Abstract
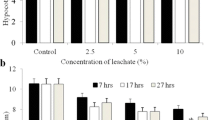
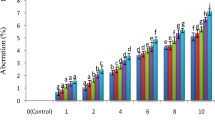
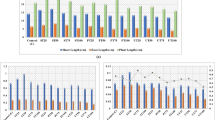
In this study, the effect of Afyonkarahisar Sugar Factory’s discharge water on germination percentage, root growth and mitotic divisions of the root tip cells of Hordeum vulgare L. were investigated. Six concentrations of wastewater and ranging from 100, 10 − 1, 10 − 2, 10 − 3, 10 − 4, 10 − 5, were applied for 6, 12, 18 and 24 h, respectively. It was observed that the treatments reduced the germination percentages of H. vulgare grains and inhibited the root growth as well as reduced mitotic index compared to the control group at all concentrations. It was also observed that the increase of the concentrations of wastewater decreased the cell division, and several mitotic anomalies such as c-mitosis, lagging chromosomes, multipolar anaphases and chromosome bridges increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2004). Türkiye çevre atlası. 300–304.
Aybeke, M., Sıdal, U., Olgun, G., & Kolankaya, D. (2000). Zeytinyağı Fabrikası atık suyunun buğday (Triticum aestivum l.) kök ucu hücrelerindeki mitoz bölünme ve total protein miktarı üzerine etkisi. Turkish Journal of Biology, 24, 127–140.
Cern′a, M., H′ajek, V., Stejskalov′a, E., Dobi′a, L., Zudov′a, Z., & Rossner, P. (1991). Environmental genotoxicity monitoring using Salmonella typhimurium strains as indicator system. Science of the Total Environment, 101, 139–147.
Chan, Y. K., Wong, C. K., Hsieh, D. P. H., Ng, S. P., Lau, T. K., & Wong, P. K. (2003). Application of a toxicity identification evaluation for a sample of effluent discharged from a dyeing factory in Hong Kong. Environmental Toxicology, 18, 312–316.
Ciǧerci, İ. H. C, Akyıl, D., Özkara, A., Korcan, S. E., & Konuk, M. (2006). Akarçay (Afyonkarahisar) suyunun mutajenik özelliklerinin Allium testi ile belirlenmesi, 18. Ulusal Biyoloji Kongresi, Aydın, 26–30 Haziran 2006.
Darlington, C. D., & La Cour, L. (1976). The handling of chromosomes (6th Ed.). London: George Allen and Univ. Ltd.
Dong, Y., & Zhang, J. (2010). Testing the genotoxicity of coking wastewater using Vicia faba and Hordeum vulgare bioassays. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 944–948. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.12.026.
El-Ghamery, A. A., El-Kholy, M. A., & Abou El-Yousser, M. A. (2003). Evaluation of cytological effects of Zn2+ in relation to germination and root growth of Nigella sativa L. and Triticum aestivum L. Mutation Research, 537(1), 29–41.
Evans, H. J., Meary, G. J., & Tomkinson, S. N. (1957). The use of colchicine as an indicator of mitotic rate in broad bean root meristem. Journal of Genetics, 55, 487.
Feretti, D., Zerbini, I., Zani, C., Ceretti, E., Moretti, M., & Monarca, S. (2007). Allium cepa chromosome aberration and micronucleus tests applied to study genotoxicity of extracts from pesticide-treated vegetables and grapes. Food Additives and Contaminants, 24, 561–572.
Grant, W. F., & Owens, E. T. (2006). Zea mays assays of chemical/radiation genotoxicity for the study of environmental mutagens. Mutation Research, 613, 17–64.
Jiang, W., & Liu, D. (2000). Effects of Pb2+ on root growth, cell division, and nucleolus of Zea mays L. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 65, 786–793.
Konuk, M., Liman, R., & Ciğerci, İ. H. (2007). Determination of genotoxic effect of boron on Allium cepa root meristematic cells. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 39(1), 73–79.
Kıran, Y., & Şahin, A. (2005). The effects of the lead on the seed germination, root growth, and root tip cell mitotic divisions of Lens Culinaris Medık G. U. Journal of Science, 18(1), 17–25.
Lah, B., Gorjane, G., Nekrep, F. V., & Marinsek-Logar, R. (2004). Comet assay of wastewater genotoxicity using yeast cells. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72, 607–616.
Leme, D. M., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2009). Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: A review on its application. Mutation Research, 682, 71–81.
Liman, R., Akyıl, D., Eren, Y., & Konuk, M. (2010). Testing of the mutagenicity and genotoxicity of metolcarb by using both Ames/Salmonella and Allium test. Chemosphere, 80, 1056–1061.
Ma, T. H., Xu, Z., Xu, C., Mc Connell, H., Rabago, E. V., Arreola, G. A., et al. (1995). The improved Allium/Vicia root tip micronucleus assay for clastogenicity of environmental pollutants. Mutation Research, 334, 185–195.
Menke, M., Chen, I. P., Angelis, K. J., & Schubert, I. (2001). DNA damage and repair in Arabidopsis thaliana as measured by the comet assay after treatment with different classes of genotoxins. Mutation Research, 493, 87–93.
Monte Egito, L. M., das Gracas Medeiros, M., Batistuzzo de Medeiros, S. R., & Agnez-Lima, L. F. (2007). Cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of surface water from the Pitimbu river, northeastern/RN Brazil. Genetic and Molecular Biology, 30, 435–431.
Odeigah, C., & Osanyinpeju, O. (1995). Genotoxic effects of two industrial effluents and ethylmethane sulfonite in Clarias lazera. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 33, 501–505.
Odeigah, P. G. C., Nurudeen, O., & Amund, O. O. (1997). Genotoxicity of oil field wastewater in Nigeria. Hereditas, 126, 161–167.
Ohe, T., White, P. A., & De Marini, D. M. (2003). Mutagenic characteristics of river waters flowing through large metropolitan areas in North America. Mutation Research. Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 534, 101–112.
Özdemir, M. A., & Uçar, H. (2006). Afyonkarahisar kent ekosisteminde su kirliliği. Afyon Kocatepe Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi, 8(2), 123–158.
Radić, S., Stipaničev, D., Vujčić, V., Marijanović, M., Širac, S. & Pevalek-Kozlina, B. (2010). The evaluation of surface and wastewater genotoxicity using the Allium cepa test. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 1228–1233.
Rank, J., & Nielsen, M. H. (1998). Genotoxicity testing of wastewater using the Allium cepa anaphase-telophase chromosome aberration assay. Mutation Research, 418, 113–119.
Samuel, O. B., Osuala, F. I., & Odeigah, P. G. C. (2010). Cytogenotoxicity evaluation of two industrial effluents using Allium cepa assay. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4(1), 21–27.
Smolders, R., Bervoets, L., & Blust, R. (2004). In situ and laboratory bioassays to evaluate the impact of effluent discharges on receiving aquatic ecosystems. Environmental Pollution, 132(2), 231–243.
Vargas, V. M. F., Migliavacca, S. B., de Melo, A. C., Horn, R. C., Guidobono, R. R., & Ferreira, I. (2001). Genotoxicity assessment in aquatic environments under the influence of heavy metals and organic contaminants. Mutation research. Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 490, 141–158.
Yi, H. L., & Meng, Z. Q. (2003). Genotoxicity of hydrated sulfurdioxide on root tips of Allium sativum and Vicia faba. Mutation Research, 537, 109–114.
Yıldız, M., & Arıkan, E. S. (2008). Genotoxicity testing of quizalofop-P-ethyl herbicide using the Allium cepa anaphase-telophase chromosome aberration assay destroy. Caryologia, 61(1), 45–52.
Zaka, R., Chenal, C., & Misset, M. T. (2002). Study of external low irradiation dose effects on induction of chromosome aberrations in Pisum sativum root tip meristem. Mutation Research, 517, 87–99.
Žegura, B., Heath, E., Černoša, A., & Filipič, M. (2009). Combination of in vitro bioassays for the determination of cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of wastewater, surface water and drinking water samples. Chemosphere, 75, 1453–1460.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkara, A., Akyıl, D., Erdoğmuş, S.F. et al. Evaluation of germination, root growth and cytological effects of wastewater of sugar factory (Afyonkarahisar) using Hordeum vulgare bioassays. Environ Monit Assess 183, 517–524 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1936-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1936-7