Abstract
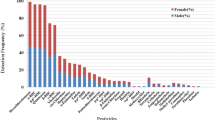
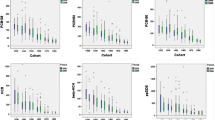
Organochlorine pesticides, due to their hydrophobic nature and persistence, accumulate in tissues rich in lipids, which had been used as a biomarker for environmental pollution. In humans, organochlorine pesticides are continuously circulating and equilibrating among body compartments. The objective of the study was to evaluate the concentrations of organochlorine pesticides in blood serum and compare their levels to the total lipid contents in Veracruz, México inhabitants. Our hypothesis is that concentrations of organochlorine pesticides will increase just as lipid concentrations. Levels of organochlorine pesticides were divided in ascending tertils according to their total lipid content. The linear trend model applied surprisingly reveals that the average level of all organochlorine pesticides decreases as the lipid concentration increases. From one tertil to the next β-HCH, it shows a decrease of −3.19 mg kg−1 on lipid basis, pp.′DDE levels decrease by −3.70 mg kg−1 on lipid basis and pp.′DDT levels decrease −1.13 mg kg−1 on lipid basis. We conclude that the levels and the orderly sequence of organochlorine pesticide distributions in the blood serum maintain an inverse relationship to total lipid blood serum concentrations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2011). http://www.spinreact.com.mx/public/instructivo/QUIMICA%20CLINICA/LIQUIDOS/1001270.pdf. Accessed November 20, 2011.
ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry) (2002). Toxicological Profile for DDT, DDE, and DDD. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp.asp?id/81&tid=20.
Chevrier, J., Dewailly, E., Ayotte, P., Mauriege, P., Despres, J. P., & Tremblay, A. (2000). Body weight loss increases plasma and adipose tissue concentrations of potentially toxic 460 pollutants in obese individuals. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders, 24(10), 1272–1278.
Daley, J. M., Paterson, G., & Drouillard, K. G. (2014). Bioamplification as a bioaccumulation mechanism for persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in wildlife. Review of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 227, 107–155.
De Roos, A. J., Ulrich, C. M., Sjodin, A., & McTiernan, A. (2012). Adiposity, body composition, and weight change in relation to organochlorine pollutant plasma concentrations. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 22(6), 617–624.
Dirtu, A. C., Dirinck, E., Malarvannan, G., Neels, H., Van Gaal, L., Jorens, P. G., & Covaci, A. (2013). Dynamics of organohalogenated contaminants in human serum from obese individuals during one year of weight loss treatment. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(21), 12441–12449.
El-Amrani, S., Pena-Abaurrea, M., Sanz-Landaluze, J., Ramos, L., Guinea, J., & Cámara, C. (2012). Bioconcentration of pesticides in zebrafish eleutheroembryos (Danio rerio). Science of the Total Environment, 425, 184–190.
Eskenazi, B., Chevrier, J., Goldman, R. L., Anderson, H. A., Bornman, M. S., Bouwman, H., et al. (2009). The pine river statement: human health consequences of DDT use. Environmental Health Perspectives, 117, 1359–1367.
Gyalpo, T., Fritsche, L., Bouwman, H., Bornman, R., Scheringer, M., & Hungerbühler, K. (2012). Estimation of human body concentrations of DDT from indoor residual spraying for malaria control. Environmental Pollution, 169, 235–241.
Herrero-Mercado, M., Waliszewski, S. M., Caba, M., Martínez-Valenzuela, C., Gómez-Arroyo, S., Villalobos-Pietrini, R., et al. (2011). Organochlorine pesticide gradient levels among maternal adipose tissue, maternal blood serum and umbilical blood serum. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 86(3), 289–293.
Hue, O., Marcotte, J., Berrigan, F., Simoneau, M., Dore, J., Marceau, P., et al. (2006). Increased plasma levels of toxic pollutants accompanying weight loss induced by hypocaloric diet or by bariatric surgery. Obesity Surgery, 16(9), 1145–1154.
Katagi, T. (2010). Bioconcentration, bioaccumulation and metabolism of pesticides in aquatic organisms. Reviews of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 204, 1–149.
Kim, M. J., Marchand, P., Henegar, C., Antignac, J. P., Alili, R., Poitou, C., Buillot, J. L., Basdevant, A., Le Bizec, B., Barouki, R., Clement, K. (2011). Fate and complex pathogenic effects of dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls in obese subjects before and after drastic weight loss. Environmental Health Perspectives, 119(3), 377–383.
Malarvannan, G., Dirinck, E., Dirtu, A. C., Pereira-Fernandes, A., Neels, H., Jorens, P. G., et al. (2013). Distribution of persistent organic pollutants in two different fat compartments from obese individuals. Environment International, 55, 33–42.
Mueller, J. F., Harden, F., Toms, L. M., Symons, R., & Furst, P. (2008). Persistent organochlorine pesticides in human milk samples from Australia. Chemosphere, 70, 712–720.
Pelletier, C., Doucet, E., Imbeault, P., & Tremblay, A. (2002). Associations between weight loss induced changes in plasma organochlorine concentrations, serum T(3) concentration, and resting metabolic rate. Toxicological Sciences, 67(1), 46–51.
Porta, M., Jariod, M., López, T., Pumarega, J., Puigdomènech, E., Malats, N., et al. (2009). Correcting serum concentrations of organochlorine compounds by lipids: alternatives to the organochlorine/total lipids ratio. Environment International, 35, 1080–1085.
Smith, A. G., & Gangolli, S. D. (2002). Organochlorine chemicals in seafood: occurrence and health concerns. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 40, 767–779.
Waliszewski, S. M., & Szymczynski, G. A. (1991). Persistent organochlorine pesticides in blood serum and whole blood. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 46, 803–809.
Waliszewski, S. M., Pardio, V. T., Waliszewski, K. N., Chantiri, J. N., Aguirre, A. A., Infanzon, R. M., & Rivera, J. (1997). Organochlorine pesticide residues in cow’s milk and butter in Mexico. Science of the Total Environment, 208(1), 127–132.
Waliszewski, S. M., Aguirre, A. A., Infanzon, R. M., Silva, C. S., & Siliceo, J. (2001). Organochlorine pesticide levels in maternal adipose tissue, maternal blood serum, umbilical blood serum, and milk from inhabitants of Veracruz, Mexico. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 40(3), 432–438.
Waliszewski, S. M., Gómez-Arroyo, S., Infanzón, R. M., Villalobos-Pietrini, R., & Hart, M. M. (2003). Comparison of organochlorine pesticide levels between abdominal and breast adipose tissue. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 71(1), 156–162.
Waliszewski, S. M., Gómez-Arroyo, S., Carvajal, O., Villalobos-Pietrini, R., & Infanzón, R. M. (2004). Uso del ácido sulfúrico en las determinaciones de plaguicidas organoclorados. Internacional de Contaminación Ambiental, 20(4), 185–192.
Waliszewski, S. M., Caba, M., Herrero-Mercado, M., Saldariaga-Noreña, H., Meza, E., Zepeda, R., et al. (2012). Organochlorine pesticide residue levels in blood serum of inhabitants from Veracruz, Mexico. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 5613–5621.
Wang, N., Shi, L., Kong, D., Cai, D., Cao, Y., Liu, Y., & Pang, G. (2011). Accumulation levels and characteristics of some pesticides in human adipose tissue samples from southeast China. Chemosphere, 84(7), 964–971.
Wang, H. S., Chen, Z. J., Wei, W., Man, Y. B., Giesy, J. P., Du, J., et al. (2013). Concentrations of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in human blood plasma from Hong Kong: markers of exposure and sources from fish. Environment International, 54, 18–25.
Whitcomb, B. W., Schisterman, E. F., Buck, G. M., Weiner, J. M., Greizerstein, H., & Kostyniak, P. J. (2005). Relative concentrations of organochlorines in adipose tissue and serum among reproductive age women. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 19(2), 203–213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caba, M., Meza, E., Waliszewski, S.M. et al. Inverse correlation among organochlorine pesticide levels to total lipid serum contents: a preliminary study in Veracruz, México. Environ Monit Assess 187, 467 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4694-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4694-0