: insights from intensity analysis applied to an African emerging city. Spatial Science. doi:10.1080/14498596.2016.1196624.
Aldwaik, S. Z., & Pontius Jr., R. G. (2012). Intensity analysis to unify measurements of size and stationarity of land changes by interval, category, and transition. Landscape and Urban Planning, 106(1), 103–114.
Aldwaik, S. Z., & Pontius Jr., R. G. (2013). Map errors that could account for deviations from a uniform intensity of land change. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 27(9), 1717–1739.
Alo, C. A., & Pontius Jr., R. G. (2008). Identifying systematic land-cover transitions using remote sensing and GIS: The fate of forests inside and outside protected areas of southwestern Ghana. Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design, 35(2), 280–295.
Asgarian, A., Amiri, B. J., & Sakieh, Y. (2015). Assessing the effect of green cover spatial patterns on urban land surface temperature using landscape metrics approach. Urban Ecosystems, 18(1), 209–222.
Barbier, E. B. (2007). Valuing ecosystem services as productive inputs. Economic Policy, 22, 177–229.
Boateng, I. (2012). GIS assessment of coastal vulnerability to climate change and coastal adaption planning in Vietnam. Coastal Conservation, 16(1), 25–36.
Bortels, L., Chan, J. C. W., Merken, R., & Koedam, N. (2011). Long-term monitoring of wetlands along the western-Greek bird migration route using landsat and ASTER satellite images: Amvrakikos Gulf (Greece). Journal for Nature Conservation, 19(4), 215–223.
Bouziani, M., Goïta, K., & He, D.-C. (2010). Automatic change detection of buildings in urban environment from very high spatial resolution images using existing geodatabase and prior knowledge. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 65, 143–153.
Camilleri, S., De Giglio, M., Stecchi, F., & Pérez-Hurtado, A. (2016). Land use and land cover change analysis in predominantly man-made coastal wetlands: towards a methodological framework. Wetlands Ecology and Management. doi:10.1007/s11273-016-9500-4.
Dahdouh-guebas, F. (2002). The use of remote sensing and GIS in the sustainable management of tropical coastal ecosystems. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 4(2), 93–112.
de Kok, J., Engelen, G., White, R., & Wind, H. G. (2001). Modeling land-use change in adecision-support system for coastal-zone management. Environmental Modelihg and Assessment, 6(2), 123–132.
Dezhkam S. 2013. Analysis of trend and pattern of urban growth using landscape ecology approach (case study: Rasht county). Dissertation, University of Tehran.
Dezhkam, S., Amiri, B. J., Darvishsefat, A. A., & Sakieh, Y. (2014). Simulating urban growth dimensions and scenario prediction through sleuth model: a case study of Rasht County, Guilan, Iran. GeoJournal, 79(5), 591–604.
Dezhkam, S., Amiri, B. J., & Darvishsefat, A. A. (2015a). Landscape change detection using synoptic analysis and satellite imagery (case study: Rasht County). Natural Environment, 68(2), 225–238 [text in Persian].
Dezhkam, S., Amiri, B. J., & Darvishsefat, A. A. (2015b). Prediction of land-use change in Rasht County using cellular automata-Markov chain model. Environmental Researches, 11, 193–204 [text in Persian].
Dezhkam, S., Amiri, B. J., Darvishsefat, A. A., & Sakieh, Y. (2016). Performance evaluation of land change simulation models using landscape metrics. Geocarto International. doi:10.1080/10106049.2016.1167967.
Ellis, J. T., Spurce, J. P., Roberta, A. S., Swann, R. A., Smoot, J. C., & Hilbert, K. W. (2011). An assessment of coastal land-use and land-cover change from 1974–2008 in the vicinity of Mobile Bay, Alabama. Coastal Conservation, 15(1), 139–149.
Eshleman, K. N. (2004). Hydrological consequences of land use changes: a review of the state-science. American Geophysical Union, Washington. doi:10.1029/153GM03.
Herold, M., Goldstein, N. C., & Clarke, K. C. (2003). The spatiotemporal form of urban growth: measurement, analysis and modeling. Journal of Remote Sensing of Environment, 86(3), 286–302.
Huang, J., Pontius Jr., R. G., Li, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2012). Use of intensity analysis to link patterns with processes of land change from 1986 to 2007 in a coastal watershed of Southeast China. Applied Geography, 34, 371–384.
Hussain, M., Chen, D., Cheng, A., Wei, H., & Stanley, D. (2013). Change detection from remotely sensed images: from pixel-based to object-based approaches. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 80, 91–106.
Iranian Statistics Center .(2012). General census of population and housing of Rasht City
Jamshidi, S., & Bastami, K. D. (2016). Metal contamination and its ecological risk assessment in the surface of Anzali Wetland, Caspian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.08.049.
Jokar, J., Helbich, M., Kainz, W., & Darvishi Boloorani, A. (2013). Integration of logistic regression, Markov chain and cellular automata models to simulate urban expansion. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 21, 265–275.
Khoshkam, M., Marzuki, A., & Al-Mulali, U. (2016). Socio-demographic effects on Anzali Wetland tourism development. Tourism Management, 54, 96–106.
Lechner, A. M., Langford, W. T., Bekessy, S. A., & Jones, S. D. (2012). Are landscape ecologist addressing uncertainty in their remote sensing data? Landscape Ecology, 7(9), 1249–1261.
Lechner, A. M., Reinke, K. J., Wang, Y., & Bastin, L. (2013). Interactions between landcover pattern and geospatial processing methods: effects on landscape metrics and classification accuracy. Ecol Complexity., 15, 71–82.
Luck, M., & Wu, J. G. (2002). A gradient analysis of urban landscape pattern: a case study from the Phoenix metropolitan region, Arizona, USA. Landscape Ecology, 17(4), 327–339.
Mahiny, A. S., & Clarke, K. C. (2012). Guiding SLEUTH land-use/land-cover change modeling using multicriteria evaluation: towards dynamic sustainable land-use planning. Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design, 39(5), 925–944.
Mahiny, A. S., & Clarke, K. C. (2013). Simulating hydrologic impacts of urban growth using SLEUTH, multi criteria evaluation and runoff modeling. Environmental Informatics, 22(1), 27–38.
Manandhar, R., Odeh, I. O. A., & Pontius Jr., R. G. (2010). Analysis of twenty years of categorical land transitions in the lower Hunter of New South Wales, Australia. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 135(4), 336–346.
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. (2005). Ecosystems and human well being: synthesis. Washington, DC: World Resources Institute.
Mortazavi, S., Bakhtiari, A. R., Sari, A. E., Bahramifar, N., & Rahbarizade, F. (2012). Phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in Anzali Wetland, Iran: elevated concentrations of 4-nonylphenol, octhylphenol and bisphenol A. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(5), 1967–1073.
Nagelkerken, I., Blaber, S. J. M., Bouillon, S., Green, P., Haywood, M., Kirton, L. G., Meynecke, J. O., Pawlik, J., Penrose, H. M., Sasekumar, A., & Somerfield, P. J. (2008). The habitat function of mangroves for terrestrial and marine fauna: a review. Aquatic Botany, 89(2), 155–185.
Noori, N., Kalin, L., Sen, S., Srivastava, P., & Lebleu, C. (2016). Identifying areas sensitive to land use/land cover change for downstream flooding in a coastal Alabama watershed. Regional Environmental Change, 16(6), 1833–1845.
Ozesmi, S. L., & Bauer, M. E. (2002). Satellite remote sensing of wetlands. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 10, 381–402.
Pickett, S. T. A., Cadenasso, M. L., Grove, J. M., Boone, C. G., Groffman, P. M., Irwin, E., Kaushal, S. S., Marsall, B., McGrath, B. P., Nilon, C. H., Pouyat, R. V., Azlavecz, K., Troy, A., & Warren, P. (2011). Urban ecological systems: scientific foundations anda decade of progress. J. Eviron. Manage., 92(3), 331–362.
Pontius Jr., R. G., Shusas, E., & McEachern, M. (2004). Detecting important categorical land changes while accounting for persistence. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 101(2–3), 251–268.
Pontius Jr., R. G., Gao, Y., Nicholas, M. G., Kohyama, T., Osaki, M., & Hirose, K. (2013). Design and interpretation of intensity analysis illustrated by land change in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Land, 2(3), 351–369.
Rafiee, R., Mahiny, A. S., Khorasani, N., Darvishsefat, A. A., & Danekar, A. (2009). Simulating urban growth in Mashad City, Iran through the SLEUTH model (UGM). Cities, 26, 19–26.
Romero-Ruiz, M. H., Flantua, S. G. A., Tansey, K., & Berrio, J. C. (2011). Landscape transitions in savannas of northern South America: land use/cover changes since 1987 in the Llanos Orientales of Colombia. Applied Geography, 32(2), 766–776.
Sakieh, Y., & Salmanmahiny, A. (2016). Treating a cancerous landscape: implications from medical sciences for urban and landscape planning in a developing region. Habitat International. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2016.03.008.
Sakieh, Y., Amiri, B. J., Danekar, A., Feghhi, J., & Dezhkam, S. (2015a). Scenario-based evaluation of urban development sustainability: an integrative modeling approach to compromise between urbanization suitability index and landscape pattern. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 17(6), 1343–1365.
Sakieh, Y., Amiri, B. J., Danekar, A., Feghhi, J., & Dezhkam, S. (2015b). Simulating urban expansion and scenario prediction using a cellular automata urban growth model, SLEUTH, through a case study of Karaj City, Iran. Journal of Housing and the Built Environment, 30(4), 591–611.
Sakieh, Y., Salmanmahiny, A., Jafarnezhad, J., Mehri, A., Kamyab, H., & Galdavi, S. (2015c). Evaluating the strategy of decentralized urban land-use planning in a developing region. Land Use Policy, 48, 534–551.
Sakieh, Y., Salmanmahiny, A., Mirkarimi, S. H., & Saeidi, S. (2016). Measuring the relationships between landscape aesthetics suitability and spatial patterns of urbanized lands: an informed modeling framework for developing urban growth scenarios. Geocarto International. doi:10.1080/10106049.2016.1178817.
Salamat, N., Etemadi-Deylami, E., Movahedinia, A., & Mohammadi, Y. (2014). Heavy metals in selected tissues and histopathological changes in liver and kidney of common moorhen (Gallinula chloropus) from Anzali Wetland, the South Caspian Sea, Iran. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 110, 298–307.
Shao, G., & Wu, W. (2004). The effects of classification accuracy on landscape indices. In R. S. Lunetta & J. G. Lyon (Eds.), Remote sensing and GIS accuracy assessment (pp. 209–220). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Shao, G., & Wu, J. (2008). On the accuracy of landscape pattern analysis using remote sensing data. Landscape Ecology, 23(5), 505–511.
Shao, G., Liu, D., & Zhao, G. (2001). Relationships of image classification accuracy and variation of landscape statistics. Can J Rem Sens, 27(1), 33–43.
Small, C., & Nicholls, R. J. (2003). A global analysis of human settlement in coastal zones. Journal of Coastal Research, 19(3), 584–599.
Sripanomyom, S., Round, P. D., Savini, T., Trisurat, Y., & Gale, G. A. (2011). Traditional salt-pans hold major concentrations of overwintering shorebirds in Southeast Asia. Biological Conservation, 144(1), 526–537.
Stevens, A., & Collins, L. (2011). Development and application of GIS datasets for assessing and managing coastal impacts and future change on the central coast of Western Australia. Coastal Conservation, 15(4), 671–685.
Teferi, E., Uhlenbrook, S., Bewket, W., Wenninger, J., & Simane, B. (2010). The use of remote sensing to quantify wetland loss in the Choke Mountain range, Upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 7(4), 2415–2428.
Teixeira, Z., Marques, J. C., & Pontius Jr., R. G. (2016). Evidence for deviations from uniform changes in a Portuguese watershed illustrated by CORINE maps: an intensity analysis approach. Ecological Indicators, 66, 382–390.
Villamor, G. B., Pontius Jr., R. G., & Van Noordwijk, M. (2014). Agroforest’s growing role in carbon losses from Jambi (Sumatra), Indonesia. Regional Environmental Change, 14(2), 825–834.
Walters, B. R., Rönnbäck, P., Kovacs, J. M., Crona, B., Hussain, S. A., Badola, R., Primavera, J. H., Barbier, E., & Dahdouh-Guebas, F. (2008). Aquatic Botany, 89, 220–236.
Wu, J. G. (2014). Urban ecology and sustainability: the state-of-the-science and future directions. Landscape and Urban Planning, 125, 209–221.
Zhou, P., Huang, J., Pontius, R. G., & Hong, H. (2014). Land classification and change intensity analysis in a coastal watershed of Southeast China. Sensors, 14(7), 11640–11658.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasani, M., Sakieh, Y., Dezhkam, S. et al. Environmental monitoring and assessment of landscape dynamics in southern coast of the Caspian Sea through intensity analysis and imprecise land-use data. Environ Monit Assess 189, 163 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5883-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5883-9