Abstract
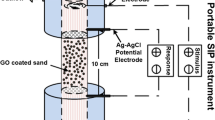
The municipal solid waste (MSW) landfill in Hangzhou, China utilized zeolite and activated carbon (AC) as permeable reactive barrier (PRB) fill materials to remediate groundwater contaminated with MSW leachates containing ammonium, chemical oxygen demand (COD), and heavy metals. The spectral induced polarization (SIP) technique was chosen for monitoring the PRB because of its sensitivity to pore fluid chemistry and mineral-fluid interface composition. During the experiment, authentic groundwater collected from the landfill site was used to permeate two columns filled with zeolite and AC, and the SIP responses were measured at the inlet and outlet over a frequency range of 0.01–1000 Hz. The results showed that zeolite had a higher adsorption capacity for COD (7.08 mg/g) and ammonium (9.15 mg/g) compared to AC (COD: 2.75 mg/g, ammonium: 1.68 mg/g). Cation exchange was found to be the mechanism of ammonium adsorption for both zeolite and AC, while FTIR results indicated that π-complexation, π–π interaction, and electrostatic attraction were the main mechanisms of COD adsorption. The Cole–Cole model was used to fit the SIP responses and determine the relaxation time (τ) and normalized chargeability (mn). The calculated characteristic diameters of zeolite and AC based on the Schwarz equation and relaxation time (τ) matched the pore sizes observed from SEM and MIP, providing valuable information on contaminant distribution. The mn of zeolite was positively linear with adsorbed ammonium (R2 = 0.9074) and COD (R2 = 0.8877), while the mn of AC was negatively linear with adsorbed ammonium (R2 = 0.8192) and COD (R2 = 0.7916), suggesting that mn could serve as a surrogate for contaminant saturation. The laboratory-based real-time non-invasive SIP results showed good performance in monitoring saturation and provide a strong foundation for future field PRB monitoring.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Aal, G. Z. A., Slater, L. D., & Atekwana, E. A. (2006). Induced-polarization measurements on unconsolidated sediments from a site of active hydrocarbon biodegradation. Geophysics, 71, H13. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2187760
Archipov, T., Santra, S., Ene, A. B., Stoll, H., Rauhut, G., & Roduner, E. (2009). Adsorption of benzene to copper in CuHY zeolite. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 113, 4107–4116. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp805976a
Bate, B., Cao, J., Zhang, C., & Hao, N. (2020). Spectral induced polarization study on enzyme induced carbonate precipitations: Influences of size and content on stiffness of a fine sand. Acta Geotechnica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-020-01059-8
Bate, B., Cao, J., Zhang, C., Hao, N., & Wang, S. (2021). Monitoring lime and cement improvement using spectral induced polarization and bender element techniques. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 13, 202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2020.06.005
Bate, B., Chen, C., Liu, P., Zhou, C., Chen, X., Nie, S., Chen, K., Chen, Y., & Zhang, S. (2022a). The migration and deposition behaviors of montmorillonite and kaolinite particles in a two-dimensional micromodel. Materials, 15, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15030855
Bate, B., Ye, J., Cao, J., You, Y., Cao, J., Zhang, S., Zhan, L. T., Zhang, C., & Hao, N. (2022b). The mechanisms and monitoring of zeolite remediating chemical oxygen demand, NH4+, and Pb2+. J Applied Geophysics, 199, 104615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2022.104615
ben Moshe, S., & Furman, A. (2022). Real-time monitoring of organic contaminant adsorption in activated carbon filters using spectral induced polarization. Water Research, 212, 118103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118103
Binley, A., Slater, L. D., Fukes, M., & Cassiani, G. (2005). Relationship between spectral induced polarization and hydraulic properties of saturated and unsaturated sandstone. Water Resources Research, 41, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005WR004202
Busl, M., Platero, G., & Jauho, A. P. (2012). Dynamical polarizability of graphene irradiated by circularly polarized ac electric fields. Physical Review B Condensed Matter Materials Physics, 85, 155449. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.85.155449
Chen, L., Wang, C., Zhang, C., Zhang, X., & Liu, F. (2022). Eight-year performance evaluation of a field-scale zeolite permeable reactive barrier for the remediation of ammonium-contaminated groundwater. Applied Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105372
Cornel, P. K., Summers, R. S., & Roberts, P. V. (1986). Diffusion of humic acid in dilute aqueous solution. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 110, 149–164.
Dong, G., Huang, L., Wu, X., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Liu, G., Wang, L., Liu, X., & Xia, H. (2018). Effect and mechanism analysis of MnO2 on permeable reactive barrier (PRB) system for the removal of tetracycline. Chemosphere, 193, 702–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.085
Elis, V. R., Ustra, A. T., Hidalgo-Gato, M. C., Pejon, O. J., & Hiodo, F. Y. (2016). Application of induced polarization and resistivity to the environmental investigation of an old waste disposal area. Environmental Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6157-5
Faisal, A. A. H., Ali, I. M., Naji, L. A., Madhloom, H. M., & Al-Ansari, N. (2020). Using different materials as a permeable reactive barrier for remediation of groundwater contaminated with landfill’s leachate. Desalination and Water Treatment, 175, 152–163. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.24890
Falzone, S., Robinson, J., & Slater, L. (2019). Characterization and monitoring of porous media with electrical imaging: A review. Transport in Porous Media, 130, 251–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1203-2
Faraday, J. C. S. (1980). Spectroscopic studies of benzene hydrogenation on platinum-loaded zeolites Part 1.-Benzene adsorption on supports.
Florian, J., Kubelkova, L., & Heyrovsk, J. (1994). Proton transfer between H-zeolite and adsorbed acetone or acetonitrile: Quantum chemical and FTIR study. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 98, 8734–8741.
Franz, M., Arafat, H. A., & Pinto, N. G. (2000). Effect of chemical surface heterogeneity on the adsorption mechanism of dissolved aromatics on activated carbon. Carbon, 38, 1807–1819.
Ghani, Z. A., Yusoff, M. S., Zaman, N. Q., Zamri, M. F. M. A., & Andas, J. (2017). Optimization of preparation conditions for activated carbon from banana pseudo-stem using response surface methodology on removal of color and COD from landfill leachate. Waste Management, 62, 177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.02.026
González-Galán, C., Luna-Triguero, A., Vicent-Luna, J. M., Zaderenko, A. P., Sławek, A., Sánchez-de-Armas, R., & Calero, S. (2020). Exploiting the π-bonding for the separation of benzene and cyclohexane in zeolites. Chemical Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125678
Gu, Z., Li, C., Wang, G., Zhang, L., Li, X., Wang, W., & Jin, S. (2010). Synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole/graphite oxide composite by in situ emulsion polymerization. Journal of Polymer Science Part b: Polymer Physics, 48, 1329–1335. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.22031
Gupta, K., & Khatri, O. P. (2019). Fast and efficient adsorptive removal of organic dyes and active pharmaceutical ingredient by microporous carbon: Effect of molecular size and charge. Chemical Engineering Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122218
Halim, A. A., Aziz, H. A., Johari, M. A. M., Ariffin, K. S., & Bashir, M. J. K. (2012). Semi-aerobic landfill leachate treatment using carbon-minerals composite adsorbent. Environmental Engineering Science, 29, 306–312. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2010.0204
Han, B., Butterly, C., Zhang, W., He, J.-z, & Chen, D. (2021). Adsorbent materials for ammonium and ammonia removal: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124611
Han, Z., Ma, H., Shi, G., He, L., Wei, L., & Shi, Q. (2016). A review of groundwater contamination near municipal solid waste landfill sites in China. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.201
Hao, N., Cao, J., Ye, J., Zhang, C., Li, C., & Bate, B. (2021a). Content and morphology of lead remediated by activated carbon and biochar: A spectral induced polarization study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 411, 124605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124605
Hao, N., Moysey, S. M. J., Powell, B. A., & Ntarlagiannis, D. (2015). Evaluation of surface sorption processes using spectral induced polarization and a 22Na tracer. Environmental Science and Technology, 49, 9866–9873. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01327
Hao, N., Ye, J., Zhao, L., Sun, M., You, Y., Zhang, C., Cao, J., Peng, Y., & Zhang, S. (2021b). Evaluating iron remediation with limestone using spectral induced polarization and microscopic techniques. Science of the Total Environment, 800, 149641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149641
Hao, N., You, Y., Zhan, L. T., & Bate, B. (2022). Evaluation of aqueous Cd2+ and Pb2+ removal by natural loess using spectral induced polarization and microscopic characterization. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19307-7
Heibati, B., Rodriguez-Couto, S., Al-Ghouti, M. A., Asif, M., Tyagi, I., Agarwal, S., & Gupta, V. K. (2015). Kinetics and thermodynamics of enhanced adsorption of the dye AR 18 using activated carbons prepared from walnut and poplar woods. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 208, 99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.03.057
Henderson, A. D., & Demond, A. H. (2007). Long-term performance of zero-valent iron permeable reactive barriers: A critical review. Environmental Engineering Science, 24, 401–423. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2006.0071
Hua, M., Zhang, S., Pan, B., Zhang, W., Lv, L., & Zhang, Q. (2012). Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 211–212, 317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.016
Huang, L., Liu, G., Dong, G., Wu, X., Wang, C., & Liu, Y. (2017). Reaction mechanism of zero-valent iron coupling with microbe to degrade tetracycline in permeable reactive barrier (PRB). Chemical Engineering Journal, 316, 525–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.096
Huang, Y., Ma, E., & Zhao, G. (2015). Thermal and structure analysis on reaction mechanisms during the preparation of activated carbon fibers by KOH activation from liquefied wood-based fibers. Industrial Crops and Products, 69, 447–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.03.002
Idris-Hermann, K. T., Raoul, T. T. D., Giscard, D., & Gabche, A. S. (2018). Preparation and characterization of activated carbons from bitter kola (Garcinia kola) nut shells by chemical activation method using H3PO4; KOH and ZnCl2. Chemical Science International Journal, 23, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.9734/csji/2018/43411
Izumoto, S., Huisman, J. A., Wu, Y., & Vereecken, H. (2020). Effect of solute concentration on the spectral induced polarization response of calcite precipitation. Geophysical Journal International, 220, 1187–1196. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggz515
Jovanovic, M., Arcon, I., Kovac, J., Tusar, N. N., Obradovic, B., & Rajic, N. (2016). Removal of manganese in batch and fluidized bed systems using beads of zeolite a as adsorbent. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 226, 378–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.02.026
Kaneco, S., Itoh, K., Katsumata, H., Suzuki, T., Masuyama, K., Funasaka, K., Hatano, K., & Ohta, K. (2003). Removal of natural organic polyelectrolytes by adsorption onto tobermorite. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 1448–1451. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020816v
Karadag, D., Akkaya, E., Demir, A., Saral, A., Turan, M., & Ozturk, M. (2008). Ammonium removal from municipal landfill leachate by clinoptilolite bed columns: Breakthrough modeling and error analysis. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 47, 9552–9557. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie800434e
Karadag, D., Koc, Y., Turan, M., & Ozturk, M. (2007). A comparative study of linear and non-linear regression analysis for ammonium exchange by clinoptilolite zeolite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 144, 432–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.10.055
Kirmizakis, P., Kalderis, D., Ntarlagiannis, D., & Soupios, P. (2020). Preliminary assessment on the application of biochar and spectral-induced polarization for wastewater treatment. Near Surface Geophysics, 18, 109–122. https://doi.org/10.1002/nsg.12076
Kjeldsen, P., Barlaz, M. A., Rooker, A. P., Baun, A., Ledin, A., & Christensen, T. H. (2002). Present and long-term composition of MSW landfill leachate: A review. Critical Reviews in Environment Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380290813462
Kong, X., Bi, E., Liu, F., Huang, G., & Ma, J. (2015). Laboratory column study for evaluating a multimedia permeable reactive barrier for the remediation of ammonium contaminated groundwater. Environmental Technology (united Kingdom), 36, 1433–1440. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2014.992482
Król, M., Mozgawa, W., Jastrzbski, W., & Barczyk, K. (2012). Application of IR spectra in the studies of zeolites from D4R and D6R structural groups. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 156, 181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.02.040
Kumarasinghe, U., Kawamoto, K., Saito, T., Sakamoto, Y., & Mowjood, M. I. M. (2018). Evaluation of applicability of filling materials in permeable reactive barrier (PRB) system to remediate groundwater contaminated with Cd and Pb at open solid waste dump sites. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 120, 118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.09.003
Lead, J. R., Wilkinson, K. J., Starchev, K., Canonica, S., & Buffle, J. (2000). Determination of diffusion coefficients of humic substances by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy: Role of solution conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 1365–1369. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9907616
Lin, L., Lei, Z., Wang, L., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Wan, C., Lee, D. J., & Tay, J. H. (2013). Adsorption mechanisms of high-levels of ammonium onto natural and NaCl-modified zeolites. Separation and Purification Technology, 103, 15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2012.10.005
Liu, D., Cui, Y., Zhang, T., Zhao, W., & Ji, P. (2021). Improving the flame retardancy and smoke suppression of epoxy resins by introducing of DOPO derivative functionalized ZIF-8. Polymer Degradation and Stability. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2021.109749
Liu, P., Sun, M., Chen, Z., Zhang, S., Zhang, F. S., Chen, Y., Chen, W., & Bate, B. (2023). Influencing factors on fines deposition in porous media by CFD–DEM simulation. Acta Geotechnica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-023-01870-z
Mellage, A., Zakai, G., Efrati, B., Pagel, H., & Schwartz, N. (2022). Paraquat sorption- and organic matter-induced modifications of soil spectral induced polarization (SIP) signals. Geophysical Journal International, 229, 1422–1433. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggab531
Mohan, D., Singh, K. P., & Singh, V. K. (2008). Wastewater treatment using low cost activated carbons derived from agricultural byproducts: A case study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152, 1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.079
Molenda, J., Swat, M., & Osuch-słomka, E. (2018). Effect of thermal conditions of pyrolysis process on the quality of biochar obtained from vegetable waste. Engineering and Protection of Environment, 21, 289–302. https://doi.org/10.17512/ios.2018.3.7
Moreno-Castilla, C. (2004). Adsorption of organic molecules from aqueous solutions on carbon materials. Carbon N Y, 42, 83–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2003.09.022
Moussavi, G., Talebi, S., Farrokhi, M., & Sabouti, R. M. (2011). The investigation of mechanism, kinetic and isotherm of ammonia and humic acid co-adsorption onto natural zeolite. Chemical Engineering Journal, 171, 1159–1169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.016
Musawwa, M. M., Ardiyanto, N. R. N., Lestari, A., Yusuf, A. K., & Solehudin, M. (2022). Synthesis of zeolite based material with aluminum sources from used beverage cans for hard water desalination. Walisongo Journal of Chemistry, 5, 37–44. https://doi.org/10.21580/wjc.v5i1.9172
Niu, Q., Zhang, C., & Prasad, M. (2020). A framework for pore-scale simulation of effective electrical conductivity and permittivity of porous media in the frequency range from 1 mHz to 1 GHz. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JB020515
Ntarlagiannis, D., Williams, K. H., Slater, L., & Hubbard, S. (2005). Low‐frequency electrical response to microbial induced sulfide precipitation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JG000024
Obiri-Nyarko, F., Grajales-Mesa, S. J., & Malina, G. (2014). An overview of permeable reactive barriers for in situ sustainable groundwater remediation. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.03.112
Pandya, V. B., Bhuniya, S., & Khilar, K. C. (1998). Existence of a critical particle concentration in plugging of a packed bed. AIChE Journal, 44, 978–981. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690440424
Pârvulescu, V., Anastasescu, C., & Su, B. L. (2003). Vanadium incorporated mesoporous silicates as catalysts for oxidation of alcohols and aromatics. Journal of Molecular Catalysis a: Chemical, 198, 249–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1169(02)00694-5
Pawluk, K., & Fronczyk, J. (2015). Evaluation of single and multilayered reactive zones for heavy metals removal from stormwater. Environmental Technology (united Kingdom), 36, 1576–1583. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2014.997299
Perraki, Th., Kakali, G., & Kontori, E. (2005). Characterization and pozzolanic activity of thermally treated zeolite. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 82, 109–113.
Placencia-Gómez, E., & Slater, L. D. (2016). On the pore water chemistry effect on spectral induced polarization measurements in the presence of pyrite. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 135, 474–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2015.11.001
Placencia-Gόmez, E., Robinson, J., Slater, L., & Qafoku, N. P. (2023). Spectral induced polarization monitoring of induced calcite precipitation in subsurface sediments. Geophysical Journal International, 232, 57–69. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggac318/6670786
Pradhan, S., Shaik, I., Lagraauw, R., & Bikkina, P. (2019). A semi-experimental procedure for the estimation of permeability of microfluidic pore network. MethodsX, 6, 704–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2019.03.025
Reinhart, D. R., Bolyard, S. C., & Chen, J. (2023). Fate of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in postconsumer products during waste management. Journal of Environmental Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1061/joeedu.eeeng-7060
Renou, S., Givaudan, J. G., Poulain, S., Dirassouyan, F., & Moulin, P. (2008). Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.077
Rep, M., Palomares, A. E., Eder-Mirth, G., van Ommen, J. G., Rösch, N., & Lercher, J. A. (2000). Interaction of methanol with alkali metal exchanged molecular sieves. 1. IR spectroscopic study. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 104, 8624–8630. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0001945
Revil, A., Atekwana, E., Zhang, C., Jardani, A., & Smith, S. (2012). A new model for the spectral induced polarization signature of bacterial growth in porous media. Water Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012WR011965
Rücker, C., Günther, T., & Wagner, F. M. (2017). pyGIMLi: An open-source library for modelling and inversion in geophysics. Computers & Geosciences, 109, 106–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2017.07.011
Savova, D., Petrov, N., Yardim, M. F., Ekinci, E., Budinova, T., Razvigorova, M., & Minkova, V. (2003). The influence of the texture and surface properties of carbon adsorbents obtained from biomass products on the adsorption of manganese ions from aqueous solution. Carbon N Y, 41, 1897–1903. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00179-9
Schwartz, N., & Furman, A. (2012). Spectral induced polarization signature of soil contaminated by organic pollutant: Experiment and modeling. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 117, 23. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JB009543
Schwarz, G. (1962). A theory of the low-frequency dielectric dispersion of colloidal particles in electrolyte solution. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 66, 2636–2642. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100818a067
Sheng, G., Xu, S., & Boyd, S. A. (1996). Mechanism(s) controlling sorption of neutral organic contaminants by surfactant-derived and natural organic matter. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 1553–1557.
Slater, L., & Binley, A. (2003). Evaluation of permeable reactive barrier (PRB) integrity using electrical imaging methods. Geophysics, 68, 911–921.
Slater, L., Ntarlagiannis, D., Personna, Y. R., & Hubbard, S. (2007). Pore-scale spectral induced polarization signatures associated with FeS biomineral transformations. Geophysical Research Letters, 34, 3–7. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL031840
Slater, L., Ntarlagiannis, D., & Wishart, D. B. (2006). On the relationship between induced polarization and surface area in metal-sand and clay-sand mixtures. Geophysics. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2187707
Strobel, C., Abramov, S., Huisman, J. A., Cirpka, O. A., & Mellage, A. (2023). Spectral induced polarization (SIP) of denitrification-driven microbial activity in column experiments packed with calcareous aquifer sediments. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022jg007190
Suratman, A., Pramita, N., Agasta, P.N., Purwaningsih, D.R., Kuncaka, A., Kunarti, E.S., Wibowo, A.H., 2020. The effect of zeolite addition and freeze-drying method on alginat beads for controlled release fertilizer. In AIP conference proceedings. American Institute of Physics Inc. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0005798
Tattibayeva, Z., Tursynbetov, M., Tazhibayeva, S., Kujawski, W., & Musabekov, K. (2019). Adsorption modification of the zeolite surface with chitosan. Chemical Bulletin of Kazakh National University. https://doi.org/10.15328/cb1073
Tsai, Y. L., Huang, E., Li, Y. H., Hung, H. T., Jiang, J. H., Liu, T. C., Fang, J. N., & Chen, H. F. (2021). Raman spectroscopic characteristics of zeolite group minerals. Minerals, 11, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11020167
Vistuba, J. P., Coral, L. A., Pizzolatti, B. S., Vitali, L., Nagel-Hassemer, M. E., Lapolli, F. R., & Lobo-Recio, M. Á. (2015). Adsorption behaviour of the zeolite, Controll M.F. 574® in removing iron and manganese from natural water. Desalination and Water Treatment, 55, 1523–1533. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.927333
Wang, Q., Song, X., Wei, C., Jin, P., Chen, X., Tang, Z., Li, K., Ding, X., & Fu, H. (2022). In situ remediation of Cr(VI) contaminated groundwater by ZVI-PRB and the corresponding indigenous microbial community responses: A field-scale study. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150260
Wang, S., Gong, W., Liu, X., Gao, B., & Yue, Q. (2006). Removal of fulvic acids using the surfactant modified zeolite in a fixed-bed reactor. Separation and Purification Technology, 51, 367–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.02.019
Wong, S., Ngadi, N., Inuwa, I. M., & Hassan, O. (2018). Recent advances in applications of activated carbon from biowaste for wastewater treatment: A short review. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.059
Yang, Y.-X., Chen, J.-K., Zhao, L., You, Y.-Q., Chen, Z.-J., Cao, J.-N., Liu, F., Zhang, S., Zhan, L.-T., Chen, Y.-M., & Bate, B. (2023). A kinetic-based zeolite PRB design method for remediating groundwater polluted by high NH4+ MSW leachate considering spatio-temporal concentration evolutions. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 29, 103020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103020
Ye, J., Chen, X., Chen, C., & Bate, B. (2019). Emerging sustainable technologies for remediation of soils and groundwater in a municipal solid waste landfill site: A review. Chemosphere, 227, 681–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.053
Yuxin, W., & Peruzzo, L. (2020). Effects of salinity and pH on the spectral induced polarization signals of graphite particles. Geophysical Journal International, 221, 1532–1541. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggaa087
Zazouli, M. A., Azari, A., Dehghan, S., & Malekkolae, R. S. (2016). Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto activated carbons developed from eucalyptus bark and Crataegus oxyacantha core. Water Science and Technology, 74, 2021–2035. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.287
Zhan, L., You, Y., Zhao, L., Hao, N., & Bate, B. (2022). A study on the competitive adsorption process of NH4+ and Zn2+ on activated carbon and zeolite. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04375-6
Zhang, C., Slater, L., Redden, G., Fujita, Y., Johnson, T., & Fox, D. (2012). Spectral induced polarization signatures of hydroxide adsorption and mineral precipitation in porous media. Environmental Science and Technology, 46, 4357–4364. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204404e
Zhang, X., & Bai, R. (2003). Mechanisms and kinetics of humic acid adsorption onto chitosan-coated granules. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 264, 30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00393-X
Zhang, Y., Cao, B., Yin, H., Meng, L., Jin, W., Wang, F., Xu, J., & Al-Tabbaa, A. (2022). Application of zeolites in permeable reactive barriers (PRBs) for in-situ groundwater remediation: A critical review. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136290
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Award No.: 2019YFC1805002, 2018YFC1802300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Award No.: 42177118, 51779219), and the Basic Science Center Program for Multiphase Evolution in Hypergravity of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Award No.: 51988101). Financial support from the Overseas Expertise Introduction Center for Discipline Innovation (B18047) is also acknowledged. The authors would also like to acknowledge the MOE Key Laboratory of Soft Soils and Geoenvironmental Engineering.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Award No.: 2019YFC1805002, 2018YFC1802300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Award No.: 42177118, 51779219) and the Basic Science Center Program for Multiphase Evolution in Hypergravity of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Award No.: 51988101). Financial support from the Overseas Expertise Introduction Center for Discipline Innovation (B18047) is also acknowledged
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yang, Yi-Xin: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Software, Writing–original draft Zhou, Sheng: Investigation Luo, Yuan-Yuan: Investigation Chen, Jia-Kai: Investigation Chen, Ze-Jian: Investigation Cao, Jun-Nan: Investigation Zhang, Shuang: Resources Zhan, Liang-Tong: Funding acquisition Chen, Yun-Min: Funding acquisition Bate, Bate: Supervision, Writing–review & editing, Funding acquisition
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, YX., Zhou, S., Luo, YY. et al. Monitoring the remediation of groundwater polluted by MSW landfill leachates by activated carbon and zeolite with spectral induced polarization technique. Environ Geochem Health 46, 1 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01796-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01796-1