Abstract
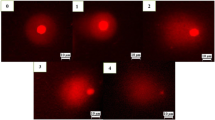
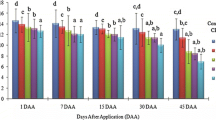
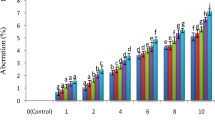
The present investigation was done to assess cytomorphologic parameters as indicators of genotoxicity as it is a simpler method and could be suggested for rapid screening of the vast range of agrochemicals used all over the world. The excessive and indiscriminate use of agrochemicals is responsible for increasing the level of pollutants in the soil environment resulting in cellular and molecular damage to the plants. The cellular damage caused manifestation of the resulting oxidative stress due to pollutants which can go up to the level of DNA. The roots of Allium cepa were treated with 0.5 mg N ml−1 concentration of ammonium nitrate fertilizer for 3, 6, 9 and 12 h, and in mitotic preparation of their respective root, mitotic index, phase indices and the genotoxic markers viz. chromosomal aberrations and binucleate cells were observed and the data statistically analysed. A significant decrease in mitotic index and increase in abnormality percentage as compared to control was observed which increased with the treatment duration. Chromosomal aberrations like stickiness, fragmentation, precocious movement, bridges and disorientations were observed in varying frequencies. A cytomorphologic study revealed that the interphase cell volume of cells of treated roots and their respective interphase nuclear volume were reduced as compared to control. The ratio between nuclear and cytoplasmic volume has been reported to relate to cell integrity. Both these markers viz. cytomorphologic and genotoxic can be used for assessment of the toxicity of agrochemicals including fertilizer; in our study, they have revealed the cytogenotoxic behaviour of ammonium nitrate fertilizer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, S. (1965). Studies on spontaneous and induced mutations in plants. Cytologia, 30, 155–172.
Abraham, S., & Nair, R. B. (1989). Production of mitotic abnormalities by magnesium sulphate in Vicia faba L. Cytologia, 54, 559–653.
Adel, E.I. (2000). The mutagenic effects of some nitrogenous fertilizers in Drosophila melanogaster. Ph.D. Thesis, Entomology Department, Faculty of Science, Cairo University.
Ahmed, M., & Grant, W. F. (1972). Cytological effects of the pesticides phosdrin and bladex in Tradescantia and Vicia faba. Canadian Journal of Genetics and Cytology, 14, 157–165.
Ananthakrishnan, M., Kumarasamy, K., & Antony, A. S. (2013). Genotoxic effects of furadan and endosulphan on (Allium cepa) root tips. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 6, 126–131.
Arora, K., Singh, N., Srivastava, S., & Srivastava, A. (2014). Evaluation of genotoxic risks due to temporal changes in soil urea: using Allium cepa L. root tip bioassay. Cytologia, 79, 85–93.
Botías, C., David, A., Hill, E. M., & Goulson, D. (2016). Contamination of wild plants near neonicotinoid seed-treated crops, and implications for non-target insects. Science of the Total Environment, 566–567, 269–278.
Chaurasia, O. P., & Sinha, S. P. (1987). Effects of urea on mitotic chromosomes of mice and onion. Cytologia, 52, 877–882.
Darlington, C. D. (1942). Chromosome Chemistry and Gene Action. Nature, 149(3768), 66–69
Das, A. B., & Mallick, R. (1993). Nuclear DNA and chromosomal changes within the tribe Ammineae. Cytobiology, 74, 197.
DeForest, J. L., Zak, D. R., & Pregitzer, K. S. (2004). Atmospheric nitrate deposition and the microbial degradation of cellobiose and vanillin in a northern hardwood forest. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 965–971.
El-Din, A. E., Abd-El-Samie, E. M., Faheem, H. B., Ibrahim, M. T., Ramzy, A., & Salama, M. S. (2009). Mutagenic effect of three nitrogenous fertilizers on Drosophila melanogaster. Cytologia, 74, 201–208.
El-Ghamery, A. A., El-Nahas, A. I., & Mansour, M. M. (2000). The action of atrazine herbicide as an inhibitor of cell division on chromosomes and nucleic acids content in root meristems of Allium cepa and Vicia faba. Cytologia, 65, 277–287.
Fisher, A., & Richter, C. (1984). Response of potato in newly reclaimed areas to mineral nitrogen fertilizer levels and nitrogen fixing biofertilizers Halex 2, Assuit. Journal of Agricultural Science, 27, 89–99.
Fiskesjo, G., & Levan, A. (1993). Evaluation of the first ten MEIC chemicals in the Allium test. ALTA, 21, 139–149.
Gömürgen, A. N. (2005). Cytological effect of the potassium metabisulphite and potassium nitrate food preservative on root tips of Allium cepa L. Cytologia, 70, 119–128.
Grant, W. F. (1999). Higher plant assays for the detection of chromosomal aberrations and gene mutations—a brief historical background on their use for screening and monitoring environmental chemicals. Mutation Research, 426, 107–112.
Grisolia, C. K. (2005). Agrotóxicos: Mutações, Câncer e Reprodução (p. 392). Brasiliap: Editora da UNB.
Helm, P. A., Milne, J., Hiriart-Baer, V., Crozier, P., Kolic, T., Lega, R., Chen, T., MacPherson, K., Gewurtz, S., Winter, J., Myers, A., Marvin, C. H., & Reiner, E. J. (2011). Lake-wide distribution and depositional history of current-and past-use persistent organic pollutants in Lake Simcoe, Ontario, Canada. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 37, 132–141.
Hidalgo, A., Gonzales-Reyes, J. A., Navas, P., & GarcIa-Herdugo, G. (1989). Abnormal mitosis and growth inhibition in Allium cepa roots induced by propham and chlorpropham. Cytobiology, 57, 7–14.
Jabee, F., Ansari, M. Y. K., & Shahab, D. (2008). Studies on the effect of maleic hydrazide on root tip cells and pollen fertility in Trigonella foenum-graecum L. Turkish Journal of Botany, 32, 337–344.
Kaufman, B. P. (1958). Cytolochemical studies of changes induced in cellular materials by ionizing radiations. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 59, 553.
Kaymak, F. (2005). Cytogenetic effects of maleic hydrazide on Helianthus annuus L. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 8, 104–108.
Kimmenade, V. R. R. J., & Januzzi, J. L. (2012). Emerging biomarkers in heart failure. Clinical Chemistry, 58(1), 127–138.
Koca, S. (2008). The cytogenetic effects of Sheffer A, a liquid fertilizer and growth regulator in root tip cells of Viciafaba L. C.B.U. J. Sci., 4, 121–126.
Kopliku, D., & Mesi, A. (2013). Assessment of cytotoxic and genotoxic potency of Cr (VI)- doped river water of nen-shkodra lowland, Albania on Allium cepa L. Journal of Environmental Research And Development, 7, 1322–1332.
Li, H. L., & Meng, Z. Q. (2003). Genotoxicity of hydrated sulfur dioxide on root tips of Allium sativum and Vicia faba. Mutation Research, 537, 109–114.
Majewska, A., Wolska, E., Sliwinska, E., Furmanowa, M., Urbanska, N., Pietrosuk, A., Zobel, A., & Kuras, M. (2003). Antimitoic effect, G2/M accumulation, chromosomal and ultrastructure changes in meristematic cells of Allium cepa L. root tips treated with the extract from. Rhadiola rosea roots, Caryologia, 56(3), 337–351.
Mesi, A., & Kopliku, D. (2013). Cytotoxic and genotoxic potency screening of two pesticides on Allium cepa L. Procedia Technology, 8, 19–26.
Mohammed, K. P., Aarey, A., Tamkeen, S., & Jahan, P. (2015). Forskolin: genotoxicity assessment in Allium cepa. Mutation Research, 777, 29–32.
Moustafa, G. G., Ibrahim, Z. S., Hashimoto, Y., Alkelch, A. M., Sakamoto, K. Q., Ishizuka, M., & Fujita, S. (2007). Testicular toxicity of profenofos in matured male rats. Archives of Toxicology, 81, 875–881.
Naksen, W., Prapamontol, T., Mangklabruks, A., Chantara, S., Thavornyutikarn, P., Robson, M. G., Ryan, P. B., Barr, D. B., & Panuwet, P. (2016). A single method for detecting 11 organophosphate pesticides in human plasma and breast milk using GC-FPD. Journal of Chromatography B, 1025, 92–104.
Pandey, R. M., & Santosh, U. (2007). Impact of food additives on mitotic chromosomes of Vicia faba L. Caryologia, 60, 309–314.
Pathiratne, A., Hemachandra, C. K., & De Silva, N. (2015). Efficacy of Allium cepa test system for screening cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of industrial effluents originated from different industrial activities. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 94, 199–203.
Saxena, M., Singh, H. K., & Yadav, S. (2007). Assessment of cytotoxic potential of Brilliant blue FCF on Vicia faba L. rootmeristems. Enviro Media, 26, 193.
Schneiderman, M. H., Dewey, W. C., & Highfield, D. P. (1971). Inhibition of DNA synthesis in synchronized Chinese hamster cell treated in G1 with cycloheleximide. Experimental Cell Research, 67, 147–155.
Sharma, A. K., & Sharma, A. (1980). Chromosome technique-theory and practice. London: Butterworths.
Sharma, S., & Vig, A. P. (2012). Genotoxicity of atrazine, avenoxan, diuron and quizalofop-P-ethyl herbicides using the Allium cepa root chromosomal aberration assay. Terrestrial and Aquatic Environmental Toxicology, 6, 90–95.
Sinsabaugh, R. L., Carreiro, M. M., & Repert, D. A. (2002). Allocation of extracellular enzymatic activity in relation to litter composition, N deposition, and mass loss. Biogeochemistry, 60, 1–24.
Sohbı, H. M., & Halıem, A. S. (1990). Effects of the herbicide rancho on root mitosis of Allium cepa. Egyptian Journal of Botany, 33, 43–50.
Srivastava, S., & Srivastava, A. (2009). Cytostatic and genotoxic effects produced by nitrogen fertilizer breakdown revealed by root mitosis bioassays. The Nucleus, 52, 79–92.
Stegeman, J. J., Brouwer, M., Di Giulio, R. T., Forlin, L., Fowler, B. A., Sanders, B. M. V., & Veld, P. A. (1992). Molecular responses to environmental contamination: enzyme and protein systems as indicators of chemical exposure and effect. In R. J. Huggett, R. A. Mehrle, & H. L. Bergman (Eds.), Biomarkers, physiological and histological markers of anthropogenic stress (pp. 235–335). Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
Sudhakar, R., Gowda, N., & Venu, G. (2001). Mitotic abnormalities induced by silk dyeing industry effluents in the cells of Allium cepa. Cytologia, 66, 235–239.
Tabur, S., & Oney, S. (2009). Effect of artificial fertilizers on mitotic index and chromosome behaviour in Vicia hybrida L. Journal of Agriculture Research, 47, 1–9.
Tsimakuridze, M., Saakadze, V., & Tsereteli, M. (2005). The characteristic state of health of ammonia nitrate producing workers. Georgian Medical News, 5, 80–83.
Türkoğlu, Ș. (2012). Determination of genotoxic effects of chlorfenvinphos and fenbuconazole in Allium cepa root cells by mitotic activity, chromosome aberration, DNA content, and comet assay. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 103(3), 224–230.
Van der Oost, R., Beyer, J., & Vermeulen, N. P. E. (2003). Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13(2), 57–149.
Vaux, D. L., & Korsmeyer, S. J. (1999). Cell death in development. Cell, 96, 245–254.
Verma, S., Arora, K., & Srivastava, A. (2016). Monitoring of genotoxic risks of nitrogen fertilizers by Allium cepa L. mitosis bioassay. Caryologia, 69(4), 343–350.
Waldrop, M. P., & Zak, D. R. (2006). Response of oxidative enzyme activities to nitrogen deposition affects soil concentrations of dissolved organic carbon. Ecosystems, 9, 921–933.
Webster, M., Witkin, K. L., & Cohen-Fix, O. (2009). Sizing up the nucleus: nuclear shape size and nuclear-envelope assembly. Journal of Cell Science, 122, 1477–1486.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the University Grant Commission (UGC), India, for financial assistance.
This work was supported by the University Grant Commission (UGC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, S., Srivastava, A. Cytomorphologic parameters in monitoring cytogenotoxic effects of fertilizer in Allium cepa L.. Environ Monit Assess 189, 159 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5873-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5873-y