Abstract
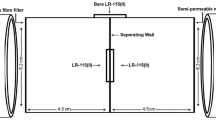
Radon and thoron, and their progeny concentrations along with equilibrium factors for gas progeny and radiological risks to the residents have been measured in dwellings of Digboi and Mashimpur areas located on anticlines during the winter season. In this present investigation, twin-cup dosemeters fitted with LR-115 (II) nuclear detectors have been employed. The present work has shown that there exist considerable house-to-house variations in values with maximum values in mud houses and minimum values in assam type (AT) houses. It has been found that mean (and geometric standard deviations (GSD)) radon concentrations are 83.8 (1.3), 113.5 (1.1) and 157.2 (1.2) Bq m−3 in AT, reinforced cement concrete (RCC) and mud houses in Digboi area and 63.0 (1.1), 87.1 (1.4) and 182.1 (1.2) Bq m−3 in AT, RCC and mud houses in Mashimpur area, respectively. The overall mean radon concentrations in Digboi and Mashimpur are estimated to be 114.4 (1.4) and 100.0 (1.7) Bq m−3. The mean radon concentrations are found to be less than the lower reference level of 200 Bq m−3 of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP 2007). The thoron concentrations in Digboi area are estimated to be 31.1 (1.3), 50.8 (1.4) and 67.0 (1.6) Bq m−3 in AT, RCC and mud houses, respectively, whereas in Mashimpur area, the thoron concentrations are estimated to be 26.4 (1.3), 44.4 (1.3) and 77.7 (1.3) Bq m−3 in AT, RCC and mud houses, respectively. The mean annual effective doses in Digboi area are found to be 1.9 (1.3), 2.7 (1.2) and 4.1 (1.4) mSv y−1 in AT, RCC and mud houses, respectively, while in the case of Mashimpur area, the mean annual effective doses are found to be 1.5 (1.4), 2.2 (1.2) and 4.9 (1.3) mSv y−1 in AT, RCC and mud houses, respectively. Nevertheless, the obtained results are much lower than the upper reference level of 10 mSv (ICRP 2007).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbu-Jarad, F., & Fremlin, J. H. (1981). A working level monitor for measurement inside houses. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 1, 221–226.
Abd-Elzaher, M. (2013). Measurement of indoor radon concentration and assessment of doses in different districts of Alexandria city, Egypt. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35, 299–309.
Akerblom, G., & Mellander, H. (1997). Geology and radon. In S. A. Durrani & R. Ilic (Eds.), Radon measurements by etched track detectors, applications in radiation protection, earth sciences and the environment (pp. 21–46). Singapore: World Scientific.
Barooah, D., & Phukan, S. (2012). Study of subsoil radon anomaly using LR-115 (II) nuclear track detectors in and around the Geleki oilfield, Assam Shelf. Indian Journal of Physics, 86(9), 801–805.
Barooah, D., Phukan, S., & Baruah, R. (2011). Study of radon exhalation rates using LR-115 (II) nuclear track detectors in coal-mining area of the foothills of Mokokchung District, Nagaland. Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics, 49, 665–668.
Brahmanandhan, G. M., Selvasekarapandian, S., Malathi, J., Khanna, D., Meenakshisundaram, V., Santhanan, S., et al. (2008). Seasonal variation of indoor gamma dose and radon, thoron measurement in the dwellings around Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant (Radhapuram Taluk, Tirunelveli District). Indoor and Built Environment, 17(4), 384–389.
Carneiro, G. L., Braz, D., da Jesus, E. F., Santos, S. M., Cardoso, K., Hecht, A. A., et al. (2013). Radon in indoor concentrations and indoor concentrations of metal dust particles in museums and other public buildings. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. doi:10.1007/s10658-12-9497-4.
Chauhan, R. P. (2010). Monitoring of radon, thoron and their progeny in dwellings of Haryana. Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics, 48, 470–472.
Durrani, S. A. (1993). Radon as a health hazard at home: what are the facts? Nuclear Tracks and Radiation Measurements, 22, 303–317.
Dwivedi, K. K., Srivastava, A., Ghosh, S., Sinha, D., Laldawngliana, C., Lalramengzami, R., et al. (1995). Measurement of indoor radon in some dwellings in Aizawl (India). Indoor Environment, 4, 362–264.
Eappen, K. P., Sahoo, B. K., Ramachandran, T. V., & Mayya, Y. S. (2008). Calibration factor for thoron estimation in cup dosimeter. Radiation Measurements, 43, 418–421.
Espinosa, G., Golzari, J. I., & Cortes, A. (1991). Radon measurements of groundwater in Mexico. Nuclear Tracks and Radiation Measurements, 19(1–4), 305–306.
Field, F. W., & Withers, B. L. (2012). Occupational and environmental causes of lung cancer. Clinic in Chest Medicine, 33, 681–703.
Field, R. W., Steck, D. J., Smith, B. J., Brus, C. P., Fisher, E. L., Neuberger, J. S., et al. (2000). Residential radon gas exposure and lung cancer: the Iowa radon lung cancer study. American Journal of Epidemiology, 151(1), 1091–1102.
Fleischer, R. L. (1997). Radon: Overview of properties, origin and transport. In S. A. Durrani & R. Ilic (Eds.), Radon measurements by etched track detectors, applications in radiation protection, earth sciences and the environment (pp. 3–10). Singapore: World Scientific.
Gupta, M., Mahur, A. K., & Verma, K. D. (2012). Indoor radon levels in some dwellings surrounding the National Thermal Power Corporations (NTPCs), India. Advances in Applied Science Research, 3, 1262–1265.
ICRP. (1993). Protection against 222 Rn at home and at work (International Commission on Radiological Protection Publication 65. Ann. ICRP 23 (2)). Oxford: Pergamon Press.
ICRP. (2007). The 2007 Recommendations of ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection Publication 103. Ann. ICRP 37 (2–4)). Oxford: Pergamon Press.
ICRP. (2012). Lung cancer risk from radon and progeny (International Commission on Radiological Protection Publication 115. Ann. ICRP 40 (1)). Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Ielsch, G., Thieblemont, D., Labed, V., Richon, P., Tymen, G., Ferry, C., et al. (2001). Radon (222Rn) level variations on regional scale: influence of the basement trace element (U, Th) geochemistry on radon exhalation rates. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 53, 75–90.
Jonsson, G. (1997). Radon measurements by etched track detectors, applications in radiation protection, earth sciences and the environment (pp. 155–176). Singapore: World Scientific.
Khan, H. A. (1991). Radon: a friend or foe? Nuclear Tracks and Radiation Measurements, 19, 353–362.
Khan, M. S., Naqvi, A. H., & Azam, A. (2008). Study of indoor radon and its progeny levels in rural areas of North India using LR-115 plastic track detectors. Radiation Measurements, 43, 385–388.
Kumar, R., & Prasad, R. (2007). Measurement of radon and its progeny levels in dwellings of Srivaikuntam, Kerela. Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics, 45, 116–118.
Kumar, J., Malhotra, R., Singh, J., & Singh, S. (1994). Radon measurements in dwellings in radioactive areas in Himachal Pradesh, India using LR-115 plastic track detectors. Nuclear Geophysics, 8(6), 601–606.
Kumar, R., Mahur, A. K., Jojo, P. J., & Prasad, R. (2007). Study of radon and its progeny levels in dwellings of Thankassery, Kerela. Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics, 45, 877–879.
Lubin, J. H. (2003). Studies of radon and lung cancer in North America and China. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 104(4), 315–319.
Mathur, L. P. & P. Evans (1964). Oil in India. In: International Geological Congress, 22nd Session, New Delhi, India.
Mayya, Y. S., Eappen, K. P., & Nambi, K. S. V. (1998). Methodology for mixed field inhalation dosimetry in Monazite areas using twin-cup dosimeter with three track detectors. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 77(3), 177–184.
Porstendorfer, J. (1994). Properties and behavior of radon and thoron and their decay products in the air. Journal of Aeorosol Science, 25(2), 219–263.
Rahman, S. U., Anwar, J. & Matiullah (2008). Measurement of indoor radon concentration levels in Islamabad, Pakistan. Radiation Measurements, 43, 401–404.
Ramachandran, T.V. & Subba Ramu, M. C. (1990). Control methods of radon and its progeny concentration in indoor atmosphere. Technical Report of Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai, India, No. 1498, 1–44.
Ramachandran, T. V., Lalit, B. Y., & Mishra, U. C. (1987). Measurement of radon permeability through some membranes. Nuclear Tracks and Radiation Measurement, 13, 81–84.
Ramachandran, T. V., Muraleedharan, T. S., Shaikh, A. N., & Subba Ramu, M. C. (1990). Seasonal variation of indoor radon and its progeny concentration in a dwelling. Atmospheric Environment, 24A(3), 639–643.
Ramachandran, T. V., Eappen, K. P., Nair, R. N., Mayya, Y. S. & Sadasivan, S. (2003). Radon-thoron levels and inhalation dose distribution patterns in Indian dwellings. Technical Report of Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai, India, No. BARC/2003/E/026.
Ramola, R. C., Rawat, R. B. S., & Kandari, M. S. (1995). Estimation of risk from environmental exposure to radon in Tehri Garhwal. Nuclear Geophysics, 9, 383–386.
Ramola, R. C., Rawat, R. B. S., Kandari, M. S., Ramachandran, T. V., & Choubey, V. M. (1997). Indoor radon levels around Uttarkashi and Pauri Gahwal district areas using solid state nuclear track detector. Radiation Protection and Dosimetry, 20(4), 198–199.
Ramola, R. C., Kandari, M. S., Rawat, R. B. S., Ramachandran, T. V., & Choubey, V. M. (1998). A study of seasonal variations of radon levels in different types of houses. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 39(1), 1–7.
Ramola, R. C., Negi, M. S., & Choubey, V. M. (2003). Measurement of equilibrium factor ‘F’ between radon and its progeny and thoron and its progeny in the indoor atmosphere using nuclear track detectors. Indoor and Built Environment, 12(5), 351–355.
Rani, A., Singh, S., & Duggal, V. (2013). Indoor radon measurements in the dwellings of Punjab and Himachal Pradesh, India. Radiation Protection Dosimetry. doi:10.1093/rpd/nct041.
Rydock, J. P., Naess-Rolstad, A., & Brunsell, J. T. (2001). Diurnal variations in radon concentrations in a school and office: implications for determining radon exposure in day-use buildings. Atmospheric Environment, 35, 2921–2926.
Sannappa, J., Chandrashekara, M. S., Sathish, L. A., Paramesh, L., & Venkataramaiah, P. (2003). Study of background radiation dose in Mysore city, Karnataka State, India. Radiation Measurements, 37, 55–65.
Schery, S. D., & Gaeddert, D. H. (1984). Factors affecting exhalation of radon from a gravelly sandy loam. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89, 7299–7309.
Segovia, N. (1991). Radon and volcanic activity: recent advances. Nuclear Tracks and Radiation Measurements, 19, 409–431.
Sevc, J. K., Kunz, E., & Placek, U. (1976). Lung cancer in uranium miners and long term exposure to radon daughters. Health Physics, 30, 433–437.
Sevc, J. K., Tomasek, L., Placek, V., & Horacek, J. (1998). Cancer in man after exposure to radon daughters. Health Physics, 54, 27–32.
Singh, S., Malhotra, R., Kumar, J., & Singh, L. (2001). Indoor radon measurements in dwellings of Kulu area, Himachal Pradesh, using solid state nuclear track detectors. Radiation Measurements, 34, 505–508.
Singh, M., Singh, K., Singh, S., & Papp, Z. (2008). Variation of indoor radon progeny concentration and its role in dose assessment. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 99, 539–545.
Sivakumar, R. (2010). A study on radon and thoron progeny levels in dwellings in South India. Iranian Journal of Radiation Research, 8(3), 149–154.
Steinhausler, F., Hofmann, W., & Lettner, H. (1994). Thoron exposure of man: a negligible issue? Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 56(1–4), 127–131.
Stranden, E., Magnus, K., James, A. C., Green, B. M. R., & Strand, T. (1988). Radon and lung cancer: an epidemiological study in Norway. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 24(1–4), 471–474.
Subba Ramu, M. C., Shaikh, G., Muraleedharan, T. S., & Ramachandran, T. V. (1988). A study of the seasonal variations in the indoor concentrations of radon and its progeny. Bulletin of Radiation Protection, 11, 81–87.
Subba Ramu, M. C., Sheikh, A. N., Mauraleedharan, T. S., & Ramachandran, T. V. (1992). Measurements of indoor radon levels in India using solid state nuclear track detectors: need for standardization. Defence Science Journal, 42(4), 219–225.
UNSCEAR (2000). Sources, effects and risks of ionizing radiation. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effect of Atomic Radiation. Report to the General Assembly, United Nations, New York
Vaupotie, J., Sikovec, M., & Kobal, I. (1999). Systematic indoor 222Rn and gamma ray measurements in Slovenian schools. Health Physics, 78, 559–662.
Virk, H. S., Sharma, N., & Bajwa, B. S. (1999). Environmental radioactivity: a case study in Himachal Pradesh, India. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 45, 119–127.
WHO. (2009). World Health Organization handbook on indoor radon: a public heath perspective. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Press.
Zubair, M., Khan, M. S., & Verma, D. (2011). Assessment of indoor radon, thoron and their decay products in the surrounding areas of Firozabad, Uttar Pradesh, India. Archives of Applied Science Research, 3(1), 77–82.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to the dwellers of the studied area for their cooperation during the field work. We are thankful to Dr. R. William Field of the University of Iowa, USA for his valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barooah, D., Barman, S. & Phukan, S. Simultaneous measurements of radon and thoron, and their progeny levels in dwellings on anticlinal structures of Assam, India. Environ Monit Assess 186, 3581–3594 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3640-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3640-x