Abstract
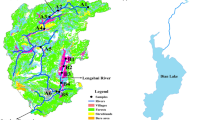
The characteristics of phosphate adsorption and the transformation of phosphorus forms in the release process of the sediments in Nanyang Lake and Weishan Lake are researched. Distribution of maximal amount of phosphorus adsorbed (Q max) is 112.76 and 93.91 mg kg−1, respectively, and the adsorption processes of Nanyang Lake and Weishan Lake reach equilibrium after 48 h. Total maximal amount of phosphorus adsorbed is the amount of Q max and native adsorbed phosphorus (NAP). The m is the sum of the adsorption efficiency of the sediments adsorbing the phosphorus coming from external sources and the phosphorus desorbed from the sediments. Mutual transformation between phosphorus forms exists in the process of phosphorus release. The contents of NH4Cl-P, BD-P, and HCl-P in the sediments reduced, and the content of NaOH-P increased in the process. But the amount of NaOH-P increased is less than the amount of NH4Cl-P, BD-P, and HCl-P reduced. So other forms of phosphorus transformation relations exist.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emil, R. (2000). Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Research, 34(7), 2037–2042.
Golterman, H. L. (1996). Fractionation of sediment phosphate with chelating compounds: a simplification, and comparison with other methods. Hydrobiologia, 335(1), 87–95.
House, W. A., & Denison, F. H. (2000). Factors influencing the measurement of equilibrium phosphate concentrations in river sediments. Water Research, 34(4), 1187–1200.
Hupfer, M., Gächter, R., & Giovanoli, R. (1995). Transformation of phosphorus species in setting seston and during early sediment diagenesis. Aquatic Sciences, 57(4), 305–324.
Jiang, X., Jin, X. C., Yao, Y., Li, L. H., et al. (2006). Effects of oxygen on the release and distribution of phosphorus in the sediments under the light condition. Environmental Pollution, 141(3), 482–487.
Jin, X. C., Wang, S. R., Pang, Y., et al. (2005). The adsorption of phosphate on different trophic lake sediments. Colloids and Surfaces A, 254, 241–248.
Jin, X. C., Wang, S. R., Pang, Y., et al. (2006). Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environmental Pollution, 139(2), 288–295.
Kim, L. H., Choi, E., & Stenstrom, M. K. (2003). Sediment characteristics, phosphorus types and phosphorus release rates between river and lake sediments. Chemosphere, 50(1), 53–61.
Lopez, P., Lluch, X., Vidal, M., et al. (1996). Adsorption of phosphorus on sediments of the Balearic Islands (Spain) related to their composition. Estuar Coast Shelf S, 42(2), 185–196.
Paul, C. M., Bocrs, I. V., et al. (1991). The influence of pH on phosphate release from lake sediments. Water Research, 25(3), 309–311.
Robarts, R. D., Waiser, M. J., Hadas, O., et al. (1998). Relaxation of phosphorus limitation due to typhoon-induced mixing in two morphologically distinct basins of Lake Biwa, Japan. Limnology and Oceanography, 43(6), 1023–1036.
Sondergaard, M., Jensen, J. P., & Jeppesen, E. (2001). Retention and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow, eutrophic lakes. The Scientific World Journal, 1(1), 427–442.
Sun, H. Q., Wang, P., & Jiang, H. L. (2012a). Behavior of phosphorus in interface of sediment-overlying water in Taihu Lake under different simulative conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 35(5), 141–146.
Sun, Y. Y., Zhang, Z. L., & Li, S. (2012b). Analysis of nutrient distribution in surface sediment of Nansihu Lake. Water Resources and Power, 30(8), 37–40.
Wang, S. R., Jin, X. C., Pang, Y., et al. (2005). The study of the effect of pH on phosphate sorption by different trophic lake sediment. Colloid and Interface Science, 285(2), 448–457.
Zhou, Q., Gibson, C. E., & Zhu, Y. (2001). Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in sediments of three contrasting lakes in China and the UK. Chemosphere, 42(2), 221–225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., An, W. & Li, X. Research on phosphorus loads and characteristics of adsorption and release in surface sediments of Nanyang Lake and Weishan Lake in China. Environ Monit Assess 187, 4103 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4103-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4103-0