Abstract
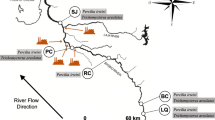
The Vicuña oil tanker exploded in Paranaguá Bay (South of Brazil), during methanol unloading operations in front of Paranaguá Harbour, on November 15th, 2004, releasing a large amount of bunker oil and methanol. Two weeks after the accident, the acute effects of the Vicuña Oil Spill (VOS) were evaluated in the demersal catfish Cathorops spixii, comparing a contaminated (at the spill site) and a reference site inside the Bay. Data were compared to previous measurements, taken before the accident, in the same species, from the same sites. The physiological biomarkers were the ones that best reflected acute effects of the spill: plasma osmolality, chloride, calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Morphological (liver and gill histopathology) and genetic (piscine micronucleus and DNA strand breaks) biomarkers revealed that damage was already present in fishes from both reference and contaminated sites inside the Bay. Thus, the reference site is not devoid of contamination, as water circulation tends to spread the contaminants released into other areas of the Bay. Acute field surveys of oil spill effects in harbour areas with a long history of contamination should thus be viewed with caution, and whenever possible previous evaluations should be considered for proper appraisal of biomarker sensitivity, especially in mobile bioindicators such as fish.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABDL/ISA (Associação Brasileira para o Desenvolvimento de Lideranças, Brazilian Association for the Development of Leaderships/Instituto Sócio-Ambiental, Social-Environmental Institute). (2005). Acesso a informação, participação e justiça ambiental no Brasil. (in Portuguese: Access to Information, Participation, and Environmental Justice in Brazil) Technical Report. 90 p. (Curitiba: ABDL/ISA)
Abou-Donia, M. B., & Menzel, D. B. (1967). Fish brain cholinesterase: its inhibition by carbamates and automatic assay. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 21, 99–108.
Akcha, F., Hubert, F. V., & Pfhol-Leszkowicz, A. (2003). Potential value of the comet assay and DNA adduct measurement in dab (Limanda limanda) for assessment of in situ exposure to genotoxic compounds. Mutation Research, 534, 21–32.
Ali, M., & Sreekrishnan, T. R. (2001). Aquatic toxicity from pulp and paper mill effluents: a review. Advances in Environmental Research, 5, 175–196.
Anjos, V. E. (2006). Especiação de cobre e arsênio no complexo estuarino da Baía de Paranaguá. (in Portuguese: Copper and arsenic speciation in the estuarine complex of Paranaguá Bay). Masters Thesis, Federal University of Paraná, Curitiba, Brazil
Arellano, J. M., Storch, V., & Sarasquete, C. (1999). Histological changes and copper accumulation in liver and gills of the Senegales Sole, Solea senegalensis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 44, 62–72.
Ayllon, F., & Garcia-Vazquez, E. (2000). Induction of micronuclei and other nuclear abnormalities in European minnow Phoxinus phoxinus and mollie Poecilia latipinna: an assessment of the fish micronucleus test. Mutation Research, 467, 177–186.
Ayllon, F., & Garcia-Vazquez, E. (2001). Micronuclei and other nuclear lesions as genotoxicity indicators in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 49, 221–225.
Babu, P. R. A., Reddy, G. R., Babu, G. R. V., & Chetty, C. S. (1989). Recovery of Benthiocarb-Inhibited AChE in fish brain: an in vitro study. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 17, 317–322.
Bernet, D., Schmidt, H., Meier, W., Burkhardt-Holm, P., & Wahli, T. (1999). Histopathology in fish: proposal or a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. Journal of Fish Diseases, 22, 25–34.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Cataldi, E., Ciccotti, E., Di Marco, P., Di Santo, O., Bronzi, P., & Cataudella, S. (1995). Acclimation trials of juvenile Italian sturgeon to different salinities: morpho-physiological descriptors. Journal of Fish Biology, 47, 609–618.
Cervigón, F., Cipriani, R., Fischer, W., Garibaldi, L., Hendrickx, M., Lemus, A. J. et al. eds. (1992). Fichas FAO de identificación de especies para los fines de la pesca. Guía de campo de las especies comerciales marinas y de aquas salobres de la costa septentrional de Sur América. Rome: FAO.
Collins, A. R., Dobson, V. L., Dusinska, M., Kennedy, G., & Stetina, R. (1997). The comet assay: what it can really tell us. Mutation Research, 375, 183–193.
Couillard, C. M., Willliams, P. J., Courtenay, S. C., & Rawn, G. P. (1999). Histopatological evaluation of Atlantic Tomcod (Microgadus tomcod) collected at estuarine sites receiving pulp and paper mill effluent. Aquatic Toxicology, 44, 263–278.
Coutinho, C., & Gokhale, K. S. (2000). Selected oxidative enzymes and histopathological changes in the gills of Cyprinus carpio and Oreochromis mossambicus cultures in secondary sewage effluent. Water Research, 34, 2997–3004.
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, K. O., Andrres, V., & Featherstone, R. M. (1961). A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochemical Pharmacology, 7, 88–95.
Fanta, E., Rios, F. S., Romão, S., Vianna, A. C. C., & Freiberger, S. (2003). Histopathology of the fish Corydoras paleatus contaminated with sublethal levels of organophosphorus in water and food. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 54, 119–130.
Ferraro, M. V. M., Fenocchio, A. S., Mantovani, M. S., Oliveira Ribeiro, C. A., & Cestari, M. M. (2004). Mutagenic effects of tributyltin and inorganic lead (Pb II) on the fish H. malabaricus as evaluated using the comet assay and the piscine micronucleus and chromosome aberration tests. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 27, 103–107.
Freire, C. A., & Prodocimo, V. (2007). Special challenges to teleost fish osmoregulation in environmentally extreme or unstable habitats. In G. Kapoor, J. M. Mancera, & B. Baldisserotto (Eds.), Fish Osmoregulation (pp. 249–276). Enfield: Science Publishers.
Frenzilli, G., Scarcelli, V., Del Barga, I., Nigro, M., Förlin, L., Bolognesi, C., & Sturve, J. (2004). DNA damage in eelpout (Zoarces viviparus) from Göteborg harbour. Mutation Research, 552, 187–195.
Galgani, F., & Bocquene, G. (1990). In vitro inhibiton of acetylcholinesterase from four marine species by organophosphates and carbamates. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 45, 234–249.
George, S. G., Wright, J., & Conroy, J. (1995). Temporal studies of the impact of the Braer oil spill on inshore feral fish from Shetland, Scotland. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 29, 530–534.
Goksøyr, A., & Förlin, L. (1992). The cytochrome P-450 system in fish, aquatic toxicology and environmental monitoring. Aquatic Toxicology, 22, 287–312.
Goobi, E. F., Gonçalves, J. E., & Reksidler, R. (2004). Simulação numérica do transporte de poluentes no interior da Baía de Paranaguá (in Portuguese, Numerical simulation of the transport of pollutants inside Paranaguá Bay). Internal Report, SIMEPAR Technological Institute. Curitiba: Brazil. Retrieved from www.simepar.br
Gravato, C., & Santos, M. A. (2002). Juvenile sea bass liver biotransformation and erythrocytic genotoxic responses to pulp mill contaminants. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 53, 104–112.
Gravato, C., & Santos, M. A. (2003). Genotoxicity biomarkers’ association with B(a)P biotransformation in Dicentrarchus labrax L. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 55, 352–358.
Guilhermino, L., Barros, P., Silva, M. C., & Soares, A. M. V. M. (1998). Should the use of inhibition of cholinesterase as a specific biomarker for organophosphate and carbamate pesticides be questioned? Biomarkers, 3, 157–163.
Harvey, J. S., Lyons, B. P., Page, T. S., Stewart, C., & Parry, J. M. (1999). An assessment of the genotoxic impact of the Sea Empress oil spill by the measurement of DNA adducts levels in selected invertebrate and vertebrate species. Mutation Research, 441, 103–114.
Hose, J. E., & Brown, E. D. (1998). Field applications of the piscine anaphase aberration test: lessons from the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Mutation Research, 399, 167–178.
Hose, J. E., McGurk, M. D., Marty, G. D., Hinton, D. E., Brown, E. D., & Baker, T. T. (1996). Sublethal effects of the Exxon Valdez oil spill on herring embryos and larvae: morphological, cytogenetic, and histopathological assessments, 1989–1991. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 53, 2355–2365.
IAP. (2005). Instituto Ambiental do Paraná. Laudo técnico do acidente do navio Vicuña, ocorrido em Paranaguá no dia 15 de novembro de 2004 (in Portuguese, Environmental Institute of Paraná. Technical Report on the accident with the ship Vicuña, which occurred in Paranaguá on November 15, 2004.) 75p. (Curitiba: IAP)
Kammann, U., Bunke, M., Steinhart, H., & Theobald, N. (2001). A permanent fish cell line (EPC) for genotoxicity testing of marine sediments with the comet assay. Mutation Research, 498, 67–77.
Kaufer, D., Friedman, A., Seidman, S., & Soreq, H. (1999). Anticholinesterases induce mutagenic transcriptional feedback response suppressing cholinergic neurotransmission. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 119, 349–360.
Khan, R. A., & Nag, K. (1993). Estimation of hemosiderosis in seabirds and fish exposed to petroleum. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 50, 125–131.
Kirby, M. F., Neall, P., & Tylor, T. (1999). EROD activity measured in flatfish from the area of the Sea Empress oil spill. Chemosphere, 38, 2929–2949.
Kobayashi, H., Sugiyama, C., Morikawa, Y., Hayashi, M., & Sofuni, T. (1995). A comparison between manual microscopic analysis and computerized image analysis in the single cell gel electrophoresis. MMS Community, 3, 103–115.
Kurelec, B., & Gupta, R. C., eds. (1993). Biomonitoring of aquatic systems (pp. 365–372). Lyon, France: IARC Science Publications.
Labrot, F., Ribera, D., Saint Denis, M., & Narbonnes, J. F. (1996). In vitro and in vivo studies of potencial biomarkers of lead and uranium contamination: lipid peroxidation, acetylcholinesterase, catalase and glutathione peroxidases activities in three nom-mammalian species. Biomarkers, 1, 21–28.
Lana, P. C., Marone, E., Lopes, R. M., & Machado, E. C. (2000). The subtropical estuarine complex of Paranaguá Bay. In U. Seeliger, & B. Kjerfve (Eds.), Coastal marine ecosystems of Latin America (pp. 131–146). Berlin: Springer.
Le Bail, P-Y., Keith, P., & Planquette, P. (2000). Atlas des poissons d’eau douce de Guyane (tome 2, fascicule II). Publications scientifiques du M.N.H.N, Paris.
Lyons, B. P., Harvey, J. S., & Parry, J. M. (1997). An initial assessment of the genotoxic impact of the Sea Empress oil spill by the measurement of DNA adduct levels in the intertidal teleost Lipophrys pholis. Mutation Research, 390, 263–268.
Lyons, B. P., Stentiford, G. D., Green, M., Bignell, J., Bateman, K., Feist, S. W., Goodsir, F., et al. (2004). DNA adducts analysis and histopathological biomarkers in European flounder (Platichthys flesus) sampled from UK estuaries. Mutation Research, 552, 177–186.
Magnotti Jr., R. A., Zaino, J. P., & McConnel, R. S. (1994). Pesticide-sensitive fish muscle cholinesterases. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 108C, 187–194.
Maria, V. L., Gravato, C., Correia, A. C., & Santos, M. A. (2002). Biotransformation and genotoxicity responses to PAHs in two teleost species. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 11, 609–615.
Marty, G. D., Hoffmann, A., Okihiro, M. S., Hepler, K., & Hanes, D. (2003). Retrospective analyses: Bile hydrocarbons and histopathology of demersal rockfish in Prince William Sound, Alaska, after the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Marine Environmental Research, 56, 569–584.
Marty, G. D., Okihiro, M. S., Brown, E. D., Hanes, D., & Hinton, D. E. (1999). Histopathology of adult Pacific herring in Prince William Sound, Alaska, after the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 56, 419–426.
Monserrat, J. M., Bianchini, A., & Bainy, A. C. D. (2002). Kinetic and toxicological characteristics of acetylcholinesterase from the gills of oysters (Crassostrea rhizophorae) and other aquatic species. Marine Environmental Research, 54, 781–785.
Monserrat, J. M., Martínez, P. E., Geracitano, L. A., Amado, L. L., Martins, C. M. G., Pinho, G. L. L., et al. (2007). Pollution biomarkers in estuarine animals: Critical review and new perspectives. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 146C, 221–234.
Norcross, B. L., Hose, J. E., Frandsen, M., & Brown, E. D. (1996). Distribution, abundance, morphological condition, and cytogenetic abnormalities of larval herring in Prince William Sound, Alaska, following the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 53, 2376–2387.
Noreña-Barroso, E., Simá-Álvarez, R., Gold-Bouchot, G., & Zapata-Pérez, O. (2004). Persistent organic pollutants and histological lesions in Mayan catfish Ariopsis assimilis from the Estuary of Chetumal, Mexico. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48, 263–269.
Oliveira Ribeiro, C. A., Vollaire, Y., Sanchez-Chardi, A., & Roche, H. (2005). Bioaccumulation and the effects of organochlorine pesticides, PAH and heavy metals in the Eel (Anguilla anguilla) at the Camargue Nature Reserve, France. Aquatic Toxicology, 74, 53–69.
Pacheco, M., & Santos, M. A. (1998). Induction of liver EROD activity and erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities by cyclophosphamide and PAHs in Anguilla anguilla L. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 40, 71–76.
Pacheco, M., & Santos, M. A. (2001). Biotransformation, endocrine, and genetic responses of (Anguilla anguilla L) to petroleum distillate products and environmentally contaminated waters. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 49, 64–75.
Pacheco, M., & Santos, M. A. (2002). Biotransformation, genotoxic, and histopathological effects of environmental contaminants in European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 53, 331–347.
Pavlov, D. F., Chuiko, G. M., & Shabrova, A. G. (1994). Adrenaline induced changes of acetylcholinesterase activity in the brain of perch (Perca fluviatilis L.). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 108C, 113–115.
Payne, J. F., Mathieu, W., Melvin, W., & Fancey, L. L. (1995). Acetylcholinesterase, an old biomarker a new future? Field trials in association with two urban rivers and a paper mill in Newfoundland. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 32, 225–231.
Plaut, I. (1998). Comparison of salinity tolerance and osmoregulation in two closely related species of blennies from different habitats. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 19, 181–188.
Plaza-Yglesias, M., Laufer, M., & Herrera, F. C. (1988). Ionic and osmotic regulation in blood, aqueous humor, gills and retina in the euryhaline fish, Eugerres plumieri. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 89A, 377–382.
Prodocimo, V., & Freire, C. A. (2001). Ionic regulation in aglomerular tropical estuarine pufferfishes submitted to sea water dilution. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 262, 243–253.
Rabitto, I. S., Alves Costa, J. R. M., Silva de Assis, H. C., Pelletier, É., Akaishi, F. M., Anjos, A., et al. (2005). Effects of dietary Pb (II) and tributyltin on neotropical fish, Hoplias malabaricus: histopatological and biochemical findings. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 60, 147–156.
Rogers, J. T., Richards, J. G., & Wood, C. M. (2003). Ionoregulatory disruption as acute toxic mechanism for lead in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquatic Toxicology, 64, 215–234.
Seyler, P., & Martin, J. M. (1990). Distribution of arsenite and total dissolved arsenic in major French estuaries: dependence on biogeochemical processes and anthropogenic inputs. Marine Chemistry, 29, 277–294.
Shailaja, M. S., & D’Silva, C. (2003). Evaluation of impact of PAH on a tropical fish Oreochromis mossambicus using multiple biomarkers. Chemosphere, 3, 835–841.
Silva de Assis, H. C. (1998). Der Einsatz Von Biomarkern zur summarischen Erfassung Von Gewässerversschmutzungen. Doctoral Thesis, Technical University of Berlin, Germany.
Singh, N. N., Das, V. J., & Srivastava, A. K. (2002). Insecticides and ionic regulation in teleosts: a review. Zoologica Poloniae, 47, 21–36.
Speit, G., & Hartmann, A. (1999). The comet assay (single cell gel test) — A sensitive genotoxicity test for the detection of DNA damage and repair. In D. S. Henderson (Ed.), Methods in molecular biology: DNA repair protocols — eukaryotic systems (vol. 113, pp. 203–212). Totowa: New Jersey.
Stegeman, J. J., & Lech, J. J. (1991). Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase systems in aquatic species: carcinogen metabolism and biomarkers for carcinogen and pollutant exposure. Environmental Health Perspectives, 90, 101–109.
Teles, M., Pacheco, M., & Santos, M. A. (2003). Anguilla anguilla L. liver ethoxyresorufin O-deethylation, Glutathione S-transferase, erythrocytic nuclear abnormalities, and endocrine responses to naphtalene and naphthoflavone. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 55, 98–107.
Thompson, H. M., Langton, S. D., & Hart, A. D. M. (1995). Prediction of inter-species differences in the toxicity of organophosphorus pesticides to wildlife — a biochemical approach. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 111C, 1–12.
Valdez Domingos, F. X. (2001). Utilização de biomarcadores imunológicos e morfológicos em Fundulus heteroclitus (Teleostei, Ciprinodontidae) na avaliação do impacto antropogênico em Pictou, Nova Scotia — Canadá. (in Portuguese: The use of immunological and morphological biomarkers in Fundulus heteroclitus (Teleostei, Ciprinodontidae) in the evaluation of anthropogenic impact in Pictou, New Scotia — Canadá.). Master Thesis, Federal University of Paraná, Brazil.
Valdez Domingos, F. X., Azevedo, M., Silva, M. D., Randi, M. A. F., Freire, C. A., Silva de Assis, H. C., et al. (2007). Multibiomarker assessment of three Brazilian estuaries using oysters as bioindicators. Environmental Research, 105, 350–363.
Weiss, C. M. (1958). Stream pollution — responses of fish to sublethal exposures of organic phosphorus insecticides. Presented at the 31st Annual Meeting of the Federation of Sewage and Industrial Wastes, Detroit.
Woo, S., Kim, S., Yum, S., Yim, U. H., & Lee, T. K. (2006). Comet assay for the detection of genotoxicity in blood cells of flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) exposed to sediments and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, 1768–1775.
Wood, C. M., Playle, R. C., & Hogstrand, C. (1999). Physiology and modeling of mechanisms of silver uptake and toxicity in fish. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 71–83.
Zodrow, J. M., Stegeman, J. J., & Tanguay, R. L. (2004). Histological analysis of acute toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorobibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in zebrafish. Aquatic Toxicology, 66, 25–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katsumiti, A., Domingos, F.X.V., Azevedo, M. et al. An assessment of acute biomarker responses in the demersal catfish Cathorops spixii after the Vicuña Oil Spill in a harbour estuarine area in Southern Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 152, 209–222 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0309-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0309-3