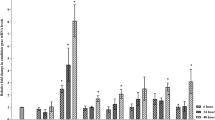
Abstract
This study investigated the biological control effect and mechanism of Variovorax sp. R1 on cucumber gray mold. In vitro experiments showed that R1 disrupted the integrity of the cell membrane and cell wall of Botrytis cinerea (B. cinerea) and inhibited its spore germination rate and germ tube length. In vivo experiments showed that R1 could be attached to the cucumber wounds and significantly inhibit the incidence of cucumber. In addition, R1 could reduce the accumulation of ROS in cucumber by inducing the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) in cucumber. At the same time, the expression of the disease resistance gene (CsCHI, CsGLU, CsPAL, CsPR1) in cucumber increased after R1 treatment. Our study showed that R1 could control postharvest cucumber gray mold by directly inhibiting the growth of B. cinerea and inducing the activities of defense-related enzymes. Overall, R1 could effectively reduce gray mold of cucumber and has great potential for biological control.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Apaliya, M.T., Zhang, H., Yang, Q., Zheng, X., Zhao, L., Kwaw, E., Mahunu, G.K. (2017). Hanseniaspora uvarum enhanced with trehalose induced defense-related enzyme activities and relative genes expression levels against Aspergillus tubingensis in table grapes. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 132, 162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2017.06.008
Apaliya, M. T., Yang, Q., Zhang, H., Zheng, X., Zhao, L., Zhang, X., Kwaw, E., & Tchabo, W. (2019). Proteomics profile of Hanseniaspora uvarum enhanced with trehalose involved in the biocontrol efficacy of grape berry. Food Chemistry, 274, 907–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.060
Bolwell, G. P., & Wojtaszek, P. (1997). Mechanisms for the generation of reactive oxygen species in plant defence – a broad perspective. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 51, 347–366. https://doi.org/10.1006/pmpp.1997.0129
Chen, J., Shen, Y., Chen, C., & Wan, C. (2019). Inhibition of key citrus postharvest fungal strains by plant extracts in vitro and in vivo: A review. Plants, 8, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8020026
Daroodi, Z., Taheri, P., & Tarighi, S. (2021). Endophytic fungus Acrophialophora jodhpurensis induced resistance against tomato early blight via interplay of reactive oxygen species, iron and antioxidants. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 115, 101681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2021.101681
Dhindsa, R. S., Plumb-Dhindsa, P., & Thorpe, T. A. (1981). Leaf senescence: Correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. Journal of Experimental Botany, 32, 93–101. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/32.1.93
Dhouib, H., Zouari, I., Ben Abdallah, D., Belbahri, L., Taktak, W., Triki, M. A., & Tounsi, S. (2019). Potential of a novel endophytic Bacillus velezensis in tomato growth promotion and protection against Verticillium wilt disease. Biological Control, 139, 104092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2019.104092
Droby, S., & Wisniewski, M. (2018). The fruit microbiome: A new frontier for postharvest biocontrol and postharvest biology. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 140, 107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.03.004
Dukare, A. S., Paul, S., Nambi, V. E., Gupta, R. K., Singh, R., Sharma, K., & Vishwakarma, R. K. (2019). Exploitation of microbial antagonists for the control of postharvest diseases of fruits: A review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 59, 1498–1513. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1417235
Elstner, E. F., & Heupel, A. (1976). Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: A simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Analytical Biochemistry, 70, 616–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90488-7
Ge, Y., Wei, M., Li, C., Chen, Y., Lv, J., Meng, K., Wang, W., & Li, J. (2018). Reactive oxygen species metabolism and phenylpropanoid pathway involved in disease resistance against Penicillium expansum in apple fruit induced by ϵ -poly- l -lysine. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 98, 5082–5088. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9046
Gill, S. S., & Tuteja, N. (2010). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 48, 909–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Hashemi, L., Golparvar, A. R., Nasr-Esfahani, M., & Golabadi, M. (2020). Expression analysis of defense-related genes in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) against Phytophthora melonis. Molecular Biology Reports, 47, 4933–4944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05520-5
He, L., Cui, K., Song, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, B., Mu, W., & Liu, F. (2018). A precisely targeted application strategy of dipping young cucumber fruit in fungicide to control cucumber gray mold: Dipping young cucumber fruit in fungicide to control cucumber gray mold. Pest Management Science, 74, 2432–2437. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5055
He, F., Zhao, L., Zheng, X., Abdelhai, M.H., Boateng, N.S., Zhang, X., Zhang, H. (2020). Investigating the effect of methyl jasmonate on the biocontrol activity of Meyerozyma guilliermondii against blue mold decay of apples and the possible mechanisms involved. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 109, 101454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2019.101454
Hodges, D. M., DeLong, J. M., Forney, C. F., & Prange, R. K. (1999). Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta, 207, 604–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050524
Hu, L.-Y., Hu, S.-L., Wu, J., Li, Y.-H., Zheng, J.-L., Wei, Z.-J., Liu, J., Wang, H.-L., Liu, Y.-S., & Zhang, H. (2012). Hydrogen sulfide prolongs postharvest shelf life of strawberry and plays an antioxidative role in fruits. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 60, 8684–8693. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf300728h
Janisiewicz, W. J., Tworkoski, T. J., Sharer, C. (2000). Characterizing the mechanism of biological control of postharvest diseases on fruits with a simple method to study competition for nutrients. Phytopathology®, 90, 1196–1200. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO.2000.90.11.1196
Keshri, P. K., Rai, N., Verma, A., Kamble, S. C., Barik, S., Mishra, P., Singh, S. K., Salvi, P., & Gautam, V. (2021). Biological potential of bioactive metabolites derived from fungal endophytes associated with medicinal plants. Mycological Progress, 20, 577–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-021-01695-8
Köhl, J., Medeiros, F. H. V., Lombaers-van der Plas, C., Groenenboom-de Haas, L., & van den Bosch, T. (2020). Efficacies of bacterial and fungal isolates in biocontrol of Botrytis cinerea and Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato and growth promotion in tomato do not correlate. Biological Control, 150, 104375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2020.104375
Lai, J., Cao, X., Yu, T., Wang, Q., Zhang, Y., Zheng, X., & Lu, H. (2018). Effect of Cryptococcus laurentii on inducing disease resistance in cherry tomato fruit with focus on the expression of defense-related genes. Food Chemistry, 254, 208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.100
Li, Z., Li, B., Li, M., Fu, X., Zhao, X., Min, D., Li, F., Li, X., & Zhang, X. (2022). Hot air pretreatment alleviates browning of fresh-cut pitaya fruit by regulating phenylpropanoid pathway and ascorbate-glutathione cycle. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 190, 111954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.111954
Lin, Y., Chen, M., Lin, H., Hung, Y.-C., Lin, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, H., & Shi, J. (2017). DNP and ATP induced alteration in disease development of Phomopsis longanae Chi-inoculated longan fruit by acting on energy status and reactive oxygen species production-scavenging system. Food Chemistry, 228, 497–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.045
Liu, J., Sui, Y., Wisniewski, M., Droby, S., & Liu, Y. (2013). Review: Utilization of antagonistic yeasts to manage postharvest fungal diseases of fruit. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 167, 153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.09.004
Ma, Q., Xu, Y., Li, D., Wu, X., Zhang, X., Chen, Y., Li, L., & Luo, Z. (2022). Potential epigenetic regulation of RNA 5’-terminal NAD decapping associated with cellular energy status of postharvest Fragaria × ananassa in response to Botrytis cinerea invasion. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 186, 111840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.111840
Moin, S., Ali, S. A., Hasan, K. A., Tariq, A., Sultana, V., Ara, J., & Ehteshamul-Haque, S. (2020). Managing the root rot disease of sunflower with endophytic fluorescent Pseudomonas associated with healthy plants. Crop Protection, 130, 105066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2019.105066
Nunes, C. A. (2012). Biological control of postharvest diseases of fruit. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 133, 181–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-011-9919-7
Nutaratat, P., Srisuk, N., Arunrattiyakorn, P., & Limtong, S. (2014). Plant growth-promoting traits of epiphytic and endophytic yeasts isolated from rice and sugar cane leaves in Thailand. Fungal Biology, 118, 683–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2014.04.010
Qin, X., Xiao, H., Xue, C., Yu, Z., Yang, R., Cai, Z., & Si, L. (2015). Biocontrol of gray mold in grapes with the yeast Hanseniaspora uvarum alone and in combination with salicylic acid or sodium bicarbonate. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 100, 160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2014.09.010
Ren, G., Ran, X., Zeng, R., Chen, J., Wang, Y., Mao, C., Wang, X., Feng, Y., & Yang, G. (2021). Effects of sodium selenite spray on apple production, quality, and sucrose metabolism-related enzyme activity. Food Chemistry, 339, 127883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127883
Romanazzi, G., Smilanick, J. L., Feliziani, E., & Droby, S. (2016). Integrated management of postharvest gray mold on fruit crops. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 113, 69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.11.003
Santoyo, G., Moreno-Hagelsieb, G., del Carmen Orozco-Mosqueda, M., & Glick, B. R. (2016). Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Microbiological Research, 183, 92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.008
Shoaib, A., Awan, Z. A., & Khan, K. A. (2019). Intervention of antagonistic bacteria as a potential inducer of disease resistance in tomato to mitigate early blight. Scientia Horticulturae, 252, 20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.02.073
Sui, G., Song, X., Zhang, B., Wang, Y., Liu, R., Guo, H., Wang, J., Chen, Q., Yang, X., Hao, H., & Zhou, W. (2019). Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel neuchromenin analogues as potential antifungal agents. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 173, 228–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.04.029
Sun, C., Huang, Y., Lian, S., Saleem, M., Li, B., Wang, C. (2021). Improving the biocontrol efficacy of Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1 with melatonin against postharvest gray mold in apple fruit. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 171, 111351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111351
Swett, C. L., Butler, B. B., Peres, N. A., Koivunen, E. E., Hellman, E. M., & Beaulieu, J. R. (2020). Using model-based fungicide programing to effectively control Botrytis and Anthracnose fruit rots in Mid-Atlantic strawberry fields and co-manage strawberry sap beetle (Stelidota geminate). Crop Protection, 134, 105175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2020.105175
Wang, Z., Jiang, M., Chen, K., Wang, K., Du, M., Zalán, Z., Hegyi, F., & Kan, J. (2018). Biocontrol of Penicillium digitatum on Postharvest Citrus Fruits by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Journal of Food Quality, 2018, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2910481
Wang, S.-Y., Shi, X.-C., Wang, R., Wang, H.-L., Liu, F., Laborda, P. (2020). Melatonin in fruit production and postharvest preservation: A review. Food Chemistry, 320, 126642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126642
Xiao, J., Zhao, L., Bai, Y., Lin, R., Legrand NgolongNgea, G., Dhanasekaran, S., Li, B., Gu, X., Zhang, X., & Zhang, H. (2022). The biocontrol efficacy of Sporidiobolus pararoseus Y16 cultured with Gamma-aminobutyric acid and its effects on the resistant substances of postharvest grapes. Biological Control, 169, 104900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2022.104900
Xu, B., Zhang, H., Chen, K., Xu, Q., Yao, Y., & Gao, H. (2013). Biocontrol of Postharvest Rhizopus decay of peaches with Pichia caribbica. Current Microbiology, 67, 255–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0359-9
Xu, D., Deng, Y., Han, T., Jiang, L., Xi, P., Wang, Q., Jiang, Z., & Gao, L. (2018). In vitro and in vivo effectiveness of phenolic compounds for the control of postharvest gray mold of table grapes. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 139, 106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2017.08.019
Xu, T., Cao, L., Zeng, J., Franco, C. M. M., Yang, Y., Hu, X., Liu, Y., Wang, X., Gao, Y., Bu, Z., Shi, L., Zhou, G., Zhou, Q., Liu, X., & Zhu, Y. (2019a). The antifungal action mode of the rice endophyte Streptomyces hygroscopicus OsiSh-2 as a potential biocontrol agent against the rice blast pathogen. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 160, 58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2019.06.015
Xu, Y., Charles, M. T., Luo, Z., Mimee, B., Tong, Z., Véronneau, P.-Y., Roussel, D., & Rolland, D. (2019b). Ultraviolet-C priming of strawberry leaves against subsequent Mycosphaerella fragariae infection involves the action of reactive oxygen species, plant hormones, and terpenes: Priming of strawberry plants by ultraviolet light. Plant, Cell and Environment, 42, 815–831. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13491
Yan, Y., Zhang, X., Zheng, X., Apaliya, M.T., Yang, Q., Zhao, L., Gu, X., Zhang, H. (2018). Control of postharvest blue mold decay in pears by Meyerozyma guilliermondii and it’s effects on the protein expression profile of pears. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 136, 124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2017.10.016
Yi, C., Qu, H. X., Jiang, Y. M., Shi, J., Duan, X. W., Joyce, D. C., & Li, Y. B. (2008). ATP-induced changes in energy status and membrane integrity of harvested Litchi fruit and its relation to pathogen resistance: Energy regulates disease resistance of Litchi fruit. Journal of Phytopathology, 156, 365–371. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0434.2007.01371.x
Yi, C., Jiang, Y., Shi, J., Qu, H., Xue, S., Duan, X., Shi, J., & Prasad, N. K. (2010). ATP-regulation of antioxidant properties and phenolics in litchi fruit during browning and pathogen infection process. Food Chemistry, 118, 42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.04.074
Zhang, Y., Shi, X., Li, B., Zhang, Q., Liang, W., Wang, C. (2016). Salicylic acid confers enhanced resistance to Glomerella leaf spot in apple. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 106, 64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.047
Zhang, Q., Zhao, L., Li, Z., Li, C., Li, B., Gu, X., Zhang, X., & Zhang, H. (2019). Screening and identification of an antagonistic yeast controlling postharvest blue mold decay of pears and the possible mechanisms involved. Biological Control, 133, 26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2019.03.002
Zhao, Y., Tu, K., Shao, X., Jing, W., & Su, Z. (2008). Effects of the yeast Pichia guilliermondii against Rhizopus nigricans on tomato fruit. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 49, 113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2008.01.001
Zhao, Y., Li, Y., & Yin, J. (2019). Effects of hot air treatment in combination with Pichia guilliermondii on postharvest preservation of peach fruit: Effects of heat treatment and Pichia guilliermondii on postharvest preservation of peach fruit. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 99, 647–655. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9229
Zhao, Y., Song, C., Brummell, D. A., Qi, S., Lin, Q., Bi, J., & Duan, Y. (2021). Salicylic acid treatment mitigates chilling injury in peach fruit by regulation of sucrose metabolism and soluble sugar content. Food Chemistry, 358, 129867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129867
Zhao, L., Lan, C., Tang, X., Li, B., Zhang, X., Gu, X., & Zhang, H. (2022). Efficacy of Debaryomyce hansenii in the biocontrol for postharvest soft rot of strawberry and investigation of the physiological mechanisms involved. Biological Control, 174, 105011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2022.105011
Zhou, X., Tan, J., Gou, Y., Liao, Y., Xu, F., Li, G., Cao, J., Yao, J., Ye, J., Tang, N., & Chen, Z. (2019). The biocontrol of postharvest decay of table grape by the application of kombucha during cold storage. Scientia Horticulturae, 253, 134–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.04.025
Zucker, M. (1965). Induction of phenylalanine deaminase by light and its relation to chlorogenic acid synthesis in potato tuber tissue. Plant Physiology, 40, 779–784. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.40.5.779
Funding
This work was supported by National Key R & D Program of China (2021YFD2100100), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32171836) and Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (LJKZ0528, 2020-MZLH-37).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Biying Yang, Zilong Li, and Shuhong Ye conceived and designed the experiments. Fengli Han and Yan Ding supervised the experimental process. Dan Chen and Min Zang contributed data analysis and mapping. Biying Yang, Zilong Li, and Min Zang wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Li, Z., Ding, Y. et al. Effect of Ginkgo biloba endophytic bacterium Variovorax sp. R1 on the biological control of postharvest cucumber gray mold and related physiological mechanisms. Eur J Plant Pathol 167, 271–284 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-023-02706-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-023-02706-y