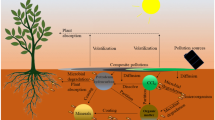
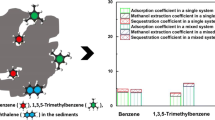
Abstract
Soil organic matter can protect plants and microorganisms from toxic substances. Beyond the tolerance limit, the toxicity of petroleum pollution to soil organisms may increase rapidly with the increase of petroleum content. However, the method for evaluating the petroleum tolerance limit of soil organic matter (SOM) is still lacking. In this study, the petroleum saturation limit in SOM was first evaluated by the sorption coefficient (Kd) of 1,2-dichlorobenzene (DCB) from water to soils containing different petroleum levels. The sorption isotherm of dichlorobenzene in several petroleum-contaminated soils with different organic matter content and the microbial toxicity test of several petroleum-contaminated soils were determined. It is found that when the petroleum content is about 5% of the soil organic matter content, the sorption of petroleum to organic matter reached saturation limit. When organic matter reaches petroleum saturation limit, the sorption coefficient of DCB by soil particles increased linearly with the increase of petroleum content (R2 > 0.991). The results provided important insights into the understanding the fate of petroleum pollutants in soil and the analysis of soil toxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Aber, J. D., Melillo, J. M., & McClaugherty, C. A. (1990). Predicting long-term patterns of mass loss, nitrogen dynamics, and soil organic matter formation from initial fine litter chemistry in temperate forest ecosystems. Canadian Journal of Botany, 68(10), 2201–2208. https://doi.org/10.1139/b90-287
Agamuthu, P., Tan, Y. S., & Fauziah, S. H. (2013). Bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil using selected organic wastes. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 18, 694–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.04.094
Balaganesh, P., Annapoorani, E., Sridevi, S., Vasudevan, M., Suneethkumar, S. M., & Natarajan, N. (2021). Sustainable practices and innovations in civil engineering. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, 79, 141–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5101-7_14
Bandura, L., Woszuk, A., Kołodyńska, D., & Franus, W. (2017). Application of mineral sorbents for removal of petroleum substances: A review. Minerals, 7(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7030037
Bhuyan, B., & Pandey, P. (2022). Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil using hydrocarbonoclastic rhizobacteria, applied through Azadirachta indica rhizosphere. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 24(13), 1444–1454. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2022.2033689
Brand, E., Lijzen, J., Peijnenburg, W., & Swartjes, F. (2013). Possibilities of implementation of bioavailability methods for organic contaminants in the Dutch Soil Quality Assessment Framework. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 261, 833–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.11.066
Chaineau, C. H., Yepremian, C., Vidalie, J. F., Ducreux, J., & Ballerini, D. (2003). Bioremediation of a crude oil-polluted soil: Biodegradation, leaching and toxicity assessments. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 144, 419–440. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022935600698
Chen, C. H., Liu, P. W. G., & Whang, L. M. (2019). Effects of natural organic matters on bioavailability of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil-water environments. Chemosphere, 233, 843–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.202
Chen, H., Chen, S., Quan, X., Zhao, H., & Zhang, Y. (2008). Sorption of polar and nonpolar organic contaminants by petroleum-contaminated soil. Chemosphere, 73(11), 1832–1837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.08.005
Chen, J., Hu, J. D., Wang, X. J., & Tao, S. (2006). Desorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soil in presence of surfactants. Environmental Sciences, 27(2), 361–365. (In Chinese)
Chen, M., Xu, P., Zeng, G., Yang, C., Huang, D., & Zhang, J. (2015). Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: Applications, microbes and future research needs. Biotechnology Advances, 33(6), 745–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.05.003
Chiou, C. T. (2002). Partition and adsorption of organic contaminants in environmental systems. Wiley.
Dorn, P. B., & Salanitro, J. P. (2000). Temporal ecological assessment of petroleum contaminated soil before and after bioremediation. Chemosphere, 40(4), 46–51.
Dror, I., Gerstl, Z., Prost, R., & Yaron, B. (2002). Abiotic behavior of entrapped petroleum products in the subsurface during leaching. Chemosphere, 49(10), 1375–1388. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00529-5
Fan, M. Y., Xie, R. J., & Qin, G. (2013). Bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil by a combined system of biostimulation–bioaugmentation with yeast. Environmental Technology, 35(4), 391–399. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.829504
Fei, Y. H., Leung, K., & Li, X. Y. (2017). Adsorption of 17 α-ethyl estradiol with the competition of bisphenol A on the marine sediment of Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 124(2), 753–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.06.068
Fu, Y. J. (2003). Effects of organic matter heterogeneity on sorption and desorption of organic contaminants by soils and sediments. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 955–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00205-6
Gerenfes, D., Giorgis, A., & Negasa, G. (2022). Comparison of organic matter determination methods in soil by loss on ignition and potassium dichromate method. International Journal of Horticulture and Food Science, 4(1), 49–53. https://doi.org/10.33545/26631067.2022.v4.i1a.85
Gong, X., Xu, W., & He, Y. (2017). Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter and its effects on the adsorption of β-HCH in the soil. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 31(1), 318–325.
Grathwohl, P. (1990). Influence of organic matter from soils and sediments from various origins on the sorption of some chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons: Implications on Koc correlations. Environmental Science & Technology, 24(11), 1687–1693.
Guo, M., Zhao, F., Tian, L., Ni, K., Lu, Y., & Borah, P. (2022). Effects of polystyrene microplastics on the seed germination of herbaceous ornamental plants. Science of the Total Environment, 809, 151100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenvol2021.151100
Hakim, S. S., Olsson, M. H., Sørensen, H. O., Bovet, N., Bohr, J., Feidenhans’l, R., & Stipp, S. L. (2017). Interactions of the calcite {10.4} surface with organic compounds: Structure and behavior at mineral–organic interfaces. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–11.
Hassett, J. P., & Anderson, M. A. (1982). Effects of dissolved organic matter on adsorption of hydrophobic organic compounds by river-and sewage-borne particles. Water Research, 16(5), 681–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043354(82)90091-4
Hedges, J. I., Baldock, J. A., Gélinas, Y., Lee, C., Peterson, M., & Wakeham, S. G. (2001). Evidence for non-selective preservation of organic matter in sinking marine particles. Nature, 409(6822), 801–804. https://doi.org/10.1038/35057247
Hoang, S. A., Sarkar, B., Seshadri, B., Lamb, D., Wijesekara, H., Vithanage, M., Liyanage, C., Kolivabandara, P. A., Rinklebe, J., Lam, S. S., & Vinu, A. (2021). Mitigation of petroleum-hydrocarbon-contaminated hazardous soils using organic amendments: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 416, 125702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125702
Hung, H. W., Sheng, G. D., Lin, T. F., Su, Y., & Chiou, C. T. (2009). The organic contamination level based on the total soil mass is not a proper index of the soil contamination intensity. Environmental Pollution, 157(11), 2928–2932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.07.007
Hunt, J. M. (1991). Generation of gas and oil from coal and other terrestrial organic matter. Organic Geochemistry, 17(6), 673–680.
Jonker, M. T., & Barendregt, A. (2006). Oil is a sedimentary supersorbent for polychlorinated biphenyls. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(12), 3829–3835. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0601080
Jonker, M., Sinke, A., Brils, J. M., & Koelmans, A. A. (2003). Sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to petroleum contaminated sediment: Unresolved complex? Environmental Science & Technology, 37(22), 5197–5203.
Karimi, A. H., & Hamidi, A. (2021). Effect of phytoremediation on the shear strength characteristics of silty clayey sand. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 80, 1–20.
Kile, D. E., Chiou, C. T., Zhou, H., Li, H., & Xu, O. (1995a). Partition of nonpolar organic pollutants from water to soil and sediment organic matters. Environmental Science & Technology, 29(5), 1401–1406.
Kile, D. E., Chiou, G. T., Zhou, H., Hui, L. I., & Ouyong, X. U. (1995b). Partition of nonpolar organic pollutants from water to soil and sediment organic matters. Environmental Science & Technology, 29(5), 1401–1406. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00005a037
Kudakwashe, M. E., Qiang, L. I., Shuai, W. U., & Yanfei, Y. U. (2022). Plant-and microbe-assisted biochar amendment technology for petroleum hydrocarbon remediation in saline-sodic soils: a review. Pedosphere, 32(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S10020160(21)60041-3
Kumar, M., Bolan, N., Jasemizad, T., Padhye, L. P., Sridharan, S., Singh, L., Bolan, S., O’Connor, J., Zhao, H., Shaheen, S. M., & Song, H. (2022). Mobilization of contaminants: potential for soil remediation and unintended consequences. Science of the Total Environment, 839, 156373.
Li, H., Gao, Y., Jiang, L., Zheng, F., & Wang, M. (2010). Impacts of petroleum pollutants on rape biomass, microbial population and the petroleum pollutants residue in soil. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 17, 1–4.
Li, X., Li, N., Jiang, L., Hu, Y., Murati, H., & Su, Y. (2023). Exploring the existing state of petroleum based on the adsorption capacity of carbon tetrachloride in petroleum-contaminated soil. Journal of Soils and Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03605-9
Li, Y., Wei, M., Liu, L., Xue, Q., & Yu, B. (2020). Adsorption of toluene on various natural soils: Influences of soil properties, mechanisms, and model. Science of the Total Environment, 740, 140104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140104
Lin, Q., Tan, X., Almatrafi, E., Yang, Y., Wang, W., Luo, H., Qin, F., Zhou, C., Zeng, G., & Zhang, C. (2022). Effects of biochar-based materials on the bioavailability of soil organic pollutants and their biological impacts. Science of the Total Environment, 826, 153956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153956
Liu, P. W. G., Wang, S. Y., Huang, S. G., & Wang, M. Z. (2012). Effects of soil organic matter and aging on remediation of diesel-contaminated soil. Environmental Technology, 33(23), 2661–2672. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2012.673017
Liu, P., Zhu, D., Zhang, H., Shi, X., & Dang, F. (2008). Sorption of polar and nonpolar aromatic compounds to four surface soil of eastern China. Environmental Pollution, 156(3), 1053–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.04.020
Lu, Y., & Pignatello, J. J. (2004). Sorption of apolar aromatic compounds to soil humic acid particles affected by aluminum(III) ion cross-linking. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33(4), 1314–1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.04.020
Ma, C., Feng, X., Ding, Y., et al. (2018). Nano-pore distribution of biochar and soil aggregates revealed with the technology of nuclear magnetic resonance cryoporometry. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 49(3), 582–587.
Mader, B. T., Uwe-Goss, K., & Eisenreich, S. J. (1997). Sorption of nonionic, hydrophobic organic chemicals to mineral surfaces. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(4), 1079–1086. https://doi.org/10.1021/es960606g
McCarthy, J. F., Roberson, L. E., & Burrus, L. W. (1989). Association of benzo(a)pyrene with dissolved organic matter: Prediction of Kdom from structural and chemical properties of the organic matter. Chemosphere, 19(12), 1911–1920. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(89)90014-3
MEE (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of PRC) and MLS (Ministry of land and resources of PRC). (2014). National soil pollution survey Bulletin [EB/OL]. http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/qt/201404/t20140417_270670.htm
Mikutta, R., Kleber, M., Torn, M. S., & Jahn, R. (2006). Stabilization of soil organic matter: Association with minerals or chemical recalcitrance? Biogeochemistry, 77(1), 25–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-0712-6
Mott, H. V. (2002). Association of hydrophobic organic contaminants with soluble organic matter: Evaluation of the database of Kdoc values. Advances in Environmental Research, 6(4), 577–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-0191(01)00104-6
Murphy, E. M., Zachara, J. M., & Smith, S. C. (1990). Influence of mineral-bound humic substances on the sorption of hydrophobic organic compounds. Environmental Science & Technology, 24(10), 1507–1516. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00080a009
Noh, S. R., Kim, J. A., Cheong, H. K., Ha, M., Jee, Y. K., & Park, M. S. (2019). Hebei spirit petroleum spill and its long-term effect on children’s asthma symptoms. Environmental Pollution, 248, 286–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.034
Novak, J. M., Jayachandran, K., Moorman, T. B., & Weber, J. B. (1995). Sorption and binding of organic compounds in soils and their relation to bioavailability. Bioremediation Science and Applications, 43, 13–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(83)90148-5
Ogboghodo, I. A., Iruaga, E. K., Osemwota, I. O., & Chokor, J. U. (2004). An assessment of the effects of crude petroleum pollution on soil properties, germination and growth of maize (zea mays) using two crude types–forcados light and escravos light. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 96(1/3), 143–152.
Paramananthan, S., Lee, P. X., Wong, M. K., Van Ranst, E., Wüst, R. A. J., & Vijiandran, J. R. (2018). A comparative study of the use of organic carbon and loss on ignition in defining tropical organic soil materials. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 49(5), 626–634. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2018.1435683
Patowary, R., Patowary, K., Kalita, M. C., & Deka, S. (2018). Application of biosurfactant for enhancement of bioremediation process of crude oil contaminated soil. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 129, 50–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2018.01.004
Petenello, M. C., Beltrán, C., & Feldman, S. R. (2014). Effect of diesel-oil addition on soil microbiological parameters in systems with and without plants. Terra Latinoamericana, 32(4), 301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-8686(98)00055-4
Ping, L. F., & Luo, Y. M. (2005). Effects of organic matter on environmental behaviors of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Soils, 37(4), 362–369.
Plaza, G., Nalecz-Jawecki, G., Ulfig, K., & Brigmon, R. (2005). The application of bioassays as indicators of petroleum-contaminated soil remediation. Chemosphere, 59(2), 289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.11.049
Pozhilenkova, P. V., Aponasenko, A. D., & Filimonov, V. S. (2004). Investigation of formation and structural characteristics of the adsorbed layer of organic matter on suspended mineral particles after the examples of humate an adsorption processes on clay minerals. Proceedings of SPIE the International Society for Optical Engineering, 15(4), 215–225.
Qian, Y., Chunsheng, Y., & Cheng, D. (2011). Adsorption of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene on three kinds of substrates from constructed wetlands. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 07, 1675–1680.
Rasul, M., Cho, J., Shin, H. S., & Hur, J. (2022). Biochar-induced priming effects in soil via modifying the status of soil organic matter and microflora: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 805, 150304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150304
Rheinländer, T., Klumpp, E., & Schwuger, M. J. (1998). On the adsorption of hydrophobic pollutants on surfactant/clay complexes: comparison of the influence of a cationic and a nonionic surfactant. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 19(2–3), 379–398. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932699808913181
Schaeffer, A. (2001). Does supersorbent soot control PAH fate? Environmental Science & Technology, 35(1), 10A. https://doi.org/10.1021/es012241s
Schumacher, B. A. (2002). Methods for the determination of total organic carbon (TOC) in soils and sediments. Ecological Risk Assessment Support Center U.S.EPA.
Schwarzenbach, R. P., & Westall, J. (1981). Transport of Nonpolar Organic Compounds from Surface Water to Groundwater. Laboratory Sorption Studies. Environmental Science & Technology, 15(11), 1360–1367. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00093a009
Shahriari, M. H., Savaghebi-Firoozabadi, G., Azizi, M., Kalantari, F., & Minai-Tehrani, D. (1998). Study of growth and germination of medicago sativa (alfalfa) in light crude petroleum-contaminated soil. Chromatographia, 47(11–12), 716–720.
Shen, L., & Jaffe, R. (2000). Interactions between dissolved petroleum hydrocarbons and pure and humic acid-coated mineral surfaces in artificial seawater. Marine Environmental Research, 49(3), 217–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(99)00066-5
Six, J., Conant, R. T., Paul, E. A., & Paustian, K. (2002). Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: Implications for c-saturation of soils. Plant and Soil, 241(2), 155–176. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016125726789
Spasojevic, J., Maletic, S., Roncevic, S., et al. (2018). The role of organic matter and clay content in sediments for bioavailability of pyrene. Water Science and Technology, 77(1/2), 439–447.
Stokes, J. D., Paton, G. I., & Semple, K. T. (2005). Behavior and assessment of bioavailability of organic contaminants in soil: Relevance for risk assessment and remediation. Soil Use and Management, 21, 475–486. https://doi.org/10.1079/SUM2005347
Styrishave, B., Bjoerklund, E., Johnsen, A., & Halling-Sorensen, B. (2012). The spatial heterogeneity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil depends on their physico-chemical properties. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 223(3), 969–977.
Sun, S., & Boyd, S. A. (1991). Sorption of polychlorobiphenyl (PCB) congeners by residual pcb-petroleum phases in soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 20(3), 557–561. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1991.00472425002000030009x
Sun, Y., Xiong, X., He, M., Xu, Z., Hou, D., Zhang, W., & Tsang, D. C. (2021). Roles of biochar-derived dissolved organic matter in soil amendment and environmental remediation: a critical review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 424, 130387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130387
Tang, J., Lu, X., Sun, Q., & Zhu, W. (2012). Aging effect of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil under different attenuation conditions. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 149, 109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.12.020
Tang, J., Wang, M., & Wang, F. (2011). Eco-toxicity of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23(5), 845–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60517-7
Tang, L., Gudda, F. O., Wu, C., Ling, W., El-Ramady, H., Mosa, A., & Wang, J. (2022). Contributions of partition and adsorption to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons sorption by fractionated soil at different particle sizes. Chemosphere, 301, 134715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134715
Thamaraiselvi, T., Brindha, S., Kaviyarasi, N. S., Annadurai, B., & Gangwar, S. K. (2012). Effect of organic amendments on the bio chemical transformations under different soil conditions. International Journal of Advanced Biological Research, 2(1), 171–173.
Ugochukwu, U. C., Jones, M. D., Head, I. M., Manning, D., & Fialips, C. I. (2014). Biodegradation and adsorption of crude oil hydrocarbons supported on “homoionic” montmorillonite clay minerals. Applied Clay Science, 87, 81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2013.11.022
Vasudevan, M., Ajithkumar, P. S., Singh, R. P., & Natarajan, N. (2016b). Mass transfer kinetics using two-site interface model for removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution with cassava peel and rubber tree bark as adsorbents. Environmental Engineering Research, 21(2), 152–163. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2015.152
Vasudevan, M., Karthika, K., Gowthaman, S., Karthick, K., Balaganesh, P., Suneeeth Kumar, S. M., & Natarajan, N. (2021). Aerobic in-vessel co-composting of dewatered sewage sludge with mixed municipal wastes under subhumid and semiarid atmospheric conditions. Energy Sources Part a: Recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects, 43(24), 3403–3414. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1624888
Vasudevan, M., Kumar, G. S., & Nambi, I. M. (2015). Numerical studies on kinetics of sorption and dissolution and their interactions for estimating mass removal of toluene from entrapped soil pores. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8, 6895–6910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1681-7
Vasudevan, M., Nambi, I. M., & Kumar, G. S. (2016a). Scenario-based modeling of mass transfer mechanisms at a petroleum contaminated field site-numerical implications. Journal of Environmental Management, 175, 9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.03.009
Vasudevan, M., Suresh Kumar, G., & Nambi, I. M. (2016c). Numerical modeling on rate-limited dissolution mass transfer of entrapped petroleum hydrocarbons in a saturated sub-surface system. ISH Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 22(1), 3–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2015.1043596
Wang, K., & Xing, B. S. (2005). Structural and sorption characteristics of adsorbed humic acid on clay minerals. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34(1), 342–349. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2005.0342
Wang, X., Guo, X., Yu, Y., Shu, T., & Xing, B. (2011). Sorption mechanisms of phenanthrene, lindane, and atrazine with various humic acid fractions from a single soil sample. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(6), 2124–2130. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102468z
Weber, W. J., & Huang, W. A. (1996). Distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments. 4. Intraparticle heterogeneity and phase-distribution relationships under nonequilibrium conditions. Environmental Science & Technology, 30(10), 880–888. https://doi.org/10.1021/es950329y
Wu, B., & Guo, S. (2020). Spatial ecological risk assessment for contaminated soil in petroleumed fields. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 403, 123984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123984
Xing, B., & Pignatello, J. J. (1996). Time-dependent isotherm shape of organic compounds in soil organic matter implications for sorption mechanism. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, 15(8), 1282–1288. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620150805
Xu, Y., & Lu, M. (2010). Bioremediation of crude oil-contaminated soil: Comparison of different biostimulation and bioaugmentation treatments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183(1–3), 395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.038
Yang, Y., Zhang, N., Xue, M., Lu, S. T., & Tao, S. (2011). Effects of soil organic matter on the development of the microbial polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) degradation potentials. Environmental Pollution, 159(2), 591–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.10.003
Zemanek, M. G., Pollard, S. J. T., Kenefick, S. L., & Hrudey, S. E. (1997). Multi-phase partitioning and co-solvent effects for polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (pah) in authentic petroleum- and creosote-contaminated soils. Environmental Pollution, 98(2), 239–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(97)00126-7
Zhang, Y., Gao, J., Wang, R., & Ren, Z. (2013). Determination of 1, 4-dichlorobenzene in water by headspace solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography. Industrial Water Treatment, 33(09), 76–79. (In Chinese).
Zhuang, S., Zhu, L., & Liang, X. (2016). Sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to soils enhanced by heavy metals: perspective of molecular interactions. Journal of Soil & Sediments, 16, 1509–1518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1341-x
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Foundation of Xinjiang Educational Commission (XJEDU2021I07) and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Market Supervision and Administration Bureau Science and technology Foundation (No. 201902)
Funding
The author declared that no funds, grants, or other support were received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL contributed to conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft. YS contributed to supervision, writing—review & editing, resources, funding acquisition. XL contributed to writing—review & editing, funding acquisition. ML contributed to writing—review & editing. NL contributed to writing—review & editing. HM contributed to writing—review & editing. LJ contributed to writing—review & editing. YH contributed to writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Li, X., Li, M. et al. Assessment of tolerance limits of petroleum residues in soil organic matter: sorption of dichlorobenzene by soil. Environ Geochem Health 46, 16 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01798-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01798-z