Abstract
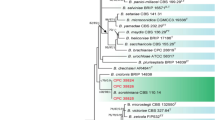
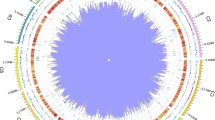
Corn is one of the most important crops globally. A new maize leaf spot disease (Exserohilum leaf spot) caused by Exserohilum rostratum has been found frequently in the Henan Province of China during the surveys of fungal diseases of maize between 2017 and 2020. A total of four Exserohilum isolates were obtained from the typical disease spots of corn leaves, which were all identified as pathogenic by inoculation tests based on Koch’s postulates. They can produce three distinctive types of conidia (A, B and C) when cultured in dark on the water agar medium with corn leaves for seven days. Based on their morphological characters and the sequence analysis of ITS, LSU, gapdh, tef1 and rpb2 gene regions, all these isolates undoubtedly belong to the species E. rostratum. To our knowledge, this is the first report of maize leaf spot caused by E. rostratum in China. Studies on the biological properties of E. rostratum showed that PDA medium, 25–30 °C, pH 6–9, and continuous light are the optimal conditions for its mycelial growth. The best carbon and nitrogen sources were starch and yeast extract, respectively. Here, we also presented the genomic assembly of E. rostratum with a size of 36.34 Mb, which is the first reported genome sequence of E. rostratum isolated from infected plant tissue. All the above research results would provide a theoretical basis for the comprehensive control of Exserohilum leaf spot disease of corn.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aregbesola, E., Ortega-Beltran, A., Falade, T., Jonathan, G., & Bandyopadhyay, R. (2020). A detached leaf assay to rapidly screen for resistance of maize to Bipolaris maydis, the causal agent of southern corn leaf blight. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 156, 133–145.
Bennett, H. Y., Hayes, R. A., & O'Hagan, S. (2019). First two cases of Exserohilum rostratum keratitis in Australia. Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology, 47, 669–671.
Berbee, M. L., Pirseyedi, M., & Hubbard, S. (1999). Cochliobolus phylogenetics and the origin of known, highly virulent pathogens, inferred from ITS and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene sequences. Mycologia, 91, 964–977.
Bunting, R. H. (1927). Local cereal diseases in the records of the Mycological Division. Year-Book Dept. of Agric., Gold Coast, 1926(Bull. 7), 25–27.
Cardona, R., & González, M. S. (2007). First report of Exserohilum rostratum associated with rice seed in Venezuela. Plant Disease, 91, 226.
Caspermeyer, J. (2016). MEGA evolutionary software re-engineered to handle today's big data demands. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33(7), 1887–1888.
CDC. (2012). Multistate outbreak of fungal infection associated with injection of methylprednisolone acetate solution from a single compounding pharmacy: USA. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 61, 839–842.
Chalupowicz, L., Dombrovsky, A., Gaba, V., Luria, N., Reuven, M., Beerman, A., Lachman, O., Dror, O., Nissan, G., & Manulis-Sasson, S. (2019). Diagnosis of plant diseases using nanopore sequencing platform. Plant Pathology, 68(2), 229–238.
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., & Jia, G. (2018). Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one fastq preprocessor. Bioinformatics, 34, i884–i890.
Choudhary, M., Sardana, H. R., Bhat, M. N., & Gurjar, M. S. (2018). First report of leaf spot disease caused by Exserohilum rostratum on bottle gourd in India. Plant Disease, 102, 1094.
Condon, B. J., Leng, Y., Wu, D., Bushley, K. E., Ohm, R. A., Otillar, R., Martin, J., Schackwitz, W., Grimwood, J., MohdZainudin, N., Xue, C., Wang, R., Manning, V. A., Dhillon, B., Tu, Z. J., Steffenson, B. J., Salamov, A., Sun, H., Lowry, S., … Turgeon, B. G. (2013). Comparative genome structure, secondary metabolite, and effector coding capacity across Cochliobolus pathogens. PLoS Genetics, 9, e1003233.
Dai, F. C., Wang, X. M., & Zhu, Z. D. (1998). Study on Curvularia leaf spot of maize. Phytopathology, 28, 123–129.
Dai, L. M., Liu, Y. X., Shi, Y. P., Li, L. L., Zhang, X., & Cai, Z. Y. (2020). The biological characteristics of Exserohilum rostratum causing leaf spot on rubber tree. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 43, 1–4.
DeHoog, G. S., & Gerrits van den Ende, A. H. G. (1998). Molecular diagnostics of clinical strains of filamentous basidiomycetes. Mycoses, 41, 183–189.
Dhara, B., Maity, A., Mondal, P., & Mitra, A. K. (2020). First report of Exserohilum leaf spot: a unique halophilic pathogen in Cucumis sativus in the South Bengal area of India. Australasian Plant Pathology, 49(3), 257–266.
Drechsler, C. (1923). Some graminicolons species of Helminthosporium. Agricultural Research, 24, 641–739.
Gao, S., Li, Y., Gao, J., Suo, Y., Fu, K., Li, Y., & Chen, J. (2014). Genome sequence and virulence variation-related transcriptome profiles of Curvularia lunata, an important maize pathogenic fungus. BMC Genomics, 15, 627.
Guo, N., Ni, X., Shi, J., Ma, J. Y., Xue, C. S., & Chen, J. (2017). Occurrence and pathogen identification of Bipolaris sorokiniana spot on corn. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 47, 1–8.
He, W., Deng H., Niu, Y. C., Zhao, X. L., & Gao J. (2011). A survey of pathogenic fungi on four common gramineous weedsin northeastern China. Plant Protection, 37(1), 99–104
He, X. L., Li, Q., Peng, W. H., Zhou, J., Cao, X. L., Wang, D., Huang, Z. Q., Tan, W., Li, Y., & Gan, B. C. (2017). Intra- and inter-isolate variation of ribosomal and protein-coding genes in Pleurotus: Implications for molecular identification and phylogeny on fungal groups. BMC Microbiology, 17, 139.
Hernández-Restrepo, M., Madrid, H., Tan, Y. P., Da Cunha, K. C., Gené, J., Guarro, J., & Crous, P. W. (2018). Multi-locus phylogeny and taxonomy of Exserohilum. Persoonia, 41, 71–108.
Hoffmann, B., Scheuch, M., Hoper, D., Jungblut, R., Holsteg, M., Schirrmeier, H., Eschbaumer, M., Goller, K. V., Wernike, K., Fisher, M., Breithaupt, A., Mettenleiter, T. C., & Beer, M. (2012). Novel orthobunyavirus in cattle, Europe, 2011. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 18, 469–472.
Holt, C., & Yandell, M. (2011). Maker 2: An annotation pipeline and genome-database management tool for second-generation genome projects. BMC Bioinformatics, 12, 491.
Honda, Y., & Aragaki, M. (1978). Photosporogenesis in Exserohilum rostratum: Temperature effects on sporulation and spore morphology. Mycologia, 70, 343–354.
Hooker, A. L. (1977). A second major gene locus in corn for chlorotic-lesion resistance to helminthosporium turicum. Crop Science, 17, 132–135.
Huelsenbeck, J. P., & Ronquist, F. (2001). MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics, 17, 754–755.
Korf, I. (2004). Gene finding in novel genomes. BMC Bioinformatics, 5, 59.
Lanfear, R., Frandsen, P. B., Wright, A. M., Senfeld, T., & Calcott, B. (2017). PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 34(3), 772–773.
Leonard, K. J., Thakur, R. P., & Leath, S. (1988). Incidence of Bipolaris and Exserohilum species in corn leaves in North Carolina. Plant Disease, 72, 1034–1038.
Lin, S. H., Huang, S. L., Li, Q. Q., Hu, C. J., Fu, G., Qin, L. P., Ma, Y. F., Xie, L., Cen, Z. L., & Yan, W. H. (2011). Characterization of Exserohilum rostratum, a new causal agent of banana leaf spot disease in China. Australasian Plant Pathology, 40, 246–259.
Litvintseva, A. P., Hurst, S., Gade, L., Frace, M. A., Hilsabeck, R., Schupp, J. M., Gillece, J. D., Roe, C., Smith, D., Keim, P., Lockhart, S. R., Changayil, S., Weil, M. R., MacCannell, D. R., Brandt, M. E., & Engelthaler, D. M. (2014). Whole-genome analysis of Exserohilum rostratum from an outbreak of fungal meningitis and other infections. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 52, 3216–3222.
Litvintseva, A. P., Hurst, S., Gade, L., Frace, M. A., Hilsabeck, R., Schupp, J. M., ... & Engelthaler, D. M. (2014). Whole-genome analysis of Exserohilum rostratum from an outbreak of fungal meningitis and other infections. Journal of clinical microbiology, 52(9), 3216–3222.
Luan, F. G., Qiang, S., Ma, D. Y., Ri, Z., & Wang, G. L. (2004). The primary studies on isolation and identification of wheat black embryo in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 41, 357–360.
Luo, Z. W., He, F., Fan, H. Y., Wang, X. H., Hua, M., Hu, F. C., & Li, X. H. (2012). First report of leaf spot disease caused by Exserohilum rostratum on pineapple in Hainan Province, China. Plant Disease, 96, 458.
Ma, Q. Z., Ma, L. L., Zhang, Y. L., Yu, S. Q., Geng, Y. H., & Zhang, M. (2017a). Molecular detection of the pathogen of corn rust in Henan Province. Journal of Plant Protection, 44, 523–524.
Ma, Q. Z., Ma, L. L., Zhang, Y. L., Yu, S. Q., Geng, Y. H., & Zhang, M. (2017b). Rapid detection of northern corn leaf spot pathogen. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 47, 154–161.
Madrid, H., da Cunha, K. C., Gene, J., Dijksterhuis, J., Sutton, D. A., Guarro, J., & Crous, P. W. (2014). Novel Curvularia species from clinical specimens. Persoonia, 33, 48–60.
Malapi-Wight, M., Salgado-Salazar, C., Demers, J. E., Clement, D. L., Rane, K. K., & Crouch, J. A. (2016). Sarcococca blight: Use of whole-genome sequencing for fungal plant disease diagnosis. Plant Disease, 100(6), 1093–1100.
Manamgoda, D. S., Cai, L., McKenzie, E. H. C., Crous, P. W., Madrid, H., Chukeatirote, E., Shivas, R. G., Tan, Y. P., & Hyde, K. D. (2012). A phylogenetic and taxonomic re-evaluation of the Bipolaris-Cochilobolus Curvularia complex. Fungal Diversity, 56, 131–144.
McGee, D. C. (1988). Seedborne and seed-transmitted diseases of maize in rice-based cropping systems. In: International Rice Research Institute (ed) Rice seed health proceedings of the international workshop on rice seed health (pp. 203–213). IRRI.
McGinnis, M. R., Rinaldi, M. G., & Winn, R. E. (1986). Emerging agents of phaeohyphomycosis: Pathogenic species of Bipolaris and Exserohilum. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 24, 250–259.
O’Donnell, K., Sarver, B. A. J., Brandt, M., Chang, D. C., Noble-Wang, J., Park, B. J., Sutton, D. A., Benjamin, L., Lindsley, M., Padhye, A., Geiser, D. M., & Ward, T. J. (2007). Phylogenetic diversity and microsphere array-based genotyping of human pathogenic fusaria including isolates from the 2005–06 multistate contact lens-associated U.S. keratitis outbreaks. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 45, 2235–2248.
Ohm, R. A., Feau, N., Henrissat, B., Schoch, C. L., Horwitz, B. A., Barry, K. W., Condon, B. J., Copeland, A. C., Dhillon, B., Glaser, F., Hesse, C. N., Kosti, I., LaButti, K., Lindquist, E. A., Lucas, S., Salamov, A. A., Bradshaw, R. E., Ciuffetti, L., Hamelin, R. C., … Grigoriev, I. V. (2012). Diverse lifestyles and strategies of plant pathogenesis encoded in the genomes of eighteen Dothideomycetes fungi. PLoS Pathogens, 8, e1003037.
Padhye, A. A., Ajello, L., Wieden, M. A., & Steinbronn, K. K. (1986). Phaeohyphomycosis of the nasal sinuses caused by a new species of Exserohilum. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 24, 245–249.
Parra, G., Bradnam, K., & Korf, I. (2007). CEGMA: A pipeline to accurately annotate core genes in eukaryotic genomes. Bioinformatics, 23, 1061–1067.
Priest, S. J., Yadav, V., & Heitman, J. (2020). Advances in understanding the evolution of fungal genome architecture. F1000 research, 9, 776.
Rehner, S. A., & Buckley, E. (2005). A Beauveria phylogeny inferred from nuclear ITS and EF-1α sequences: Evidence for cryptic diversification and links to Cordyceps teleomorphs. Mycologia, 97, 84–98.
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572–1574.
Sharma, K., Goss, E. M., Dickstein, E. R., Smith, M. E., Johnson, J. A., Southwick, F. S., & van Bruggen, A. H. (2014). Exserohilum rostratum: Characterization of a cross-kingdom pathogen of plants and humans. PLoS One, 9, e108691.
Sherry, N. L., Porter, J. L., Seemannd, T., Watkins, A., Stinear, T. P., & Howden, B. P. (2013). Outbreak investigation using high-throughput genome sequencing within a diagnostic microbiology laboratory. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 51, 1396–1401.
Stamatakis, A. (2014). RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 30(9), 1312–1313.
Sun, Q., Li, L., Guo, F., Zhang, K., Dong, J., Luo, Y., & Ma, Z. (2021). Southern corn rust caused by Puccinia polysora Underw: A review. Phytopathology Research, 3(1), 1–11.
Sun, X., Qi, X., Wang, W., Liu, X., Zhao, H., Wu, C., Chang, X., Zhang, M., Chen, H., & Gong, G. (2020). Etiology and symptoms of maize leaf spot caused by Bipolaris spp. in Sichuan, China. Pathogens, 9, 229.
Ter-Hovhannisyan, V., Lomsadze, A., Chernoff, Y. O., & Borodovsky, M. (2008). Gene prediction in novel fungal genomes using an ab initio algorithm with unsupervised training. Genome Research, 18, 1979–1990.
Tsai, J. N., Tsai, W. H., & Chen, J. L. (2001). Pathogenicity of Exserohilum rostratum on corn and weeds in the corn fields. Plant Pathology Bull, 10, 181–186.
Vaidya, G., Lohman, D. J., & Meier, R. (2011). SequenceMatrix: Concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics, 27(2), 171–180.
Vilgalys, R., & Hester, M. (1990). Rapid gentic indentification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal DNA from several species of Cryptococcus. Journal of Bacteriology, 172, 4238–4246.
Visscher, P. M., Brown, M. A., McCarthy, M. I., & Yang, J. (2012). Five years of GWAS discovery. American Journal of Human Genetics, 90, 7–24.
Weems, J. D., & Bradley, C. A. (2018). Exserohilum turcicum race population distribution in the north Central United States. Plant Disease, 102(2), 292–299.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S. J. W. T., & Taylor, J. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications, 18(1), 315–322.
Xu, H., Luo, X., Qian, J., Pang, X., Song, J., Qian, G., Chen, J., Chen, S., & Daniel. (2012). Fastuniq: A fast de novo duplicates removal tool for paired short reads. PLoS One, 7, e52249.
Young, G. Y., Lefebvre, C. L., & Johnson, A. G. (1947). Helminthosporium rostratum on corn, sorghum, and pearl millet. Phytopathology, 37(3), 180–183.
Zhang, C. C., Wang, H., & He, C. (2016). Identification of the pathogen of hybrid elephant grass leaf spot in Guimu no.1 and analysis of its biological characteristics. Genomics and Applied Biology, 35, 1232–1239.
Zhao, Y., Tsang, C. C., Xiao, M., Cheng, J., Xu, Y., Lau, S. K., & Woo, P. C. (2015). Intra-genomic internal transcribed spacer region sequence heterogeneity and molecular diagnosis in clinical microbiology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16, 25067–25079.
Zhu, X., Reid, L. M., Woldemariam, T., Tenuta, A., & Schaafsma, A. W. (2002). First report of gray leaf spot caused by Cercospora zeae-maydis on corn in Ontario, Canada. Plant Disease, 86, 327.
Zummo, N. (1986). Red spot (helminthosporium rostratum) of sweet sorghum and sugarcane, a new disease resembling anthracnose and red rot. Plant Disease, 70, 800.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province (18IRTSTHN021) and Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (162300410149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The research involved neither human participants nor animals in this article.
Conflict of interest
We have no any conflict of interest with others.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published text, maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(XLSX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Q., Cheng, C., Geng, Y. et al. The draft genome sequence and characterization of Exserohilum rostratum, a new causal agent of maize leaf spot disease in Chinese Mainland. Eur J Plant Pathol 165, 57–71 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-022-02588-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-022-02588-6