Abstract
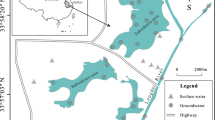
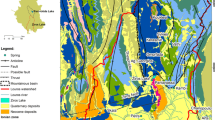
Fourteen (14) characters from six (6) water samples collected from springs, ponds, and streams located in Lower Cretaceous sedimentary area of Afikpo Basin have been analyzed. These include pH, turbidity, conductivity, total dissolved solid, hardness, Fe2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, NO3 −, Cl−, SO4 2−, and Na+. These sediments, which are Turonian and Coniacian in age, are subdivided into two by a basic rock dyke. Results of the analyses show clearly that the Turonian sediments, intruded by dolerite, have net Fe2+, HCO3 −, Ca2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Cl−, and SO4 2− concentration while those from the younger Coniacian sediment have net higher amounts of K+, Na+, and Mn2+. The overriding mafic minerals in the basic intrusive rock possibly led to higher leaching into ground water system near it. On the other hand, the presence of feldsparthic to kaolinitic sands of the younger Coniacian units led to higher K+ and Na+ matter in the water from these zones. The formations dip away from the older sediments. Concentrations of these characters are within acceptable drinking water standards by World Health Organization but noticeable anomalous zones for Fe2+, Mg2+, and Ca2+ are zones of basic rock suites. Areas with greater Na+ and K+ are traceable to sandy units. It is thus concluded that more analysis of surface, subsurface, and pond water samples can be utilized for minerals search and geological mapping. At this stage, it forms a veritable reconnaissance tool.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abia State Government Borehole Report (2003). Unpublished report of the ministry of environment of Abia State Government, Nigeria.
Degens, E. T. (1965). Geochemistry of sediments—a brief survey. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 360 p.
Dike, G. K. (2005). Geology of area NW of Afikpo. Unpublished HND, project, Federal University of Technology Owerri Nigeria.
Goldberge, C. D. (1954). Marine geochemistry and chemical scavengers of the sea. The Journal of Geology, 62, 249–262.
Heckle, P. H. (1973). Nature, origin and significance of tully limestone: An anomalous units in the Catskill Delta Devonian of New York. Geological Soc. of America special paper No. 138, 106 107.
Ibe, K. K., & Nwobi, B. (1996). Dracunculiasis transmission and variation in geological formation: A preliminary study in Afikpo–Amasiri–Okpobi region of south-eastern Nigeria. The Journal of Parasitology, 17, 75–81.
Kasumu, Y. (2000). Geology of area north of Alayi South Eastern Nigeria. Unpublished Thesis, University of Jos, Nigeria.
Oteri, A. U. (1982). Geoelectric investigation of saline contamination of a chalk aquifer by mine water at Tilmanstone, England. Geoexploration, 19, 179–192. doi:10.1016/0016-7142(81)90002-8.
Zaborsk, P., Ugoduluwa, F. X. O., Idornigie, A., Nnabo, P., & Ibe, K. K. (1997). Stratigraphy and structure of the Cretaceous Congeal Basin, North Eastern Nigeria. Bulletin Du Centre De Recherche Elf Exploration Production, 21(1), 153–186.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibe, K.K., Akaolisa, C.C.Z. Hydrogeochemical data as a tool for exploration and mapping: a case study from part of Afikpo Basin southeastern Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess 160, 393–400 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0703-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0703-x