Abstract
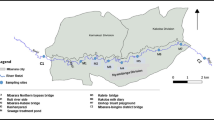
The concentrations of cadmium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, manganese, nickel, and zinc in water and bed sediments of river Gomti have been studied in a fairly long stretch of 500 km from Neemsar to Jaunpur. Grab samples of water (October 2002–March 2003) and bed sediments (December 2002 and March 2003) were collected from 10 different locations following the standard methods. The river water and sediment samples were processed and analyzed for heavy metals viz., Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Mn, Ni, and Zn, and using ICP-AES. The heavy metals found in the river water were in the range: Cd (0.0001–0.0005 mg/L); Cr (0.0015–0.0688 mg/L); Cu (0.0013–0.0.0043 mg/L); Fe (0.0791–0.3190 mg/L); Mn (0.0038–0.0.0973 mg/L); Ni (0.0066–0.011 mg/L); Pb (0.0158–0.0276 mg/L); and Zn (0.0144–0.0298 mg/L) respectively. In the sediments the same were found in the range: Cd (0.70–7.90 μ g/g); Cr (6.105–20.595 μ g/g); Cu (3.735–35.68 μ g/g); Fe (5051.485–8291.485 μ g/g); Mn (134.915–320.45 μ g/g); Ni (13.905–37.370 μ g/g); Pb (21.25–92.15 μ g/g); and Zn (15.72–99.35 μ g/g) of dry weight respectively. Some physico-chemical parameters viz., pH, total solids, total dissolved solids, total suspended solids, dissolved oxygen, biological oxygen demand, chemical oxygen demand, hardness etc. were estimated as these have direct or indirect influence on the incidence, transport and speciation of the heavy metals. Based on the geoaccumulation indices, the Gomti river sediments from Neemsar to Jaunpur are considered to be unpolluted with respect to Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, and Zn. It is unpolluted to moderately polluted with Pb. In case of Cd it varies from moderately polluted to highly polluted. As far as Ni is concerned the sediment is very highly polluted at Barabanki and Jaunpur D/s. No correlation was found between enrichment factor and geoaccumulation index.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmal, M., Khan, M. A. and Nomain, A. A.: 1985, ‘Distributions of heavy metals in water and sediments of selected sites of Tamuna river (India)’, Environ. Monit. Assess 5, 205–214.
Ajmal, M., Khan, R. and Khan, A. U.: 1987, ‘Heavy metals in water sediments, fish and plants of River Hindon, UP India’, Hydrobiologica 148, 151–157.
Akcay, H., Oguz, A. and Karapire, C.: 2003, ‘Study of heavy metal pollution and speciation in Buyak Menderes and Gediz river sediments’, Water Res. 37, 813–822.
APHA: 1998, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Dekov, D. M., Araujo, F., Subramanian, V. and Van Grieken, R.: 1998, ‘Chemical composistion of sediments and suspended matter from the Cauvery and Brahamputra river(India)’, Science Total. Environ. 212, 89–105.
Forstner, U., Wittman, G. T. W.: 1979, Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, NY.
Forstner, U., Wittman, G. T. W.: 1981, Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, NY.
Forstner, U., Ahalf, W., Calmano, W. and Kersten, M.: 1990, Sediment Criteria Development-Contributions from Environmental Geochemistry to Water Quality Management’, in: D. Heling, P. Rothe, U. Forstner and P. Stoffers (eds), Sedimets and Environmental Geochemistry: Selected Aspects and Case Histories, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Hidelberg, pp. 311–338.
Gonzalez, A. E., Rodriguez, M. T., Sanchez, J. C. J., Espinosa A. J. F. and De La Rosa, F. J. B.: 2000, ‘Assessment of metals in sediments in a tributary of Guadalquivir river (Spain), Heavy metal partitioning and relation between the water and sediment system’, Water Air, Soil Pollut. 121(1–4), 11–29.
Gupta, L. P. and Subramanian, V.: 1994, ‘Environmental geochemistry of the river Gomti: A tributary of Ganges river’, Environ. Geol. 24, 235–243.
Indian Standard: Tolerance Limits For Inland Surface waters Subject To Pollution. IS, 2296–1982.
Kumar, S. and Singh, I. B.: 1979, ‘Sedimentological study of Gomti River sediments, Uttar Pradesh, India’. Example of a river in alluvial plain. Senckenbergiania Marit 10(4/6), 145–211.
Loska, K. and Wiechula, D.: 2003, ‘Application of principal component analysis of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir’, Chemosphere 57, 723–733.
Mathur, A., Shrama, Y. C., Rupainwar, D. C., Murthy, R. C. and Chandra, S.: 1987, ‘A study of river Ganga at Varanasi with special emphasis on heavy metal pollution’, Poll. Res. 6, 37–44.
Modak, D. P., Singh, K. P., Chandra, H. and Ray, P. K.: 1992, ‘Mobile and bound forms of trace metals in sediments of the lower Ganges’, Water Res. 26(11), 1541–1548.
Muller, G.: 1979, ‘Schwermetalle in den Sedimenten des Rheins Veranderungen seit 1971’, Umschau 79(24), 778–783.
Muller, G., Yahya, A. and Gentner, P.: 1993, ‘Die Schwermetallbelastung der Sedimente des Neckars und seiner Zuflusse: Bestandsaufnahme 1990 und Vergleich mit früheren Untersuchungen’, Heidelberger Geowissenschaftliche Abhandlungen 69, 1–91.
Nrigau, J. O.: 1989, ‘A global assessment of natural sources of atmosphere trace metals’, Nature 338, 47–49.
Prasad, S., Mathur, A. and Rupaniwar, D. C.: 1989, ‘Heavy metal distribution in the sediment and river confluence points of river Ganga in Varanasi – Mirzapur region’, Asian Environ. 11, 73–82.
Saikia, D. K., Mathur, R. P. and Srivastava, S. K.: 1988, ‘Heavy metals in water and sediments of upper Ganga’, Indian J. Environ. Hlth. 31, 11–17.
Sakai, H., Kojima, Y. and Satio, K.: 1986, ‘Distribution of heavy metals in water and sieved sediments in the Toyohira river’, Water Res. 20, 559–567.
Sakai, H., Kojima, Y. and Saito, K.: 1986, ‘Distribution of heavy metals in water and sieved sediments in the Toyohira river’, Water Res. 20, 559–567.
Salomonas, W. and Forstner, U.: 1984, Metals in the Hydrocycle, Springer-Verlag, NY.
Singh, H. P. and Mahaveer, L. R.: 1997, ‘Preliminary observations on heavy metals in water and sediments in a stretch of river Ganga and some of its tributaries’, J. Environ. Biol. 18, 49–53.
Singh, H. P., Chandra, R. and Singh, B.: 1993, ‘Status of heavy metals in water, sediments, and fish flesh in the middle stretch of the river Ganga’, J. Inland Fish. Soc. (India). 25, 62–65.
Singh, H. P., Mahaveer, L. R. and Mishra, J. P.: 1992, ‘Heavy metals in sediments and water in river Ganga’, J. Assam. Sci. Soc. 34, 52–56.
Singh, M.: 2001, ‘Heavy metal pollution in freshly deposited sediments of the Yamuna River (the Ganga river tributary): A case study from Delhi and Agra urban centers India’, Environ. Geol. 40(6), 664–671.
Srivastava, S. K., Gupta, V. K. Anupam and Mohan, D.: 1994, ‘Status of some toxic heavy metal ions in the upper reaches of river Gnages’, Indian J. Chem. Soc. 71, 29–34.
Stamatis, N., Ionnidou, D., Christoforidis, A. and Koutrakis, E.: 2002, ‘Sediment pollution by heavy metals in the strymonikos and ierissos gulf, North Aegean Sea, Greece’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 80, 33–49.
Subramanian, V.: 1979, ‘Chemical and suspended sediments characteristics of rivers of India’, J. Hydrol. 44, 37–55.
Subramanian, V., Van Grieken, R. and Vant dack, L.: 1987, ‘Heavy metals distribution in the sediments of Ganges and Brahamputra rivers’, Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 9, 93–108.
Subramanian, V., Van Grieken, R. and Van’t dack, L.: 1987, ‘Heavy metal distribution in the sediments of Ganges and Brahamputra rivers’, Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 9, 93–108.
Turekian, K. K. and Wedepohl, K. H.: 1961, ‘Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer. 72, 175–192.
Woitke, P., Wellmitz, J., Helm, D., Kube, P., Lepom, P. and Litheraty, P.: 2003, ‘Analysis and assessment of heavy metal pollution in suspended solids and sediments of the river Danube’, Chemosphere 51, 633–342.
Zonta, R., Zaggia, L. and Argrse, E.: 1994, ‘Heavy metal and grain size distributions in estuarine shallow water sediments of the Cona Marsh (Venice Lagoon, Italy)’, Sci. Total Environ. 15, 19–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, V.K., Singh, K.P. & Mohan, D. Status of Heavy Metals in Water and Bed Sediments of River Gomti – A Tributary of the Ganga River, India. Environ Monit Assess 105, 43–67 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-2816-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-2816-9