Abstract
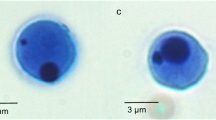
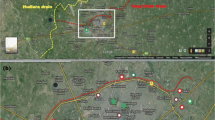
Micronuclei tests is a system of mutagenicity testing used for determining the pollution and chemicals causing changes in DNA fragments such as micronuclei in the cytoplasm of interphase cells. Damage caused on the DNA by genotoxic pollutants is the first consequence occurring in the aquatic organisms. Thus, it was attempted to determine whether pollution affected the erythrocytes and gills of fish Gobius niger and haemolymph and gills of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis living in Izmir Bay at the level of DNA by the means of micronuclei (MN) test. Organisms used in the MN test were collected from seven locations (Alsancak, Alaybey Shipyard, Karsiyaka, Bostanli, Göztepe, Konak and Pasaport) which are known as the most polluted part of inner Bay of Izmir (Western Coast of Turkey). According to the results of the present study, frequency of MN was found at high level in Alaybey Shipyard and Pasaport where wastes from existing dockyard contributed to high level of pollution. In conclusion, this study indicates that the micronuclei test gives sensitive results in monitoring the pollution, especially the pollution of harbor, and thus it might be used as standard method in regular monitoring of pollution of coastal ecosystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Sabti, K., Franko, M., Andrijanic, B., Knez, S., & Stegnar, P. (1994). Chromium induced micronuclei in fish. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 14, 333–336. doi:10.1002/jat.2550140503.
Al-Sabti, K., & Metcalfe, C. D. (1995). Fish micronuclei for assessing genotoxicity in water. Mutation Research, 343, 121–135. doi:10.1016/0165-1218(95)90078-0.
Arkhipchuk, V. V., & Garanko, N. N. (2005). Using the nucleolar biomarker and the micronucleus test on in vivo fish fin cells. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 62, 42–52. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.01.001.
Baršienė, J. (1994). Chromosome set changes in mollusks from highly polluted habitats. In A. Beaumont (Ed.), Genetics and evolution of aquatic organisms (pp. 434–446). London: Chapman, Hall.
Baršienė, J., & Baršytė, L. D. (2000). Environmental genotoxicity in Klaipeda port area. International Review of Hydrobiology, 85, 663–672. doi:10.1002/1522-2632(200011)85:5/6<663::AID-IROH663>3.0.CO;2-S.
Baršienė, J., Schiedek, D., Rybakovas, A., Šyvokienė, J., Kopecka, J., & Förlin, L. (2006). Cytogenetic and cytotoxic effects in gill cells of the blue mussel Mytilus spp. from different zones of the Baltic Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 53(8–9), 469–478. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.11.015.
Bolognesi, C., Landini, E., Roggieri, P., Fabbri, R., & Viarengo, A. (1999). Genotoxicity biomarkers in the assessment of heavy metal effects in mussels: Experimental studies. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 33, 287–292. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(1999)33:4<287::AID-EM5>3.0.CO;2-G.
Bolognesi, C., Perrone, E., Roggieri, P., & Sciutto, A. (2006). Bioindicators in monitoring long term genotoxic impact of oil spill: Haven case study. Marine Environmental Research, 62, 287–291. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2006.04.047.
Boyacıoğlu, M. (2004). İzmir Körfezi sedimentlerinde direkt mutajenlerin belirlenmesi. E.U. Su ürünleri Dergisi, 21(1–2), 23–27
Bryan, G. W. (1976). Some aspects of heavy metal tolerance in aquatic organisms. In A. P. M. Lockwood (Ed.), Effects of pollutants on aquatic on aquatic organisms (pp. 7–34). London: Cambridge University Pres.
Buschini, A., Martino, A., Gustavino, B., Monfrinotti, M., Poli, P., & Rossi, C. (2004). Comet assay and micronucleus test in circulating erythrocytes of Cyprinus carpio specimens exposed in situ to lake waters treated with disinfectants for potabilization. Mutation Research, 557, 119–129.
Cavas, T., & Ergene-Gözükara, S. (2003). Micronuclei, nuclear lesions and interphase silver stained nucleolar organizer regions (AgNORs) as cyto-genotoxicity indicators in Oreochromis niloticus exposed to textile mill effluent. Mutation Research, 534, 93–99.
Dailianis, S., Domouhtsidou, G. P., Raftopoulou, E., Kalayianni, M., & Dimitriadis, V. K. (2003). Evaluation of neutral red retention assay, micronucleus test, acetylcholinesterase activity and a signal transduction molecule (cAMP) in tissues of Mytilus galloprovincialis (L.), in pollution monitoring. Marine Environmental Research, 56, 443–470. doi:10.1016/S0141-1136(03)00005-9.
De Flora, S., Vigario, L., D’Agostini, F., Camoirano, A., Bagnasco, M., Bennecelli, C., et al. (1993). Multiple biomarkers in fish exposed in situ to polluted river water. Mutation Research, 319, 167–177. doi:10.1016/0165-1218(93)90076-P.
Dixon, D. R., Pruski, A. M., Dixon, L. R. J., & Jha, A. N. (2002). Marine invertebrate eco-genotoxicology: A methodological overview. Mutagenesis, 17, 495–507. doi:10.1093/mutage/17.6.495.
Dolcetti, L., & Venier, P. (2002). Susceptibility to genetic damage and cell types in Mediterranean mussels. Marine Environmental Research, 54, 487–491. doi:10.1016/S0141-1136(02)00142-3.
Fenech, M. (2000). The in vitro micronucleus technique. Mutation Research, 455, 81–95. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(00)00065-8.
Harvey, J. S., Lyons, B. P., Page, T. S., Stewart, C., & Parry, J. M. (1999). An assessment of the genotoxic impact of the sea empress oil spill by the measurement of DNA adducts levels in selected invertebrate and vertebrate species. Mutation Research, 441, 103–114.
Hayashi, M., Ueda, T., Uyeno, K., Wada, K., Kinae, N., Saotome, K., et al. (1998). Development of genotoxicity assay systems that use aquatic organisms. Mutation Research, 399, 125–133. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(97)00251-0.
Hooftman, R. N., & Raat, W. K. (1982). Induction of nuclear anomalies (micronuclei) in the peripheral blood erythrocytes of the eastern mudminow Umbra pygmaea by ethylmethanesulphonata. Mutation Research, 104, 147–152. doi:10.1016/0165-7992(82)90136-1.
Izquierdo, J. I., Machado, G., Ayllon, F., d’Amico, V. L., Bala, L. O., Vallarino, E., et al. (2003). Assessing pollution in coastal ecosystems: A preliminary survey using the micronucleus test in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 55, 24–29. doi:10.1016/S0147-6513(02)00041-6.
Kligerman, D. (1982). Fishes as biological detectors of the effects of genotoxic agents. In J. Heddle (Ed.), Mutagenicity: New horizons in genetic toxicology (pp. 435–456). New York: Academic Press.
Klobucar, G. I. V., Pavlica, M., Erben, R., & Papes, D. (2003). Application of the micronucleus and comet assays to mussel Dreissena polymorpha haemocytes for genotoxicity monitoring of freshwater environments. Aquatic Toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 64, 15–23. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(03)00009-2.
Kucuksezgin, F., Kayatekin, B. M., Uluturhan, E., Uysal, N., Acikgoz, O., & Gonenc, S. (2008a). Preliminary investigation of sensitive biomarkers of trace metal pollution in mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from Izmir Bay (Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 141, 339–345. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9900-2.
Kucuksezgin, F., Uluturhan, E., & Batki, H. (2008b). Distribution of heavy metals in water, particulate matter and sediments of Gediz River (Eastern Aegean). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 141, 213–225. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9889-6.
Lemos, C. T., Rödel, P. M., Terra, N. R., D’Avila, O. N. C., & Erdtmann, B. (2007). River water genotoxicity evaluation using micronucleus assay in fish erythrocytes. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 66(3), 391–401. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.01.004.
Manna, G. K., Banerjee, G., & Gupta, S. (1985). Micronucleus test in the peripheral erythrocytes of the exotic fish. The Nucleus, 23, 176–179.
Metcalfe, C. D. (1988). Induction of micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities in the erythrocytes of mudminowa (Umbra limi) and brown bulheads (Ictalurus nebulosus). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 40, 489–495. doi:10.1007/BF01688371.
Mitchell, S., & Kennedy, S. (1992). Tissue concentrations of organochlorine compounds in common seals from the coast of Northern Ireland. The Science of the Total Environment, 115, 235–240. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(92)90040-Y.
OECD (2004). Oecd guideline for the testing of chemicals draft proposal for a new guideline 487: In Vitro micronucleus test, 487.
Park, E., Lee, J., Etoh, H., & Etoh, Y. I. A. (1993). Fish cell line (ULF-23HU) derived from the fin of the central mud minnow (Umbra limi): Suitable characteristics for clastogenicity assay. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology, 25, 987–994. doi:10.1007/BF02624131.
Rodriguez-Ariza, A., Abril, N., Navas, J. I., Dorado, G., Lopez-Barea, J., & Pueyo, C. (1992). Metal mutagenicity and biochemical studies on bivalve mollusks from Spanish Coasts. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 19, 112–124. doi:10.1002/em.2850190205.
Schmid, W. (1975). The micronucleus test. Mutation Research, 31, 9–15.
Vahl, H. H., Karbe, L., & Westendorff, J. (1997). Genotoxicity assessment of suspended particulate matter in the Elbe River, comparison of Salmonella microsome test, arabinosine resistance test, and umu-test. Mutation Research, 394, 81–93.
Venier, P., Maron, S., & Canova, S. (1997). Detection of micronuclei in gill cells and haemocytes of mussels exposed to benzo[a]pyrene. Mutation Research, 390, 33–44.
Venier, P., & Zampieron, C. (2005). Evidence of genetic damage in grass gobies and mussels from the Venice lagoon. Environment International, 31, 1053–1064. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.05.016.
Virgano, L. A., Bagnasco, M., Bennicelli, C., & Melodia, F. (1993). Xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in uninduced and induced rainbow trout (O.mykiss): Effects of diets and food deprivation. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 104, 51–55.
Wóznicki, P., Lewandowska, R., Brzuzan, P., Ziomek, E., & Bardega, R. (2004). The level of DNA damage and the frequency of micronuclei in haemolymph of fresh water mussels Anodonta woodiana exposed to Benzo[a] pyrene. Acta Toxicologa, 12(1), 41–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çakal Arslan, Ö., Parlak, H., Katalay, S. et al. Detecting micronuclei frequency in some aquatic organisms for monitoring pollution of Izmir Bay (Western Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 165, 55–66 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0926-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0926-5