Abstract
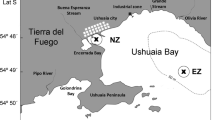
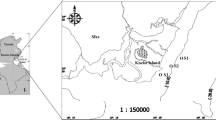
This study focused on the seasonal and spatial analysis of the mesozooplankton community in a human-impacted subantarctic bay in Argentina and aimed to detect assemblages associated with environmental variability. Mesozooplankton samples and environmental data were obtained in the Ushuaia Bay (UB) seasonally, from August 2004 to June 2005, and spatially, from coastal (more polluted), middle (less influenced) and open sea water (free polluted) sampling stations. Remarkable seasonal changes on the mesozooplankton community were observed. Nitrogenated nutrients, chlorophyll a, salinity and temperature were the prevailing environmental conditions likely associated with the different mesozooplankton assemblages found in the bay. The copepods Eurytemora americana, Acartia tonsa, Podon leuckarti and Nematoda were particularly observed on the northwest coast of the bay, characterized by the highest level of urban pollution, eutrophicated by sewage and freshwater inputs from the Encerrada Bay which is connected to it. The stations situated in the northeast area, mostly influenced by freshwater input from rivers and glacier melting, showed low mesozooplankton abundances and an important contribution of adventitious plankton. The copepods Ctenocalanus citer, Clausocalanus brevipes and Drepanopus forcipatus were mostly observed at the stations located near the Beagle Channel, characterized by open sea and free polluted waters. Our findings suggest that the variations observed in the mesozooplankton assemblages in the UB seem to be modulated by environmental variables associated with the anthropogenic influence, clearly detected on the coast of the bay. Certain opportunistic species such as A. tonsa and E. americana could be postulated as potential bioindicators of water quality in subantarctic coastal ecosystems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adami, M. L., & Gordillo, S. (1999). Structure and dynamics of the biota associated with Macrocystis pyrifera (Phaeophyta) from the Beagle Channel, Tierra del Fuego. Scientia Marina, 63, 183–191. Suppl.1.
Albania, A., Villate, F., & Uriarte, I. (2009). Zooplankton communities in two contrasting Basque estuaries (1999–2001): reporting changes associated with ecosystem health. Journal of Plankton Research, 31(7), 739–752.
Aguirre, G. E., Capitanio, F. L., Lovrich, G. A., & Esnal, G. B. (2011). Seasonal variability of metazooplankton in coastal sub-Antarctic waters (Beagle Channel). Marine Biology Research, 00, 1–13.
Amin, O., Comoglio, L., Spetter, C., Duarte, C., Astesuain, R., Freije, R. H., & Marcovecchio, J. (2010). Assessment of land influence on a high latitude marine coastal system: Tierra del Fuego, southernmost Argentina. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 175(1–4), 63–73.
Antezana, T. (1999). Hydrographic features of Magellan and Fuegian inland passages and adjacent Subantarctic waters. Scientia Marina, 63, 23–34. Suppl.1.
APHA. (1980). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (15th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Avent, S. R. (1998). Distribution of Eurytemora americana (Crustacea, Copepoda) in the Duwamish River estuary. University of Washington, USA: School of Oceanography Report of Project.
Balestrini, C., Vinuesa, J. H., Lovrich, G. A., Mattenet, C. E., Cantú, C. E., & Medina, P. V. (1990). Estudio de las corrientes marinas en los alrededores de la Península Ushuaia. Tierra del Fuego: Contribución Científica CADIC.
Berasategui, A. A., Hoffmeyer, M. S., Biancalana, F., Fernandez Severini, M., & Menendez, M. C. (2009). Temporal variation in abundance and fecundity of the invading copepod Eurytemora americana in Bahía Blanca Estuary during an unusual year. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 85, 82–88.
Berasategui, A. A., Hoffmeyer, M. S., Dutto, M. S., & Biancalana, F. (2012). Seasonal variation in the egg morphology of the copepod Eurytemora americana and its relationship with reproductive strategy in a temperate estuary in Argentina. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 69(3), 380–388.
Biancalana, F., & Torres, A. I. (2011). Variations of mesozooplankton composition in a eutrophicated semi-enclosed system (Encerrada Bay, Tierra del Fuego, Argentina). Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 59(2), 195–199.
Biancalana, F., Barría de Cao, M. S., & Hoffmeyer, M. S. (2007). Micro and mesozooplankton composition during winter in Ushuaia and Golondrina Bays (Beagle Channel, Argentina). Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 55(2), 83–97.
Biancalana, F., Menéndez, M. C., Berasategui, A. A., Fernández-Severini, M., & Hoffmeyer, M. S. (2012a). Sewage pollution effects on mesozooplankton structure in a shallow temperate estuary. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(6), 3901–13.
Biancalana, F., Diodato, M. S., & Hoffmeyer, M. S. (2012b). Seasonal and spatial variation of mesozooplankton biomass in Ushuaia and Golondrina Bays (Beagle Channel, Argentina). Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 60(1), 99–106.
Bianchi, F., Acri, F., Bernardi Aubry, F., Berton, A., Boldrin, A., Camatti, E., Cassin, D., & Comaschi, A. (2003). Can plankton communities be considered as bio-indicators of water quality in the Lagoon of Venice? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46, 964–971.
Boltovskoy, D. (1981). Características biológicas del Atlántico Sudoccidental. In D. Boltovskoy (Ed.), Atlas del zooplancton de Atlántico Sudoccidental y métodos de trabajo con el zooplancton marino (pp. 239–248). Mar del Plata: INIDEP Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones y Desarrollo Pesquero.
Calbet, A., Garrido, S., Saiz, E., Alcaraz, M., & Duarte, C. M. (2001). Annual zooplankton succession in coastal NW Mediterranean waters: the importance of the smaller size fractions. Journal of Plankton Research, 23(3), 319–331.
Caulleaud, K., Forget-Leray, J., Peluhet, L., LeMenach, K., Souissi, S., & Budzinski, H. (2009). Tidal influence on the distribution of hydrophobic organic contaminants in the Seine Estuary and biomarker responses on the copepod Eurytemora affinis. Environmental Pollution, 157(1), 64–71.
Chang, K. H., Doi, H., Nishibe, Y., Obayashi, Y., & Nakano, S. I. (2009). Spatial and temporal distribution of zooplankton communities of coastal marine waters receiving different human activities (fish and pearl oyster farmings). The Open Marine Biology Journal. doi:10.2174/187445080903010083.
Chen, G. T., Herman, R. L., & Vincx, M. (1999). Meiofauna communities from the Straits of Magellan and the Beagle Channel. Scientia Marina, 63, 167–174. Supl.1.
Chiesa, I. L., Alonso, G. M., & Zelaya, D. G. (2005). Species richness and faunistic affinities of the Gammaridae and Corophiidae (Amphipoda) from shallow waters of southern Tierra del Fuego, Argentina: preliminary results. Scientia Marina, 69, 167–174. Suppl.2.
Clarke, K. R., & Warwick, R. M. (1994). Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. Cambridge: Natural Environment Research Council.
Duarte, C. A., Giarratano, E., Amin, O. A., & Comoglio, L. I. (2011). Heavy metal concentrations and biomarkers of oxidative stress in native mussels (Mytilus edulis chilensis) from Beagle channel coast (Tierra del Fuego, Argentina). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62, 1895–1904.
Dutto, M. S., Lopez Abbate, M. C., Biancalana, F., Berasategui, A. A., & Hoffmeyer, M. S. (2012). The impact of sewage on environmental quality and the mesozooplankton community in a highly eutrophic estuary in Argentina. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 69(3), 399–409.
Fernández-Severini, M. D., & Hoffmeyer, M. S. (2005). Mesozooplankton assemblages in two different bays in the Beagle Channel (Argentina) during January, 2001. Scientia Marina, 69, 27–37. Suppl.2.
Gil, M., Torres, A. I., Amin, O., & Esteves, J. L. (2011). Assessment of recent sediment influence in an urban polluted subantarctic coastal ecosystem. Beagle Channel (Southern Argentina). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(1), 201–207.
Head, E. J. H., & Harris, L. R. (1992) Chlorophyll and carotenoid transformation and destruction by Calanus spp. grazing on diatoms. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 86, 229–238.
Hernandez-Carmona, G., Robledo, D., & Serviare-Zaragoza, E. (2001). Effect of nutrient availability on Macrocystis pyrifera recruitment and survival near its southern limit of Baja California. Botanica Marina, 44(3), 221–229.
Hoffmeyer, M. S. (2004). Decadal change in zooplankton seasonal succession in the Bahia Blanca estuary, Argentina, following introduction of two zooplankton species. Journal of Plankton Research, 26(2), 181–189.
Hoffmeyer, M. S., Berasategui, A. A., Beigt, D., & Piccolo, M. C. (2008). Environmental regulation of the estuarine copepod Acartia tonsa and Eurytemora americana during coexistence period. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 89(2), 355–361.
Kontas, A., Kucuksezgin, F., Altay, O., & Uluturhan, E. (2004). Monitoring of eutrophication and nutrient limitation in The Izmir Bay (Turkey) before and aster wastewater treatment plant. Environment International, 29(8), 1057–1062.
Kühnemann, O. (1970). Algunas consideraciones sobre los bosques de Macrocystis pyrifera. Physis, 29(79), 273–296.
Leandro, M. S., Morgado, F., Pereira, F., & Queiroga, H. (2007). Temporal changes of abundance, biomass and reproduction of Copepoda community in a shallow temperate estuary (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal). Estuarine Coast and Shelf Research, 74(1–2), 215–222.
Leps, J., & Smilauer, P. (2003). Multivariate analysis of ecology data using CANOCO. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Li, K. Z., Yan, J. Q., Huang, L. M., & Tan, Y. H. (2006). Spatial and temporal variations of mesozooplankton in the Pearl River estuary, China. Estuarine Coast and Shelf Research, 67(4), 543–552.
Lovrich, G. A. (1999). Seasonality of larvae of Brachyura and Anomura (Crustacea Decapoda) in the Beagle Channel, Argentina. Scientia Marina, 63(1), 347–354.
Mafalda, Jr. P., Pérez de Rubín, J., & Sampaio de Souza, C. (2007) Mesozooplankton composition and distribution in relation to oceanographic conditions in the Gulf of Cádiz, Spain. Revista UDO Agricola, 7(1), 274–284.
Marques, S. C., Azeiteiro, U. M., Martinho, F., Viegas, I., & Pardal, M. A. (2009). Evaluation of estuarine mesozooplankton dynamics at a fine temporal scale: the role of seasonal, lunar and diel cycles. Journal of Plankton Research, 31(10), 1249–1263.
Mazzocchi, M. G., & Ianora, A. (1991). A faunistic study of the copepod assemblages in the Strait of Magellan. Bollettino di Oceanologia Teorica ed Applicata, 9(2–3), 163–177.
Onbé, T., Tanimura, A., Fukuchi, M., Hattori, H., Sasaki, H., & Matsuda, O. (1996). Distribution of marine cladocerans in the northern Bering sea asn the Chukchi sea. Proceedings of the NIPR Symposium on Polar Biology, 9, 141–152.
Pallares, R. E., & Hall, M. A. (1974). Analisis bioestadistico-ecologico de la fauna de copepodos asociados a 10s bosques de Macrocystis pyrifera. Physis (A), 33, 275–319.
Park, G. S., & Marshall, H. G. (2000). Estuarine relationship between zooplankton community structure and trophic gradients. Journal of Plankton Research, 22(1), 121–136.
Pielou, E. C. (1975). Ecological diversity. New York: Wiley.
Rosenberg, P., & Palma, S. (2003). Cladóceros de los fiordos y canales patagónicos localizados entre el golfo de Penas y el estrecho de Magallanes. Investigaciones Marinas, 31(1), 15–24.
Sabatini, M. E., Giménez, J., & Rocco, V. (2001). Características del zooplancton del área costera de la plataforma patagónica austral (Argentina). Boletin del Instituto Espanol de Oceanografia, 17(3–4), 245–254.
Sage, L. E., & Herman, S. S. (1772). Zooplankton of the Sandy Hook Bay area, N.J. Chesapeake Science, 13(1), 29–39.
Santelices, B., & Ojeda, F. P. (1984). Population dynamics of coastal forests of Macrocystis pyrifera in Puerto Toro, Isla Navarino, Southern Chile. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 14, 175–183.
Saunders, J. E., Al Zahed, K. M., & Paterson, D. M. (2007). The impact of organic pollution on the macrobenthic fauna of Dubai Greek (UAE). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54, 1715–1723.
Silva, A. P., Neumann-Leitão, S., Schwamborn, R., Oliveira Gusmão, L. M., Almeida, E., & Silva, T. (2004). Mesozooplankton of an impacted bay in North Eastern Brazil. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 47(3), 485–493.
Siokou-Frangou, I., & Papathanassiou, E. (1991). Differentiation of zooplankton populations in a polluted area. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 76, 41–51.
Siokou-Frangou, I., Papathanassiou, E., Lepretre, A., & Frontier, S. (1998). Zooplankton assemblages and influence of environmental parameters on them in a Mediterranean coastal area. Journal of Plankton Research, 20(5), 847–870.
Siokou-Frangou, I., Yannopoulos, C., & Morautou-Apostolopoulou, M. (1995). Differentiation of zooplankton communities in two neighboring shallow areas. In A. Eleftheriou, D. Ansell, & C. J. Smith (Eds.), Biology and ecology of shallow coastal waters (pp. 87–97). Fredensborg: Olsen & Olsen.
Smith, V. H., Tilman, G. D., & Nekola, J. C. (1999). Eutrophication, impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environmental Pollution, 100, 179–196.
Small, C., & Nicholls, R. J. (2003). A global analysis of human settlement in coastal zones. Journal of Coast Research, 19(3), 584–599.
Thatje, S., Schnack-Schiel, S., & Arntz, W. E. (2003). Developmental trade-offs in Subantarctic meroplankton communities and the enigma of low decapod diversity in high Southern latitudes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 260, 195–207.
ter Braak, C. J. F. (1986). Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology. doi:10.2307/1938672.
Thompson, B., Adelsbach, T., Brown, C., Hunt, J., Kuwabara, J., Neale, J., Ohlendorf, H., Schwarzbach, S., Spies, R., & Taberski, K. (2007). Biological effects of anthropogenic contaminants in the San Francisco Estuary. Environmental Research, 105, 156–174.
Torres, A. I., Gil, M. N., Amin, O., & Esteves, J. L. (2009). Environmental characterization of a eutrophicated semi-enclosed system: nutrient budget (Encerrada Bay, Tierra del Fuego Island, Patagonia, Argentina). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 204(1–4), 259–270.
Uriarte, I., & Villate, F. (2004). Effects of pollution on zooplankton abundance and distribution in two estuaries of the Basque coast (Bay of Biscay). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49(3), 220–228.
Uye, S. I. (1994). Replacement of large copepods by small ones with eutrophication of embayments: cause and consequence. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/BF00229979.
Uye, S., & Fleminger, A. (1976). Effects of various environmental factors on egg development of several species of Acartia in Southern California. Marine Biology, 38(3), 252–262.
Valiela, I. (1995). Long-term and large-scale change in marine ecosystems. In I. Valiela (Ed.), Marine ecological processes (pp. 499–544). New York: Springer.
Vieira, L., Azeiteiro, U., Ré, P., Pastorinho, R., Marques, J. C., & Morgado, F. (2003). Zooplankton distribution in a temperate estuary (Mondego estuary southern arm: Western Portugal). Acta Oecologica, 24, 163–173.
Webb, D. N., & Parsons, T. R. (1992). Winter-spring recruitment patterns of epiphytic harpacticoid copepods in temperate-zone seagrass bed. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 81, 151–162.
Zar, J. H. (1996). Biostatistical analysis (3rd ed.). New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Zervoudaki, S., Nielsen, T. G., & Carstensen, J. (2009). Seasonal succession and composition of the zooplankton community along an eutrophication and salinity gradient exemplified by Danish waters. Journal of Plankton Research, 31(12), 1475–1492.
Acknowledgments
Funds were provided by FONCYT-ANPCyT (PICTR090/2002). We are grateful to (i) the staff of the Centro Austral de Investigaciones Científicas (CADIC-CONICET), (ii) the staff of the Centro Nacional Patagónico (CENPAT-CONICET) especially to Dr. M. N. Gil and Dr. J. L Esteves and (iii) to Dr. Erika Giarratano and Dr. Américo I. Torres for their collaboration and support during the sampling period. We are also grateful for the assistance of the research staff at the Deutsches Zentrum für Marine Biodiversitätsforschung, particularly the help of Dr. Grittae Veit-Köhler in determining the different harpacticoid species.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biancalana, F., Dutto, M.S., Berasategui, A.A. et al. Mesozooplankton assemblages and their relationship with environmental variables: a study case in a disturbed bay (Beagle Channel, Argentina). Environ Monit Assess 186, 8629–8647 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4032-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4032-y