Abstract
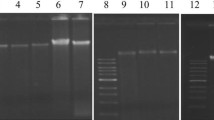
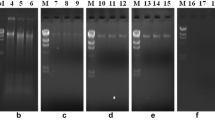
The assessment of the microbial diversity of the entire community of a given habitat requires the extraction of the total environmental DNA. Metagenomic investigations of a petroleum-polluted habitat have its unique challenges. The specific methods were developed for the extraction of high-quality metagenome in good quantity from the petroleum-polluted saline and non-saline sites in Gujarat (India). The soil samples were washed to remove the toxic, hazardous organic pollutants which might interfere with the recovery of the metagenomic DNA. The metagenomic DNA extraction results were encouraging with the mechanical bead beating, soft lysis, and combination of both. The extracted DNA was assessed for its purity and yield followed by its application in the amplification of the 16S rRNA region. The amplicons were used for judging the molecular diversity by the denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). The microbial diversity was also analyzed statistically by calculating various diversity indices and principal component analysis (PCA). The results on the metagenomic diversity of the bacterial population among the three cohorts based on the culture-independent technique exhibited significant difference among the PAH sites and Okha–Madhi and Porbandar Madhavpur habitats.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aislabie, J. M., Ryburn, J., Gutierrez-Zamora, M. L., Rhodes, P., Hunter, D., et al. (2012). Hexadecane mineralization activity in hydrocarbon-contaminated soils of Ross Sea region, Antarctica may require nutrients and inoculation. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 45, 49–60.
Amann, R. I., Amann, R. I., Ludwig, W., & Schleifer, K. H. (1995). Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiological Reviews, 59(1), 143–169.
Amorim, J. H., Macena, T. N. S., Lacerda-Junior, G. V., Rezende, R. P., Dias, J. C. T., Brendel, M., & Cascardo, J. C. M. (2008). An improved extraction protocol for metagenomic DNA from a soil of the Brazilian Atlantic rainforest. Genetics and Molecular Research, 7(4), 1226–1232.
Bachoon, D. S., Otero, E., & Hodson, R. E. (2001). Effects of humic substances on fluorometric DNA quantification and DNA hybridization. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 47, 73–82.
Boon, N., De Windt, W., Verstraete, W., & Top, E. M. (2002). Evaluation of nested PCR-DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) with group-specific 16S rRNA primers for the analysis of bacterial communities from different wastewater treatment plants. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 39, 101–112.
Delmont, T. O., Robe, P., Cecillon, S., Clark, I. M., Constancias, F., Simonet, P., Hirsch, P. R., & Vogel, T. M. (2011). Accessing the soil metagenome for studies of microbial diversity. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77(4), 1315–1324.
Desai, C., & Madamwar, D. (2007). Extraction of inhibitor-free metagenomic DNA from polluted sediments, compatible with molecular diversity analysis using adsorption and ion-exchange treatments. Bioresource Technology, 98, 761–763.
Desai, C., Pathak, H., & Madamwar, D. (2010). Advances in molecular and “-omics” technologies to gauge microbial communities and bioremediation at xenobiotic/anthropogen contaminated sites. Bioresource Technology, 101, 1558–1569.
Ercolini, D. (2004). PCR-DGGE fingerprinting: novel strategies for detection of microbes in food. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 56, 297–314.
Fortin, N., Beaumier, D., Lee, K., & Greer, C. W. (2004). Soil washing improves the recovery of total community DNA from polluted and high organic content sediments. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 56, 181–191.
Ghosh, A. B., Dey, N., Bera, A., Tiwari, A., Sathyaniranjan, K. B., Chakrabarti, K., & Chattopadhyay, D. (2010). Culture independent molecular analysis of bacterial communities in the mangrove sediment of Sundarban, India. Saline Systems, 6(1), 1.
Hadibarata, T., Tachibana, S., & Itoh. (2009). Biodegradation of chrysene, an aromatic hydrocarbon by Polyporus sp. S133 in liquid medium. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 911–917.
Hall, T. A. (1999). BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95–98.
Hammer, Ø., Harper, D. A. T., & Ryan, P. D. (2001). PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica, 6, 1–9.
Ibekwe, A. M., Papiernik, S. K., Gan, J., Yates, S. R., Yang, C. H., & Crowley, D. E. (2001). Impact of fumigants on soil microbial communities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 3245–3257.
Igwo-Ezikpe, M. N., Okpuzor, J., Awodele, O., Nwaokorie, F. O., Fowora, M. A., & Akinbo, M.O. (2010). Prevalence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) degrading bacteria in contaminated tropical soil in Lagos, Nigeria: involvement of plasmid in degradation. International Journal of Biological and Chemical Sciences, (4), 6.
Inceoglu, O., Hoogwout, E. F., Hill, P., & van Elsas, J. D. (2010). Effect of DNA extraction method on the apparent microbial diversity of soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 3378–3382.
Jiao, W., Lu, Y., Li, J., Han, J., Wang, T., Luo, W., Shi, Y., & Wang, G. (2009). Identification of sources of elevated concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in an industrial area in Tianjin, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 158(1–4), 581–592.
Kauffmann, I. M., Schmitt, J., & Schmid, R. D. (2004). DNA isolation from soil sample for cloning in different host. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 64, 665–670.
Li, J., Lu, Y., Shi, Y., Wang, T., Wang, G., Luo, W., Jiao, W., Chen, C., & Yan, F. (2011). Environmental pollution by persistent toxic substances and health risk in an industrial area of China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23(8), 1359–1367.
Marusenko, Y., Herckes, P., & Hall, S. (2011). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils of an arid urban ecosystem. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 219, 473–487.
McBain, A. J., Bartolo, R. G., Catrenich, C. E., Charbonneau, D., Ledder, R. G., & Gilbert, P. (2003). Growth and molecular characterization of dental plaque microcosms. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 94, 655–664.
Miller, D. N., Bryant, J. E., Madsen, E. L., & Ghiorse, W. C. (1999). Evaluation and optimization of DNA extraction and purification procedures for soil and sediment samples. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 4715–4724.
Morita, H., Kuwahara, T., Ohshima, K., Sasamoto, H., Itoh, K., et al. (2007). An improved DNA isolation method for metagenomic analysis of the microbial flora of the human intestine. Microbes and Environments, 22, 214–222.
Muller, A. K., Westergaard, K., Christensen, S., & Sorensen, S. J. (2001). The effect of long-term mercury pollution on the soil microbial community. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 36, 11–19.
Muyzer, G., & Smalla, K. (1998). Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) in microbial ecology. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 73, 127–141.
Ogino, A., Koshikawa, H., Nakahara, T., & Uchiyama, H. (2001). Succession of microbial communities during a biostimulation process as evaluated by DGGE and clone library analyses. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 91, 625–635.
Okere, U. V., & Semple, K. T. (2012). Biodegradation of PAHs in ‘Pristine’ soils from different climatic regions. Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation, S1, 006. doi:10.4172/2155-6199.S1-006.
Page, R. D. (1996). TreeView an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Computer Applications in the Biosciences, 12, 357–358.
Pongsilp, N., Nimnoi, P., & Lumyong, S. (2012). Genotypic diversity among rhizospheric bacteria of three legumes assessed by cultivation-dependent and cultivation-independent techniques. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 28, 615–626.
Purohit, M. K., & Singh, S. P. (2009). Assessment of various methods for extraction of metagenomic DNA from saline habitats of coastal Gujarat (India) to explore molecular diversity. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 49(3), 338–344.
Sagova-Mareckova, M., Cermak, L., Novotna, J., Plhackova, K., Forstova, J., & Kopecky, J. (2008). Innovative methods for soil DNA purification tested in soils with widely differing characteristics. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74, 2902–2907.
Salonen, A., Nikkila, J., Jalanka-Tuovinen, J., Immonen, O., & Rajilic-Stojanovic, M. (2010). Comparative analysis of fecal DNA extraction methods with phylogenetic microarray: effective recovery of bacterial and archaeal DNA using mechanical cell lysis. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 81, 127–134.
Santosa, A. (2001). Rapid extraction and purification of environmental DNA for molecular cloning applications and molecular diversity studies. Molecular Biotechnology, 17, 59–64.
Siddhapura, P. K., Vanparia, S., Purohit, M. K., & Singh, S. P. (2010). Comparative studies on the extraction of metagenomic DNA from the saline habitats of Coastal Gujarat and Sambhar Lake, Rajasthan (India) in prospect of molecular diversity and search for novel biocatalysts. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 47(3), 375–379.
Sipila, T. P., Keskinen, A. K., Kerman, M. L. A., Fortelius, C., Haahtela, K., & Kim, Y. (2008). High aromatic ring-cleavage diversity in birch rhizosphere: PAH treatment-specific changes of I.E.3 group extradiol dioxygenases and 16S rRNA bacterial communities in soil. The ISME Journal, 2, 968–981.
Stach, J. E., Bathe, S., Clapp, J. P., & Burns, R. G. (2001). PCR-SSCP comparison of 16S rDNA sequence diversity in soil DNA obtained using different isolation and purification methods. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 36(2–3), 139–151.
Susarla, S., Medina, V. F., & McCutcheon, S. C. (2002). Phytoremediation: an ecological solution to organic chemical contamination. Ecological Engineering, 18, 647–658.
Tannock, G. W. (2002). Analysis of the intestinal microflora using molecular methods. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 56(Suppl. 4), S44–S49.
Theron, J., & Cloete, T. E. (2000). Molecular techniques for determining microbial diversity and community structure in natural environments. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 26, 37–57.
Torsvik, V., Salte, K., Sorheim, R., & Goksoyr, J. (1990). Comparison of phenotypic diversity and DNA heterogeneity in a population of soil bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 56, 776–781.
Van der Gucht, K., Sabbe, K., De Meester, L., Vloemans, N., Zwart, G., Gillis, M., & Vyverman, W. (2001). Contrasting bacterioplankton community composition and seasonal dynamics in two neighbouring hypertrophic freshwater lakes. Environmental Microbiology, 3, 680–690.
Vaz-Moreira, I., Egas, C., Nunes, O. C., & Manaia, C. M. (2013). Bacterial diversity from the source to the tap: a comparative study based on 16S rRNA gene-DGGE and culture-dependent methods. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 83(2), 361–374. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12002.
Ward, D. M., Weller, R., & Bateson, M. M. (1990). 16S rRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community. Nature, 345, 63–65.
Watson, R. J., & Blackwell, B. (2000). Purification and characterization of a common soil component which inhibits the polymerase chain reaction. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 46(7), 633–642.
Widmer, F., Bach, A., Laczko, E., Schulze-Aurich, J., & Zeyer, J. (2001). Assessing soil biological characteristics: a comparison of bulk soil community DNA-, PLFA-, and Biolog(TM)-analyses. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 1029–1036.
Yang, K., Zheng, B., Li, F., Wen, X., & Zhao, C. (2005). Preparation of DNA-encapsulated polyethersulfone hollow microspheres for organic compounds and heavy metal removal. Desalination, 175, 297–304.
Zhang, L., Foxman, B., Janet, R., Carl, G., & Marrs, F. (2005). Bacterial genomic DNA isolation using sonication for microarray analysis. Biotechnology Techniques, 39, 640–644.
Zhou, J., Bruns, M. A., & Tiedje, J. M. (1996). DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol, 62, 316–322.
Acknowledgments
Ms. Viral Akbari and Ms. Rupal Pandya are the recipients of the UGC-Meritorious Research Fellowship, sponsored by the UGC, New Delhi, India. We also acknowledge the support of the UGC, New Delhi by sanctioning the ‘Centre of Advance Studies’ to the Department of Biosciences, Saurashtra University. The financial and other supports by the Saurashtra University are also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbari, V.G., Pandya, R.D. & Singh, S.P. Extraction of the metagenomic DNA and assessment of the bacterial diversity from the petroleum-polluted sites. Environ Monit Assess 186, 6351–6362 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3859-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3859-6