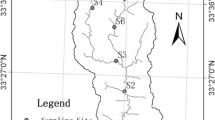
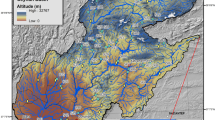
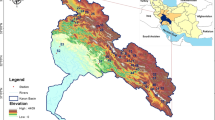
Abstract
The relationships of macroinvertebrate communities with abiotic factors in lake and river system were well documented, but their relationships with biotic factors were few explored. The macroinvertebrate communities in two river-disconnected lakes (Poyang Lake and Shijiu Lake) and the rivers connected to Shijiu Lake were investigated to reveal the differences in communities and explore the relationships with biotic factors. A total of 34 species were recorded in the three water bodies. Combined with the previous study results, the dominant species in Poyang Lake is almost unchanged since 1997. Mollusks were dominated in abundance in Poyang Lake and the rivers connected to Shijiu Lake, while oligochaetes dominated the communities in Shijiu Lake. The alpha diversity indices of macroinvertebrates in Poyang Lake and the rivers connected to Shijiu Lake were distinctly higher than that of Shijiu Lake, and the beta diversity index of Shijiu Lake was the highest, supporting the rules that alpha diversity of macroinvertebrates achieves a maximum at a moderate level of connectivity and beta diversity seems to be higher when the connectivity is weaker. The differences in communities were significant between the Poyang Lake and Shijiu Lake, while the differences in the Poyang Lake and the rivers connected to Shijiu Lake were not significant. According to the results of canonical correspondence analysis (CCA), protozoon densities and phytoplankton biomass affected the distribution of macroinvertebrates in Shijiu Lake. Species number of planktonic crustaceans influenced the distribution of macroinvertebrates in rivers connected to Shijiu Lake, while species number of rotifer and densities of phytoplankton distinctly impacted on the distribution of macroinvertebrates in Poyang Lake.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoros, C., & Bornette, G. (2002). Connectivity and biocomplexity in waterbodies of riverine floodplains. Freshwater Biology, 47(4), 761–776.
Bowman, M. F., Ingram, R., Reid, R. A., Somers, K. M., Yan, N. D., Paterson, A. M., et al. (2011). Temporal and spatial concordance in community composition of phytoplankton, zooplankton, macroinvertebrate, crayfish, and fish on the Precambrian shield. Canadian Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences, 65(5), 919–932.
Brucet, S., Boix, D., Nathansen, L. W., Quintana, X. D., Jensen, E., Balayla, D., et al. (2012). Effects of temperature, salinity and fish in structuring the macroinvertebrate community in shallow lakes: implications for effects of climate change. PloS One, 7(2), e30877.
Cai, R., Huang, W., Liu, Y., Zheng, F., Wang, H., & Li, Z. (1991). Fauna of Zhejiang: mollusks (in Chinese). Hangzhou: Zhejiang Science and Technology Publishing House.
Cai, Y., Gong, Z., & Qin, B. (2010). Community structure and diversity of macrozoobenthos in Lake Taihu, a large shallow eutrophic lake in China (in Chinese). Biodiversity Science, 18(1), 50–59.
Cai, Y., Jiang, J., Zhang, L., & Chen, Y. (2013). Structure of macrozoobenthos in lakes along the Yangtze River and relationships with environmental characteristics (in Chinese). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 16(16), A581.
Cai, Y., Lu, Y., Wu, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, L., & Lu, Y. (2014). Community structure and decadal changes in macrozoobenthic assemblages in Lake Poyang, the largest freshwater lake in China. Knowledge & Management of Aquatic Ecosystems, 414.
Castella, E., Richardot-Coulet, M., Roux, C., & Richoux, P. (1991). Aquatic macroinvertebrate assemblages of two contrasting floodplains: the rhǒne and Ain rivers, France. Regulated Rivers Research & Management, 6(6), 289–300.
Chen, X., Gao, W., Liu, W., Sun, C., & Kang, L. (2013). Characteristics of macrobenthos community structure and its relationship to environmental factors within a typical plain river network (in Chinese). Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(8), 1310–1316.
Chi, G., Zhao, Y., Guan, Z., Wang, J., & Tong, X. (2010). Relationship between macroinvertebrate and environmental variables in Hengshishui River (in Chinese). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(11), 2836–2845.
Clenaghan, Giller, O’halloran, & Hernan (1998). Stream macroinvertebrate communities in a conifer-afforested catchment in Ireland: relationships to physico-chemical and biotic factors. Freshwater Biology, 40(1), 175–193.
Dalu, T., Clegg, B., & Nhiwatiwa, T. (2012). Macroinvertebrate communities associated with littoral zone habitats and the influence of environmental factors in Malilangwe reservoir. Knowledge & Management of Aquatic Ecosystems, 406(6), 1–15.
Danilov, R., & Ekelund, N. G. A. (1999). The efficiency of seven diversity and one similarity indices based on phytoplankton data for assessing the level of eutrophication in lakes in Central Sweden. Science of the Total Environment, 234(1), 15–23.
Davidson, T. A., Mackay, A. W., Wolski, P., Mazebedi, R., Murray-Hudson, M., & Todd, M. (2012). Seasonal and spatial hydrological variability drives aquatic biodiversity in a flood-pulsed, sub-tropical wetland. Freshwater Biology, 57(6), 1253–1265.
Doi, H., Chang, K. H., Ando, T., Imai, H., Nakano, S. I., Kajimoto, A., et al. (2008). Drifting plankton from a reservoir subsidize downstream food webs and alter community structure. Oecologia, 156(2), 363–371.
Gao, F., Yin, H., Hu, W., Deng, J., & Gao, J. (2010). Ecological characteristics of macrobenthos communities in Chaohu basin in spring and their relationships with environmental factors (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21(8), 2132–2139.
Gong, Z., Xie, P., Tang, H., & Wang, S. (2001). The influence of eutrophycation upon community structure and biodiversity of macrozoobenthos (in Chinese). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25(3), 210–216.
Gower, A. M., Myers, G., Kent, M., & Foulkes, M. E. (1994). Relationships between macroinvertebrate communities and environmental variables in metal-contaminated streams in south-west England. Freshwater Biology, 32(1), 199–221.
Herlong, D. D., & Mallin, M. A. (1985). The benthos-plankton relationship upstream and downstream of a blackwater impoundment. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 3(1), 47–59.
Hu, H. (1980). Freshwater algae in China (In Chinese). Shanghai: Scientific and Technical Publisher.
Hu, Q., Feng, S., Guo, H., Chen, G., & Jiang, T. (2007). Interactions of the Yangtze river flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. Journal of Japanese History of Medicine, 60(1), 49–64.
Jenkins, R. A., Wade, K. R., & Pugh, E. (1984). Macroinvertebrate–habitat relationships in the river Teifi catchment and the significance to conservation. Freshwater Biology, 14(14), 23–42.
Jiang, X., & Du, N. (1979). Fauna Sinica-freshwater Cladocera (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press.
Jurado, B., Matson, Harrington, Baars, J.-R, & Kelly-Quinn, M. (2008). Macroinvertebrate diversity in constructed ponds: community structure and driving environmental factors. International Association of Theoretical & Applied Limnoloy, 30(3), 489–492.
Kennen, J. G., Riva-Murray, K., & Beaulieu, K. M. (2010). Determining hydrologic factors that influence stream macroinvertebrate assemblages in the northeastern US. Ecohydrology, 3(3), 88–106.
Lazarina, M., Sgardeli, V., Kallimanis, A. S., & Sgardelis, S. P. (2013). An effort-based index of beta diversity. Methods in Ecology & Evolution, 4(3), 217–225.
Macphee, S. A., Arnott, S. E., & Keller, W. (2011). Lake thermal structure influences macroinvertebrate predation on crustacean zooplankton. Journal of Plankton Research, 33(10), 1586–1595.
McCune, Grace, B., & James, B. (2002). Analysis of ecological communities. Mjm Software Design Gleneden Beach, 289(03), 448.
Mcnaughton, S. J. (1967). Relationships among functional properties of Californian grassland. Nature, 216(5111), 168–169.
Meerhoff, M., Clemente, J. M., Mello, F. T. D., Iglesias, C., Pedersen, A. R., & Jeppesen, E. (2007). Can warm climate-related structure of littoral predator assemblies weaken the clear water state in shallow lakes? Global Change Biology, 13(9), 1888–1897.
Mehler, K., Acharya, K., Sada, D., & Yu, Z. B. (2014). Factors affecting spatiotemporal benthic macroinvertebrate diversity and secondary production in a semi-arid watershed. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 30(2), 197–214.
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (1997). Analasis in water and wastewater (in Chinese). China: China Environmental Science Press.
Morse, J. C., Yang, L., & Tian, L. (1994). Aquatic insects of China useful for monitoring water quality. Nanjing: Hohai University Press.
Niu, Y., Shen, H., Xie, P., Yang, X., Tao, M., Ma, Z., et al. (2011). Phytoplankton community succession shaping bacterioplankton community composition in Lake Taihu, China. Water Research, 45(14), 4169–4182.
Obolewski, K. (2011). Macrozoobenthos patterns along environmental gradients and hydrological connectivity of oxbow lakes. Ecological Engineering, 37(5), 796–805.
Obrdlik, P., & Fuchs, U. (1991). Surface water connection and the macrozoobenthos of two types of floodplains on the upper Rhine. Regulated Rivers Research & Management, 6(4), 279–288.
Ormerod, S. J. (1988). The micro-distribution of aquatic macroinvertebrates in the wye river system: the result of abiotic or biotic factors? Freshwater Biology, 20(2), 241–247.
Ou, J., Wang, Y., Yang, H., Hu, J., Chen, X., Zou, J., et al. (2013). Eco-environmental Evolution Inferred from n-Alkanes and δ ∼ (13) C Records in the Sediments of Shijiu Lake (In Chinese). Environmental Science, 34(2), 484–493.
Pan, B., Wang, H., Liang, X., & Wang, H. (2011). Macrozoobenthos in Yangtze floodplain lakes: patterns of density, biomass, and production in relation to river connectivity. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 30(2), 589–602.
Pan, G., Wang, S., & Zhao, K. (2015). The ecological condition at present and the main problems faced by Shijiu lake (in Chinese). Pollution Contol Technology, 28(2), 23–27.
Reckendorfer, W., Baranyi, C., Funk, A., & Schiemer, F. (2006). Floodplain restoration by reinforcing hydrological connectivity: expected effects on aquatic mollusc communities. Journal of Applied Ecology, 43(3), 474–484.
Ren, H., Yuan, X., Liu, H., Zhang, Y., & Zhou, S. (2015). The effects of environment factors on community structure of benthic invertebrate in rivers (in Chinese). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(10), 3148–3156.
Sagrario, M. D. L. Á. G., & Balseiro, E. (2010). The role of macroinvertebrates and fish in regulating the provision by macrophytes of refugia for zooplankton in a warm temperate shallow lake. Freshwater Biology, 55(10), 2153–2166.
Sandin, L., & Johnson, R. K. (2004). Local, landscape and regional factors structuring benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in Swedish streams. Structure, 4(5), 531–541.
Shen, J. (1979). Fauna Sinica-freshwater copepods (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press.
Shen, Y., Gu, M., Gong, X., Shi, Z., Wei, Y., & Zheng, Y. (1990). New microbial monitoring technique (In Chinese). Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press.
Shokri, M., Rossaro, B., & Rahmani, H. (2014). Response of macroinvertebrate communities to anthropogenic pressures in Tajan River (Iran). Biologia, 69(10), 1395–1409.
Šmilauer, P., & Lepš, J. (2003). Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO 5. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Sun, G., Sheng, L., & Li, M. (2001). Community characteristics of benthonic animals and its relationship to environmental factors in the Nanhu Lake, Changchun (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 12(2), 319–320.
Takao, A., Kawaguchi, Y., Minagawa, T., Kayaba, Y., & Morimoto, Y. (2008). The relationships between benthic macroinvertebrates and biotic and abiotic environmental characteristics downstream of the Yahagi dam, Central Japan, and the state change caused by inflow from a tributary. River Research & Applications, 24(5), 580–597.
Thomaz, S. M., Bini, L. M., & Bozelli, R. L. (2007). Floods increase similarity among aquatic habitats in river-floodplain systems. Hydrobiologia, 579(1), 1–13.
Tockner, K., Schiemer, F., Baumgartner, C., Kum, G., Weigand, E., Zweimüller, I., et al. (1999). The Danube restoration project: species diversity patterns across connectivity gradients in the floodplain system. Regulated Rivers Research & Management, 15(1–3), 245–258.
Tolonen, K. T., Hämäläinen, H., Holopainen, I. J., & Karjalainen, J. (2001). Influences of habitat type and environmental variables on littoral macroinvertebrate communities in a large lake system. Fundamental & Applied Limnology, 152(1), 39–67.
Vaughn, C. C., & Hakenkamp, C. C. (2001). The functional role of burrowing bivalves in freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater Biology, 46(11), 1431–1446.
Wan, R., Yang, G., Wang, X., Qin, N., & Dai, X. (2014). Progress of research on the relationship between the Yangtze River and its connected lakes in the middle reaches (in Chinese). Journal of Lake Sciences, 26(1), 1–8.
Wang, H. (2002). Studies on taxonomy, distribution and ecology of microdrile oligochaetes of China, with description of two new species from the vicinity of the Great Wall station of China, Antarctica (in Chinese). Beijing: Higher Education Press.
Wang, W. (2006). Development mechanisms and their effects of Poyang Lake’s water resource exploitation and protection (in Chinese). Bulletin of Soil & Water Conservation, 26(4), 106–110.
Wang, R., & Zhang, J. (2011). Water quality assessment and status of eutrophication in Shijiu wetland (In Chinese). Wetland Science & Management, 7(2), 26–28.
Wang, Y., Xiong, B., & Chen, C. (2005). The effect of environment factors on life activity of zoobenthos (In Chinese). Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 24(3), 253–257.
Wang, H., Xu, Q., Cui, Y., & Liang, Y. (2007). Macrozoobenthic community of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake of China, in the Yangtze floodplain. Limnology, 8(1), 65–71.
Wang, H., Chen, Y., Liu, Z., Zhu, D., & Duan, Y. (2015). Correlation analysis of macroinvertebrate community and habitat factors in the middle reaches of Mudan River (in Chinese). China Environmental Science, 35(4), 1197–1204.
Weatherhead, M. A., & James, M. R. (2001). Distribution of macroinvertebrates in relation to physical and biological variables in the littoral zone of nine New Zealand lakes. Hydrobiologia, 462(1–3), 115–129.
Xing, W., Zheng, B., Liu, L., Wang, L., Li, L., & Huang, D. (2012). Correlation analysis of macroinvertebrate composition and environmental factors of typical sections in Dongting Lake (in Chinese). China Environmental Science, 32(12), 2237–2244.
Xu, Q., Wang, H., & Zhang, S. (2003). The impact of overstocking of mitten crab, eriocheir sinensis, on lacustrine zoobenthic community (In Chinese). Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, (1), 41–46.
Xu, C., Yu, Q., Xu, F., Hu, X., & You, W. (2012). Niche analysis of phytoplankton’s dominant species in Dianshan Lake of East China (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23(9), 2550–2558.
Yin, X., Xu, Z., Gao, X., Bai, H., Wu, W., & Song, J. (2013). Macrobenthos community structure and its relationships with environmental factors in Weihe River basin, Northwest China (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(1), 218–226.
Zhang, Z., & Huang, X. (1991). Research methods of freshwater plankton (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press.
Zhang, M., Xu, L., Xie, G., Liu, Y., Liu, X., Song, S., et al. (2013). Species diversity, distribution and conservation of freshwater mollusk in Poyang Lake basin (in Chinese). Marine Sciences, 37(8), 114–124.
Zheng, J., Chi, S., Li, D., Zhou, L., & Hu, J. (2015). Protozoan population distribution and its homogeneity in Shijiu Lake (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(4), 1052–1059.
Zhuge, Y. (1997). Study on the typical area of China rotifers (In Chinese). Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Funds (No. 51409178). The authors thank Sheng Chen, Wei Chen, Jufang Zhang, and Dan Li for field assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript, and manuscript is approved by all authors for publication. I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part. All the authors listed have approved the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chi, S., Zheng, J., Zhao, X. et al. Macroinvertebrate communities and the relationships with biotic factors in river-connected lakes in the lower reaches of Yangtze River, China. Environ Monit Assess 188, 577 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5602-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5602-y