Abstract
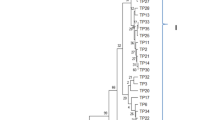
Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn, a highly variable pathogen, causes sheath blight of rice globally leading to serious yield losses under favourable environmental conditions. Sixty-four Rhizoctonia isolates collected from diverse rice growing agro-ecological zones of the north Indian state of Punjab were analyzed for species identification, genetic diversity, morphological features and virulence pattern. Accurate identification of the fungal species using internal transcribed spacer species-specific primers confirmed presence of R. solani (84.4 %), R. oryzae-sativae (10.9 %), R. oryzae (1.5 %) and mixed infection of these Rhizoctonia sp. Genetic structure of the isolates resolved using inter simple sequence repeat primers revealed high degree of polymorphism (PIC value ranging from 0.80 to 0.90), clustering the pathogen population into four major groups. The virulence pattern of 18 isolates representing genetically diverse groups generated by ISSR profile was quantified on seven rice genotypes/cultivars i.e., Tetep, Jasmine 85, Te-Qing, D-256, D-6766, PR108 and PAU201 with different levels of resistance to rice sheath blight. The hierarchical cluster analysis based on different disease variables classified isolates into six main groups. Reaction of individual isolate to each genotype revealed different levels of virulence pointing towards high evolutionary potential, thus enabling it to adapt to diverse geographical regions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, N. A. (1982). The genetics and pathology of Rhizoctonia solani. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 20, 329–347.
Anonymous. (2012). Production oriented survey. Hyderabad: Directorate Rice Research.
Banniza, S., & Rutherford, M. A. (2001). Diversity of isolates of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA and their relationship to other anastomosis groups based on pectic zymograms and molecular analysis. Mycological Research, 105, 33–40.
Banniza, S., Sy, A. A., Bridge, P. D., Simons, S. A., & Holderness, M. (1999). Characterization of populations of Rhizoctonia solani in paddy rice fields in Cote d’ Ivoire. Phytopathology, 89, 414–420.
Burpee, L. L., & Martin, B. (1992). Biology of Rhizoctonia species associated with turfgrass. Plant Disease, 76, 112–117.
Carling, D. E., Pope, E. J., Brainard, K. A., & Carter, D. A. (1999). Characterization of mycorrhizal isolates of Rhizoctonia solani from an orchid, including AG-12, a new anastomosis group. Phytopathology, 89, 942–946.
Carling, D. E., Baird, R. E., Gitaitis, R. D., Brainard, K. A., & Kuninaga, S. (2002). Characterization of AG-13, a newly reported anastomosis group of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology, 92, 893–899.
Chahal, K. S., Sokhi, S. S., & Rattan, G. S. (2003). Investigations on sheath blight of rice in Punjab. Indian Phytopathology, 56, 22–26.
Channamallikarjuna, V., Sonah, H., Prasad, M., Rao, G. J. N., Chand, S., Upreti, H. C., Singh, N. K., & Sharma, T. R. (2010). Identification of major quantitative trait loci qSBR11-1 for sheath blight resistance in rice. Molecular Breeding, 25, 155–166.
Duncan, S., Barton, J. E., & O’Brien, P. A. (1993). Analysis of variation in isolates of Rhizoctonia solani by random amplified polymorphic DNA assay. Mycological Research, 97, 1075–1082.
Gangopadhyay, S., & Chakrabarti, N. K. (1982). Sheath blight of rice. Annual Review of Plant Pathology, 61, 451–460.
Gou, Q., Kamio, A., Sharma, B. S., Sagara, Y., Arakawa, M., & Inagaki, K. (2006). Survival and subsequent dispersal of rice sclerotial disease fungi, Rhizoctonia oryzae and Rhizoctonia oryzae-sativae in paddy fields. Plant Disease, 90, 615–622.
Guleria, S., Aggarwal, R., Thind, T. S., & Sharma, T. R. (2007). Morphological and pathological variability in rice isolates of Rhizoctonia solani and molecular analysis of their genetic variability. Journal of Phytopathology, 155, 654–661.
Johanson, A., Turner, H. C., McKay, G. J., & Brown, A. E. (1998). A PCR-based method to distinguish fungi of the rice sheath-blight complex, Rhizoctonia solani, R. oryzae, and R. oryzae-sativae. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 162, 289–294.
Khodayari, M., Safaie, H., & Shambakhsh, M. (2009). Genetic diversity of Iranian AG1-IA isolates of Rhizoctonia solani, the cause of rice sheath blight, using morphological and molecular markers. Journal of Phytopathology, 157, 708–714.
Linde, C. C., Zala, M., Pauraj, R. S. D., McDonald, B. A., & Gnanamanickam, S. S. (2005). Population structure of the rice sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 1A from India. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 112, 113–121.
Liu, G., Jia, Y., Correa-Victoria, F. J., Prado, G. A., Yeaton, K. M., Mcclung, A., & Correll, J. C. (2009). Mapping quantitatively trait loci responsible for resistance to sheath blight in rice. Phytopathology, 99, 1078–1084.
Lore, J. S., Hunjan, M. S., Singh, P., Willocquet, L., Sri, S., & Savary, S. (2013). Phenotyping of partial physiological resistance to rice sheath blight. Journal of Phytopathology, 161, 224–229.
Murry, M. G., & Thompson, W. F. (1980). Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 8, 4321–4325.
Ou, S. H. (1985). Rice diseases (2nd ed.). Kew Surrey: Commonwealth Mycological Institute.
Pan, X. B., Rush, M. C., Sha, X. Y., Xie, Q. J., Linscombe, S. D., Stetina, S. R., & Oard, J. H. (1999). Major gene, non-allelic sheath blight resistance from the rice cultivars Jasmine 85 and Te-Qing. Crop Science, 39, 338–346.
Perrier, X., Flori, A., & Bannot, F. (2003). Data analysis methods. In P. Hamon, M. Seguin, X. Perrier, & J. C. Glaszmann (Eds.), Genetic diversity of cultivated tropical plants (pp. 43–76). Montpellier: Enfield, Science Publishers.
Pillai, P. K., & Singh, V. P. (1994). Differential reaction of rice cultivars to isolates of Rhizoctonia solani. Indian Phytopathology, 47, 96–98.
Pinson, S. R. M., Capdevielle, F. M., & Oard, J. H. (2005). Confirming QTLs and finding additional loci conditioning sheath blight resistance in rice using recombinant inbred lines. Crop Science, 45, 503–510.
Savary, S., Willocquet, L., Elazegui, F. A., Castilla, N., & Teng, P. S. (2000). Rice pest constraints in tropical Asia: quantification of yield losses due to rice pests in a range of production situations. Plant Disease, 84, 357–369.
Sharma, M., Gupta, S. K., & Sharma, T. R. (2005). Characterization of variability in Rhizoctonia solani by using morphological and molecular markers. Journal of Phytopathology, 153, 449–456.
Singh, V., Singh, U. S., Singh, K. P., Singh, M., & Kumar, A. (2002). Genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani isolates from rice differentiation by morphological characteristics, pathogenicity, anastomosis behaviour and RAPD fingerprinting. Journal of Mycology and Plant Pathology, 32, 332–334.
Taheri, P., Gnanamanickam, S., & Hoffe, M. (2007). Characterization, genetic structure and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. associated with rice sheath diseases in India. Phytopathology, 97, 373–383.
Toda, T., Mushika, T., & Hyakumachi, M. (2004). Development of specific PCR primers for the detection of Rhizoctonia solani AG 2–2 LP from the leaf sheaths exhibiting large-patch symptom on zoysia grass. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 232, 67–74.
Willocquet, L., Lore, J. S., Srinivasachary, S., & Savary, S. (2011). Quantification of the components of resistance to rice sheath blight using a detached tiller test under controlled conditions. Plant Disease, 95, 1507–1515.
Acknowledgments
Dr C. M. Vera Cruz, International Rice Research Institute, the Philippines is thankfully acknowledged for generously providing the seed material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
Morphological characters of Rhizoctonia isolates (DOCX 20 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
PCR amplification of Rhizoctonia isolates using R. solani specific ITS primers (M; Gene ruler molecular weight marker, catalogue # SM0311), isolates are abbreviated in Table 1 (PPTX 147 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
PCR amplification of Rhizoctonia isolates using R. oryzae-sativae specific primers (M;Promega molecular weight marker, catalogue # G7511), isolates are abbreviated in Table 1 (PPTX 303 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
PCR amplification of Rhizoctonia isolates using R. oryzae specific primers (M;Promega molecular weight marker, catalogue # G7511), isolates are abbreviated in Table 1 (PPTX 264 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
a DNA profile of Rhizoctonia isolates obtained with ISSR primer R28 (M; Gene ruler molecular weight marker, catalogue # SM0311). The serial number 1 to 55 are shown in Table 1 b DNA profile of Rhizoctonia isolates obtained with ISSR primer R30 (M; Gene ruler molecular weight marker, catalogue # SM0311). The serial number 1 to 55 are shown in Table 1 (PPTX 517 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 5
a-c Different types of sclerotia arrangement in Rhizoctonia isolates. a) scattered arrangement b) ring in centre c) ring in centre and at periphery (PPTX 1336 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 6
Dendogram showing different groups of Rhizoctonia isolates according to their morphological characters (PPTX 68 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 7
Dendogram showing different groups of Rhizoctonia isolates according to their virulence spectrum (PPTX 69 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 8
a-b Reaction of Rhizoctonia isolates on rice cultivar Jasmine 85. a) Shb-1105 showing lower lesion length compared to b) Shb-905 (PPTX 665 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lore, J.S., Jain, J., Hunjan, M.S. et al. Virulence spectrum and genetic structure of Rhizoctonia isolates associated with rice sheath blight in the northern region of India. Eur J Plant Pathol 143, 847–860 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0736-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0736-2