Abstract
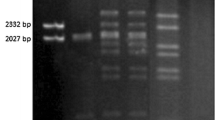
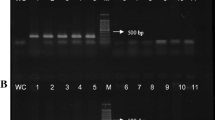
Erwinia amylovora, the causal agent of fire blight, carries the common plasmid pEA29 of 29 kb. To screen for occurrence of natural strains without plasmid pEA29, we applied PCR analysis with primers from the plasmid and the chromosomal ams region. In addition, a described TaqMan probe from pEA29 and newly designed primers from the ams-region were used for identification by real-time PCR. One strain isolated in Iran, one strain from Spain and two strains from Egypt lacked plasmid pEA29. From a recent screening series in southern Germany, in 123 E. amylovora strains from necrotic fire blight host plants, one strain was found without the common plasmid. The strains without pEA29 were virulent in assays with immature pears and on apple seedlings, but showed a reduced growth level in minimal medium without amino acids and thiamine. Transposon-labelled pEA29 was transformed into the plasmid-free strains resulting in restoration of this growth deficiency. The plasmid was stably maintained in these E. amylovora cells. The newly designed chromosomal primers for conventional and for real-time PCR identified E. amylovora strains in field samples lacking pEA29. These variants are apparently rare, but were detected in isolates from different regions in the world with fire blight.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellemann, P., Jahn, N., Theiler, R., & Geider, K. (1990). Transposon mutagenesis of Erwinia amylovora. Acta Horticulturae, 273, 233–237.
Bereswill, S., Bugert, P., Bruchmüller, I., & Geider, K. (1995). Identification of the fire blight pathogen, Erwinia amylovora, by PCR assays with chromosomal DNA. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61, 2636–2642.
Bereswill, S., Jock, S., Bellemann, P., & Geider, K. (1998). Identification of Erwinia amylovora by growth morphology on agar containing copper sulfate and by capsule staining with lectin. Plant Disease, 82, 158–164. doi:10.1094/PDIS.1998.82.2.158.
Bereswill, S., Pahl, A., Bellemann, P., Zeller, W., & Geider, K. (1992). Sensitive and species-specific detection of Erwinia amylovora by polymerase chain reaction analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 58, 3522–3526.
Brennan, J. M., Doohan, F. M., Egan, D., Scanlan, H., & Hayes, D. (2002). Characterization and differentiation of Irish Erwinia amylovora isolates. Journal of Phytopathology, 150, 414–422. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0434.2002.00789.x.
Bugert, P., & Geider, K. (1995). Molecular analysis of the ams operon required for exopolysaccharide synthesis of Erwinia amylovora. Molecular Microbiology, 15, 917–933. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02361.x.
Falkenstein, H., Bellemann, P., Walter, S., Zeller, W., & Geider, K. (1988). Identification of Erwinia amylovora, the fire blight pathogen, by colony hybridization with DNA from plasmid pEA29. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54, 2798–2802.
Falkenstein, H., Zeller, W., & Geider, K. (1989). The 29 kb plasmid, common in strains of Erwinia amylovora, modulates development of fire blight symptoms. Journal of General Microbiology, 135, 2643–2650.
Hildebrand, M., Aldridge, P., & Geider, K. (2006). Characterization of hns genes from Erwinia amylovora. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 275, 310–319. doi:10.1007/s00438-005-0085-5.
Jock, S., Kim, W. K., Donat, V., Lopez, M. M., Bazzi, C., & Geider, K. (2002). Following spread of fire blight in Western, Central and Southern Europe by molecular differentiation of Erwinia amylovora strains with PFGE analysis. Environmental Microbiology, 4, 106–114. doi:10.1046/j.1462-2920.2002.00277.x.
Jock, S., Jacob, T., Hildebrand, M., Vosberg, H.-P., & Geider, K. (2003). Instability of short-sequence DNA repeats of pear pathogenic Erwinia strains from Japan and Erwinia amylovora fruit tree and raspberry strains. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 268, 739–749.
Kritzman, G., Shwartz, H., Marcus, R., Manulis, S., Klietman, F., Oppenheim, D., Zilberstaine, M., & Shtienberg, D. (2003). Testing a rapid diagnostic medium for Erwinia amylovora and development of a procedure for sampling blossoms in pear orchards. Phytopathology, 93, 931–940. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.2003.93.8.931.
Laurent, J., Barny, M. A., Kotoujansky, A., Dufriche, P., & Vanneste, J. L. (1989). Characterization of an ubiquitous plasmid in Erwinia amylovora. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2, 160–164.
Llop, P., Donat, V., Rodríguez, M., Cabrefiga, J., Ruz, L., Jalomo, J. L., Montesinos, E., & López, M. M. (2006). An indigenous virulent strain of Erwinia amylovora lacking the ubiquitous plasmid pEA29. Phytopathology, 96, 900–907. doi:10.1094/PHYTO-96-0900.
Maes, M., Garbeva, P., & Crepel, C. (1995). Identification and sensitive endophytic detection of the fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora with 23S ribosomal DNA sequences and the polymerase chain reaction. Plant Pathology, 45, 1139–1149. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3059.1996.d01-186.x.
McGhee, G. C., & Jones, A. L. (2000). Complete nucleotide sequence of ubiquitous plasmid pEA29 from Erwinia amylovora strain Ea88: Gene organization and intraspecies variation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66, 4897–4907. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.11.4897-4907.2000.
Metzger, M., Bellemann, P., Schwartz, T., & Geider, K. (1992). Site-directed and transposon-mediated mutagenesis with pfd-plasmids by electroporation of Erwinia amylovora and Escherichia coli cells. Nucleic Acids Research, 20, 2265–2270. doi:10.1093/nar/20.9.2265.
Salm, H., & Geider, K. (2004). Real-time PCR for detection and quantification of Erwinia amylovora, the causal agent of fire blight. Plant Pathology, 53, 602–610. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3059.2004.01066.x.
Sambrook, J., & Rusell, W. (2001). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Shaw, J. J., Settles, L. G., & Kado, C. I. (1988). Transposon Tn4431 mutagenesis of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris: Characterization of a nonpathogenic mutant and cloning of a locus for pathogenicity. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 1, 39–45.
Shoeib, A. (1986). Studies on the fire blight disease of pears in Egypt. Egypt: Dissertation Alexandria University.
Schwyn, B., & Neilands, J. B. (1987). Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores Analytical Biochemistry, 160, 47–56. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9.
Vanneste, J. (Ed.).2000. Fire blight, the Disease and its Causative Agent Erwinia amylovora. Wallingford, UK: CABI Publishing.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation in Bonn, Germany, for a Georg Forster research fellowship to MM, Mandy Viehrig for help in strain isolation from field samples and Bernd Schneider for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, M., Moltmann, E., Zeller, W. et al. Characterisation of naturally occurring Erwinia amylovora strains lacking the common plasmid pEA29 and their detection with real-time PCR. Eur J Plant Pathol 124, 293–302 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9417-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-008-9417-8