Abstract
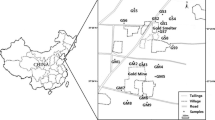
In order to investigate the metal distribution, speciation, correlation and origin, risk assessment, 86 surface soil samples from the catchment area around the Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, including samples from gold and iron mine areas, were monitored for fractions of heavy metal and total contents. Most of the metal concentrations in the gold and iron mine soil samples exceeded the metal background levels in Beijing. The contents of most elements in the gold mine tailings were noticeably higher than those in the iron mine tailings. Geochemical speciation data of the metals showed that the residual fraction dominated most of the heavy metals in both mines. In both mine areas, Mn had the greatest the acid-soluble fraction (F1) per portion. The high secondary-phase fraction portion of Cd in gold mine samples indicated that there was a direct potential hazard to organisms in the tested areas. Multivariate analysis coupled with the contents of selected metals, showed that Hg, Pb, Cr, and Ni in gold mine areas represented anthropogenic sources; Cd, Pb, and Cr in iron mine areas represented industrial sources. There was moderate to high contamination of a few metals in the gold and iron soil samples, the contamination levels were relatively higher in gold mine than in iron mine soils.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta, J. A., Faz, A., Martínez-Martínez, S., Zornoza, R., Carmona, D. M., & Kabas, S. (2011). Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to evaluate heavy metals behavior in mine sites for future reclamation. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 109, 8–17.
Alvarez, J. M., Lopez-Valdivia, L. M., Novillo, J., Obrador, A., & Rico, M. I. (2006). Comparison of EDTA and sequential extraction tests for phytoavailability prediction of manganese and zinc in agricultural alkaline soils. Geoderma, 132, 450–463.
Bro, R., & Smilde, A. K. (2003). Centering and scaling in component analysis. Journal of Chemometrics, 17, 16–33.
Burt, R., Wilson, M. A., Keck, T. J., Dougherty, B. D., Strom, D. E., & Lindahl, J. A. (2003). Trace element speciation in selected smelter-contaminated soils in Anaconda and Deer Lodge Valley, Montana, USA. Advances in Environmental Research, 8, 51–67.
Chen, T. B., Zheng, Y. M., Chen, H., & Zheng, G. D. (2004). Background concentrations of soil heavy metals in Beijing. Acta Science Circumstantiae, 25, 117–122.
Chlopecka, A. (1996). Assessment of form of Cd, Zn and Pb in contaminated calcareous and gleyed soils in southwest Poland. Science of the Total Environment, 188, 253–262.
Dantu, S. (2009). Heavy metals concentration in soils of southeastern part of Ranga Reddy district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environment Monitoring Assessment, 149, 213–222.
Davidson, C. M., Urquhart, G. J., Ajmone-Marsan, F., Biasioli, M., Duarte, A. C., et al. (2006). Fractionation of potentially toxic elements in urban soils from five European cities by means of a harmonised sequential extraction procedure. Analytica Chimica Acta, 565, 63–72.
Du, C. Y., Zu, Y. Q., & Li, Y. (2005). Effect of pH and organic matter on the bioavailability Cd and Zn in soil. Journal of Yunnan agricultural University, 20, 539–543.
Einax, J. W., & Soldt, U. (1999). Geostatistical and multivariate statistical methods for the assessment of polluted soils—merits and limitations Geostatistical and multivariate statistical methods for the assessment of polluted soils—merits and limitations. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 46, 79–91.
Facchinelli, A., Sacchi, E., & Mallen, L. (2001). Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environmental Pollution, 114(3), 313–324.
Filgueiras, A. V., Lavilla, I., & Bendicho, C. (2004). Evaluation of distribution, mobility and binding behaviour of heavy metals in surficial sediments of Louro River (Galicia, Spain) using chemometric analysis: a case study. Science of the Total Environment, 330, 115–129.
Gao, Z. D., & Liao, H. J. (2007). Investigation and assessment on pollution of soil heavy metals in upstream of Miyun Reservoir. China. Environmental Protection Industry, 8, 23–26.
Ghrefat, H., & Yusuf, N. (2006). Assessing Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn and Cd pollution in bottom sediments of Wadi Al-Arab Dam, Jordan. Chemosphere, 65, 2114–2121.
Guevara, R. A., Sahuquillo, A., Rubio, R., & Rauret, G. (2004). Assessment of metal mobility in dredged harbour sediments from Barcelona (Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 321, 241–255.
He, Z. L., Yang, X. E., & Stoffella, P. J. (2005). Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 19, 125–140.
Henrion, R. (1994). N-way principal component analysis: theory, algorithms and applications. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 25, 1–23.
Huan, G., Jun, Y., Minmin, C., & Yiguang, Q. (2012). Effects of petroleum contamination on soil microbial numbers, metabolic activity and urease activity. Chemosphere, 87, 1273–1280.
Jain, C. K., Malik, D. S., & Yadav, R. (2004). Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India. Water Research, 38, 569–578.
Javed, I., & Munir, H. S. (2011). Distribution, correlation and risk assessment of selected metals in urban soils from Islamabad, Pakistan. Jouranal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 887–898.
Kartal, S., Aydin, Z., & Tokalioğlu, S. (2006). Fractionation of metals in street sediment samples by using the BCR sequential extraction procedure and multivariate statistical elucidation of the data. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 132, 80–89.
Klutte, A. (1986). Methods of soil analysis. Madison, WI: American Society of Agronomy.
Leardi, R., Armanino, C., Lanteri, S., & Alberotanza, L. (2000). Three-mode principal component analysis of monitoring data from Venice lagoon. Journal of Chemometrics, 14(3), 187–195.
Li, J. L., He, M., Han, W., & Gu, Y. (2009). Analysis and assessment on heavy metal sources in the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits using multivariate statistical methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164, 976–981.
Liao, H. J. (2007). Investigate and assessment of pollution of heavy metals in soil of the upstream area of Miyun Reservoir, Beijing. City Geology, 2(3), 31–34.
Liu, X. D., Xu, Q., Ge, X. L., Liu, L., & Wu, D. W. (2005). Chemical forms of heavy metal contaminants in sediments of Miyun reservoir. Science In China Ser D Earth Sciences, 48(2), 341–350.
Lu, X. W., Wang, L. J., Li, L. Y., Lei, K., Huang, L., & Kang, D. (2010). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 744–749.
Luo, X. S., Zhou, D. M., Liu, X. H., & Wang, Y. J. (2006). Solid/solution partitioning and speciation of heavy metals in the contaminated agricultural soils around a copper mine in eastern Nanjing city, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 131, 19–27.
Luo, W., Lu, Y. L., Zhang, Y., Fu, W. Y., & Wang, B. (2010). Watershed-scale assessment of arsenic and metal contamination in the surface soils surrounding Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China. Journal of Environmental Management, 91, 2599–2607.
Manzoor, S., Shah, M. H., Shaheen, N., Khalique, A., & Jaffar, M. (2006). Multivariate analysis of trace metals in textile effluents in relation to soil and groundwater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137, 31–37.
Meza-Figueroa, D., O-Villanueva, M. D., & Luisa, M. (2007). Heavy metal distribution in dust from elementary schools in Hermosillo, Sonora, México. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 276–288.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Journal of Geology, 2, 108–118.
Nyamangara, J. (1998). Use of sequential extraction to evaluate zinc and copper in a soil amended with sewage sludge and inorganic metal salts. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 69, 135–141.
Pardo, R., Helena, B. A., Cazurro, C., Guerra, C., Deban, L., Guerra, C. M., & Vega, M. (2004). Application of two- and three-way principal component analysis to the interpretation of chemical fractionation results obtained by the use of the B.C.R. procedure. Analytica Chimica Acta, 523(1), 125–132.
Peris, M., Recatalá, L., Micó, C., Sánchez, R., & Sánchez, J. (2008). Increasing the knowledge of heavy metal contents and sources in agricultural soils of the European Mediterranean region. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 192, 25–37.
Ramos-Arroyo, Y. R., & Siebe, C. (2007). Weathering of sulfide minerals and trace element speciation in tailings of various ages in the Guanajuato mining district, Mexico. Catena, 71, 497–506.
Rath, P., Panda, U. C., Bhatta, D., & Sahu, K. C. (2009). Use of sequential leaching, mineralogy, morphology and multivariate statistical technique for quantifying metal pollution in highly polluted aquatic sediments-a case study: Brahamani and Nandira rivers, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 632–644.
Rodríguez, L., Ruiz, E., Alonso, A. J., & Rincón, J. (2009). Heavy metal distribution and chemical speciation in tailings and soils around a Pb–Zn mine in Spain. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 1106–1116.
Rojas, J., & Vandecasteele, C. (2007). Influence of mining activities in the North of Potosi Bolivia on the water quality of the Chayanta River, and its consequences. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 132, 321–330.
Samuel, K., Pearn, W. L., & Dean, W. (1984). Eigenvalue–eigenvector analysis for a class of patterned correlation matrices with an application. Statistics & Probability Letters, 2, 119–125.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., Singh, V. K., & Sinha, S. (2006). Multi-way data analysis of soils irrigated with wastewater—a case study. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 83(1), 1–12.
Sterckeman, T., Douay, F., Proix, N., & Fourrier, H. (2000). Vertical distribution of Cd, Pb and Zn in soils near smelters in the North of France. Environmental Pollution, 107, 377–389.
Sundaray, S. K., Panda, U. C., Nayak, B. B., & Bhatta, D. (2006). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in water quality of Mahanadi River-Estuarine System (India)—a case study. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28, 317–330.
Tahri, M., Benyaich, F., Bounakhla, M., Bilal, E., Gruffat, J. J., Moutte, J., & Garcia, D. (2005). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contents in soils, sediments and water in the region of Meknes (central Morocco). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 102, 405–417.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1985). The continental crust: its composition and evolution (pp. 1–328). Palo Alto, CA: Blackwell.
Uria, A. F., Mateo, C. L., Roca, E., & Marcos, M. L. F. (2008). Source identification of heavy metals in pasturelands by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 1008–1015.
Vega, F. A., Covelo, E. F., Cerqueira, B., & Andrade, M. L. (2009). Enrichment of marsh soils with heavy metals by effect of anthropic pollution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170, 1056–1063.
Weng, L. P., Temminghoff, E. J. M., Lofts, S., Tipping, E., & Riemsdijk, W. H. V. (2002). Complexation with dissolved organic matter and solubility control of heavy metals in a sandy soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 4804–4810.
Yalcin, M. G., Narin, I., & Soylak, M. (2008). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contents of sediments from Gumusler Creek Nigde—Turkey. Environmental Geology, 54(6), 1155–1163.
Yalcin, M. G., Tumuklu, A., Sonmez, M., & Erdag, D. S. (2010). Application of multivariate statistical approach to identity heavy metal sources in bottom soil of the Seyhan River (Adana), Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 164, 311–322.
Yan, C. Z., Li, Q. Z., Zhang, X., & Li, G. X. (2009). Mobility and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Xiamen Bay and its adjacent areas, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 60, 1469–1479.
Zhang, C. (2006). Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environmental Pollution, 142, 501–511.
Zheng, Y. M., Chen, T. B., & He, J. Z. (2008). Multivariate geostatistical analysis of heavy metals in topsoils from Beijing, China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 8, 51–58.
Zhong, X. L., Zhou, S. L., Zhu, Q., & Zhao, Q. Q. (2011). Fraction distribution and bioavailability of soil heavy metals in the Yangtze River Delta—a case study of Kunshan City in Jiangsu Province, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 198, 13–21.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Yao Jun and Dr. Chen Huilun, Wang Fei and Zhu Xianfang for their advice regarding this study. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 41173113, 41103058) and the Hundred Talents Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Zhu, Y. & Ji, H. Distribution, speciation, and risk assessment of selected metals in the gold and iron mine soils of the catchment area of Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China. Environ Monit Assess 185, 8525–8545 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3193-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3193-4