Abstract
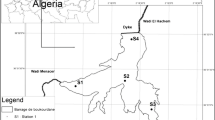
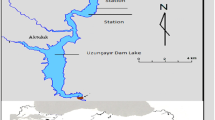
The relationships between water discharge, temperature, total dissolved solids (TDS) conductivity, turbidity, nitrate, ammonium, phosphate and the seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages of two inlets of a shallow hypertrophic lake (Lake Manyas, Turkey) were studied between January 2003 and December 2004. The results showed that different levels of water discharge, turbidity, conductivity, TDS and nutrients could lead to the development of significantly different phytoplankton assemblages in inlets of shallow hypertrophic lakes. The multiple regression analysis identified water discharge, turbidity and water temperature as the driving factors behind the dynamics of phytoplankton biovolume in the studied inlets. The first two axes of Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) explained 78% of the total variance in dominant phytoplankton species at Siğirci Inlet and 88% at Kocaçay Inlet, respectively. The purpose of this study was to determine the relationships between water discharge, temperature, conductivity, turbidity, pH, TDS, nitrate, ammonium, phosphate and the seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages of two inlets of the shallow hypertrophic Lake Manyas, Turkey by means of multivariate statistical analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albay, M. & Akcaalan, R. (2003). Comparative study of periphyton colonisation on common reed (Phragmites australis) and artificial substrate in a shallow lake, Manyas, Turkey. Hydrobiologia, 506–509, 531–540.
APHA (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (13th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
BaileyWatts, A.E., Kirika, A., May, L., & Jones, D.H. (1990). Changes in phytoplankton over various timescales in a shallow, eutrophic loch: the Loch Leven experience with special reference to the influence of flushing rate. Freshwater Biology, 23, 85–112.
Bali k, S., & Ustaoglu, R. (1987). Search for the current status assessment of kuscenneti national park and the reclamation solutions. Technical Report, No: 1987/050, Ege University Research Foundation, Izmir, Turkey (in Turkish).
Birien, J.L., Wafar, M.V.M., Le Corre, P., & Riso, R. (1991). Nutrients and primary production in a shallow stratified ecosystem in the Iroise Sea. Journal of Plankton Research, 4, 721–742.
Bourrelly, P. (1970). Les Algues D'eau Douce Tome III: Les Algues Bleues et Rouges, Eugleniens, Peridiniens, et Cryptomonadines, Boubee Paris.
Brookes, J.D., & Ganf, G.G. (2001). Variations in the buoyancy response of Microcystis aeruginosa to nitrogen, phosphorus and light. Journal of Plankton Research, 23, 1399–1411.
Büyükicsik, B., & Parlak, H. (1989). Investigation on ecology of the Bird lake Bandirma. Ankara University Journal of Fisheries, 6, 160–175 (in Turkish).
Carpenter, S.R., Ludwig, D., & Brock, W.A. (2000). Management of eutrophication in lakes subject to potentially irreversible change. Ecological Applications, 9, 751–771.
Clarke, K.R., & Ainsworth, M. (1993). A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables. Marine Ecological Progress Series, 92, 205–219.
Dokulil, M.T., & Padisák, J. (1994). Long-term compositional response of phytoplankton in a shallow, turbid environment, Neusiedlersee (Austria/Hungary). Hydrobiologia, 276, 125–137.
Geitler, L. (1925). Cyanophyceae. In Pascher (Heft 12), Die Süsswasser Flora Deutschland. Österreichs und der Schweiz, Gustav Fischer Dub., Jena.
Harris, G.P., Haffner, G.D., & Piccinin, B.B. (1980). Physical variability and phytoplankton communities: II. Primary productivity by phytoplankton in a physically variable environment. Archive of Hydrobiology, 88, 393– 25.
Havens, K.E., Thomas, J., Therese, R., East, L., & Smith, V.H. (2003). N: P ratios, light limitation, and Cyanobacterial dominance in a subtropical lake impacted by non-point source nutrient pollution. Environmental Pollution, 122, 379–390.
Hecky, R.E., & Kilham, P. (1988). Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: a review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography, 33, 796–822.
Huber-Pestalozzi, G. (1983). Das phytoplankton des süsswassers systematik und biologie, 7. Teil, 1. Halffe Chlorophyceae (Grünalgen) Ordnung: Chlorococcales. E. Schweizerbarth'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung (Nagele u. Obermiller), Stuttgart.
Husted, F. (1930). Bacillariophyta (Diatome) Heft. 10 In: Pascher die Süsswasser Flora-Mitteleuropas), Gustav Fischer Dub. Jena.
Ibelings, B.W., Mur, L.R., & Walsby, A.E. (1991). Diurnal changes in buoyancy and vertical distribution in populations of Microcystis in 2 shallow lakes. Journal of Plankton Research, 13, 419–436.
Jensen, N.G. (1985). The Pennate Diatoms (Hustedt's Die Kieselalgen, 2. Teil). Koenigstein: Koeltz Scientific Books.
Johnson, R.E., Tuchman, N.C., & Peterson C.G. (1997). Changes in the vertical microdistribution of diatoms within a developing periphyton mat. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc., 16, 503–519.
Karafistan, A., & Ari k-Colakoglu, F. (2005). Physical, chemical and microbiological water quality of the Manyas Lake, Turkey. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 10, 127–143.
Kelly, M. (2000). Identification of common benthic diatoms in rivers. AIDGAP Guides, Field Studies Council.
Leroy, S., Kazanci, N., Ileri, Ö., Kibar, M., Emre, O., McGee, E., & Griffiths, H.I. (2002). Abrupt environmental changes within a late Holocene lacustrine sequence south of the Marmara Sea (Lake Manyas, N-W Turkey): possible links with seismic events. Marine Geology, 190, 531–552.
Leibowitz, S.G., Loehle, C., Li, B.L., & Preston, E.M. (2000). Modeling landscape functions and effects: A network approach, Ecological Modeling, 132, 77–94.
Marker, A.F.H., & Collett, G.D. (1997). Spatial ad temporal characteristics of algae in the River Graet Ouse. II. The epiphytic algal flora. Regulate Rivers. Research and Management, 13, 235–244.
Murakami, T., Isaji, C., Kuroda, N., Yoshida, K., & Haga, H. (1992). Potamoplanktonic diatoms in the Nagara river; flora, populations dynamics and influences on water quality. Japanese Journal of Limnology, 53, 1–12.
Muylaert, K., Sabbe, K., & Vyverman, W. (2000). Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Phytoplankton Communities in a Freshwater Tidal Estuary (Schelde, Belgium). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 50, 673–687.
OECD. (1982). Eutrophication of waters. Monitoring, assessment and control. Paris: OECD.
Reynolds, C.S., Huszar, V., Kruk, C., Naselli-Flores, L., & Melo, S. (2002). Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. Journal of Plankton Research, 24, 417–428.
Reynolds, C.S., Reynolds, S.N., Munawar, I.F., & Munawar, M. (2000). The regulation of phytoplankton population dynamics in the world's largest lakes. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management, 3, 1–21
Reynolds, C.S., & Descy, J.P. (1996). The production, biomass and structure of phytoplankton in large rivers. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 10, 161–187.
Reynolds, C.S. (1984). The ecology of freshwater phytoplankton. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press.
SAS Institute (1990). SAS/STAT Users Guide (4th ed.). NC: Cary.
Schindler, D.W. (1977). Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science, 195, 260–262.
Shipin, O.V., Rose, P.D., & Meiring, P.G.J. (1999). Microbial processes underlying the PETRO concept (trickling filter variant). Water Research, 33, 1645–1651.
Smith, V.H. (1986). Light and nutrient effects on the relative biomass of blue-green algae in lake phytoplankton. Canadian Journal of Fish Aquatic Science, 43, 143–153.
Temponeras, M., Kristiansen, J., & Moustaka-Gouni, M. (2000). Seasonal variation in phytoplankton composition and physical-chemical features of the shallow Lake Doïrani, Macedonia, Greece. Hydrobiologia, 424, 109–122.
ter Braak, C.J.F., & Similauer, P. (1997). Biometris-Plant Research International. Wageningen, The Netherlands.
ter Braak, C.J.F., & Verdonschot, P.M.F. (1995). Canonical correspondence analysis and related multivariate methods in aquatic ecology. Aquatic Sciences, 57, 255–289.
Turkish Ministry of Environment (1997). The environmental report for the city of Balikesir. Ankara (in Turkish).
Utermöhl, H. (1958). Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton. Methodik. Mitteilungen Internationale Limnologie, 9, 1–38.
Yalti rak, C. (2002). Tectonic evolution of the Marmara Sea and its surroundings. Marine Geology, 190, 493–529.
Wetzel, R.G., & Likens, G.E. (1991). Limnological analyses. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çelik, K., Ongun, T. The Relationships Between Certain Physical and Chemical Variables and the Seasonal Dynamics of Phytoplankton Assemblages of Two Inlets of a Shallow Hypertrophic Lake with Different Nutrient Inputs. Environ Monit Assess 124, 321–330 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9229-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9229-2