Abstract
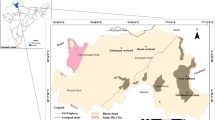
Wetlands are important ecosystems both at regional and global scales. They are home to a diverse group of flora and fauna, and provide water for drinking, irrigation, and recreational purposes. Miangaran endorheic wetland in SW Iran serves as the discharge point of the municipal wastewater of a nearby city; it receives agricultural return flows as well. To identify the consequences of the wastewater input, 29 water samples from the wetland’s body and inlet streams were analyzed for physico-chemical parameters. The average EC of the wetland was 405 μS/cm; calcium, magnesium, and bicarbonate were the dominant ions. The average pH was high, about 8.6, due to carbonate dissolution in the drainage area which was exacerbated by photosynthesis process inside the wetland. The concentration of phosphate was over the eutrophication limit of 0.1 mg/L. Nitrate contents varied from 5.7 to 12.3 mg/L. Trophic state index based on total nitrogen was about 63, falling within the eutrophic group. Heavy metal concentrations were generally higher than WHO drinking limits. Highest values of EC, nutrients, and metals were observed in the south and northwest, clearly signifying the role of wastewater input as the main source of contamination, which has resulted in the eutrophication of the wetland.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2007). Assessment of the spring water quality in the Shoubak area, Jordan. Environmentalist, 28, 203–215.
Altun, O., Saçan, M. T., & Erdem, A. K. (2009). Water quality and heavy metal monitoring in water and sediment samples of the Kuçukçekmece lagoon, Turkey (2002–2003). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 151(1-4), 345.362.
Atici, T., Ahiska, S., Altindag, A., & Aydin, D. (2008). Ecological effects of some heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Hg, Cr) pollution of phytoplanktonic algae and zooplanktonic organisms in Sar’yyar Dam Reservoir in Turkey. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7(12), 1972–1977.
Ayers, R. S., Westcot, D. W. (1998). Water quality for agriculture, University of California.
Bajkiewicz-Grabowska, E. (2007). Trophic diversity of lakes—present state, the place in trophic classification, Lakes of the Kashubian Landscape Park (pp. 293–305). Gdańsk: KLUG.
Bing, H. J., Wu, Y. H., Sun, Z. B., & Yao, S. C. (2011). Historical trends of heavy metal contamination and their sources in lacustrine sediment from Xijiu Lake, Taihu Lake Catchment, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23(10), 1671–1678.
Carlson, R. E. (1977). A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 22, 361–639.
Carpenter, S. R., Caraco, N. F., Correll, D. L., Howarth, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Smith, V. H. (1998). Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications, 8(3), 559–568.
Chandra, R., Nishadh, K. A., & Azeez, P. A. (2010). Monitoring water quality of Coimbatore wetlands, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 169, 671–676.
Erwin, K. L. (2009). Wetlands and global climate change: the role of wetland restoration in a changing world. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 17(1), 71–84.
Esmaeili, M. (2014). Water quality monitoring and environmental assessment of Miangaran wetland in Khuzestan, Dissertation, University of Shahrood [In Farsi].
Ikem, A., Odueyungbo, S., Egiebor, N. O., & Nyavor, K. (2002). Chemical quality of bottled waters from three cities in eastern Alabama. The Science of the Total Environment, 285, 165–175.
Jarosiewicz, A., Ficek, D., & Zapadka, E. (2011). Eutrophication parameters and Carlson-type trophic state indices in selected Pomeranian lakes. Limnological Review, 11(1), 15–23.
Jiang, X., Wang, W., Wang, S., Zhang, B., & Hu, J. (2012). Initial identification of heavy metals contamination in Taihu Lake, a eutrophic lake in China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(9), 1539–1548.
Kalantari, N., Pawar, N. J., & Keshavarzi, M. R. (2009). Water resource management in the intermountain Izeh Plain, southwest of Iran. Journal of Mountain Science, 6, 25–41.
Karthick, B., Alkananda, B., & Ramachandra, T. V. (2009). Diatom based pollution monitoring in urban wetlands of Coimbatore. Tamil Nadu: Environmental Information System (ENVIS). Technical Report No. 31.
Keshavarzi M, Kalantari N, Charchi A (2006) Evaluating lakes of Izeh in supplying water for rainfed agricultural lands. Proceedings of the National Conference on Managing Irrigation and Drainage Networks, Iran [In Farsi].
Khan, F. A., & Ansari, A. A. (2005). Eutrophication: an ecological vision. The Botanical Review, 71(4), 449–482.
Khan, M. A. (2008). Chemical environment and nutrient fluxes in a flood plain wetland ecosystem, Kashmir Himalayas, India. Indian Forester, 134(4), 505–514.
Kratzer, C. R., & Brezonik, P. L. (1981). A Carlson-type trophic state index for nitrogen in Florida Lakes. Water Resources Bulletin, 17, 713–715.
Lalah, J. O., Ochieng, E. Z., & Wandig, S. O. (2008). Sources of heavy metal input into Winam Fulf, Kenya. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 81(3), 277–284.
Mikhlafi AS‚ Das, B. K., & Kaur, P. (2003). Water chemistry of Mansar lake (India): an indication of source area weathering and seasonal variability. Environmental Geology, 44, 645–653.
Mitsch, W. J., & Gosselink, J. G. (2000). Wetlands (3rd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Naseri, H. R., Alijani, F., & Mirzaei, L. (2009). Environmental characterization of a karst polje: an example from Izeh polje, southwest Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 59, 99–108.
Nouri, J., Mirbagheri, S. A., Farrokhian, F., Jaafarzadeh, N., & Alesheikh, A. A. (2010). Water quality variability and eutrophic state in wet and dry years in wetlands of the semiarid and arid regions. Environmental Earth Sciences, 59, 1397–1407.
Parkhurst, D. L., Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (version 2)—a computer program for speciation, batch reaction, one-dimensional transport and inverse geochemical calculations. Water Resources Investigations Report (United States Geological Survey), pp. 95–4259.
Pawar, A. L. (2010). Seasonal variation in physicochemical quality of Lonar lake water. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2(4), 225–231.
Rand, G. M., Wells, P. G., & McCarty, L. S. (2003). Introduction to aquatic toxicology. In G. M. Rand (Ed.), Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology (pp. 3–67). New York: Taylor & Francis.
Reddy, M. V., Babu, K. S., Balaram, V., & Satyanarayanan, M. (2012). Assessment of the effects of municipal sewage, immersed idols and boating on the heavy metal and other elemental pollution of surface water of the eutrophic Hussainsagar lake (Hyderabad, India). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 1991–2000.
Riahinia A (2008) Investigating the organic pollutants of Miangaran wetland using qualitative factors and environmental indices. Proceedings of the First National Conference of Iran’s Wetlands, Iran [In Farsi].
Sener S‚ Davraz, A., & Karaguzel, R. (2013). Evaluating the anthropogenic and geologic impacts on water quality of the Egirdir lake, Turkey. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70, 2527–2544.
Singh, A. P., Srivastava, P. C., & Srivastava, P. (2008). Relationships of heavy metals in natural lake waters with physico-chemical characteristics of waters and different chemical fractions of metals in sediments. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 188, 181–193.
Solanki, V. R., Hussain, M. M., & Raja, S. S. (2010). Water quality assessment of Lake Pandu Bodhan, Andhra Pradesh State, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 163, 411–419.
Talbot, C. J., & Jarvis, R. J. (1984). Age, budget and dynamics of an active salt extrusion in Iran. Journal of Structural Geology, 6, 521–533.
Wang, Y., Wang, P., Bai, Y., Tian, Z., Li, J., Shao, X., Mustavich, L. F., & Li, B. L. (2013). Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research, 7, 30–40.
WHO. (2004). Guidelines for drinking-water quality (3rd ed.). Geneva: WHO.
Yu, F. C., Fang, G. H., & Ru, X. W. (2010). Eutrophication, health risk assessment and spatial analysis of water quality in Gucheng Lake, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 59, 1741–1748.
Acknowledgments
The cooperations of Khuzestan Water & Wastewater Company and University of Shahrood are highly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafari, H., Bagheri, R., Forghani, G. et al. The consequences of disposing wastewater in an endorheic wetland in southwest Iran. Environ Monit Assess 187, 357 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4560-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4560-0