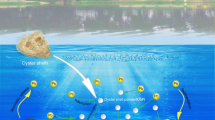
Abstract
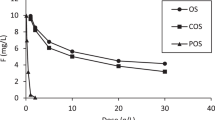
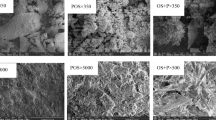
Groundwater pollution caused by lead ions has become a widespread issue worldwide due to the ever-increasing development of industrial activities. Such pollution poses significant threats to both humans and the environment. Oyster shell powder–peanut shell biochar mixture (OSP–PSB mixture) was used for lead-contaminated groundwater treatment by permeable reactive barrier (PRB) technology. Basic characteristics of materials proved that OSP–PSB mixture has good adsorption properties; OSP with particle sizes ranging from 0.85 to 1.18 mm was used in this research; according to engineering and adsorption characteristics, OSP–PSB mixture (5:1) showed excellent permeability (4.35 × 10−4 cm/s) and lead adsorption capacity(27 mg/g); long-term permeability of the OSP–PSB mixture slightly decreased over time and met the permeability requirements for PRB; the removal mechanisms of lead ions by OSP–PSB mixture include precipitation, surface complexation, ion exchange, and physical adsorption. The experiment results showed that the OSP–PSB mixture fulfills the actual project requirements of PRB.
Graphical Abstract
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agency E.P., 2000. Constructed wetlands treatment of municipal wastewaters [electronic resource]. United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Alidoust, D., Kawahigashi, M., & Yoshizawa, S. (2015). Mechanism of cadmium biosorption from aqueous solutions using calcined oyster shells. Journal of Environmental Management, 150, 103–110.
Al-Shayea, N. A. (2001). The combined effect of clay and moisture content on the behavior of remolded unsaturated soils. Engineering Geology, 62(4), 319–342.
Alvarenga, R. A. F. D., Galindro, B. M., Helpa, C. D. F., & Soares, S. R. (2012). The recycling of oyster shells: An environmental analysis using Life Cycle Assessment. Journal of Environmental Management, 106, 102–109.
ASTM D422 2007., 2007. Standard test method for particle-size analysis of soils.
Bansal, R. C., & Goyal, M. (2005). Activated carbon adsorption. CRC Press.
Bensaida, K., Maamoun, I., Eljamal, R., Falyouna, O., Sugihara, Y., & Eljamal, O. (2021). New insight for electricity amplification in microbial fuel cells (MFCs) applying magnesium hydroxide coated iron nanoparticles. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021(249), 114877.
Bohart, G. S., & Adams, E. Q. (1920). Some aspects of the behavior of charcoal with respect to chlorine. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 42(3), 523–544.
Budania, R., & Dangayach, S. (2023). A comprehensive review on permeable reactive barrier for the remediation of groundwater contamination. Journal of Environmental Management, 332(117343), 1–10.
Calero, M., Hernáinz, F., & Blázquez, G. (2009). Study of Cr (III) biosorption in a fixed-bed column. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171(1–3), 886–893.
Chao, H. P., Chang, C. C., & Nieva, A. (2014). Biosorption of heavy metals on Citrus maxima peel, passion fruit shell, and sugarcane bagasse in a fixed-bed column. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20(5), 3408–3414.
Dórea, J. G. (2019). Environmental exposure to low-level lead (Pb) co-occurring with other neurotoxicants in early life and neurodevelopment of children. Environmental Research, 177(2), 108641.
Eljamal, O., Jinno, K., & Hosokawa, T. (2008). Modeling of solute transport with bioremediation processes using sawdust as a matrix. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 195(1), 115–127.
Eljamal, O., Jinno, K., & Hosokawa, T. (2009). Modeling of solute transport and biological sulfate reduction using low cost electron donor. Environmental Geology, 56(8), 1605–1613.
Eljamal, O., Maamoun, I., Alkhudhayri, S., Eljamal, R., Falyouna, O., Tanaka, K., Kozai, N., & Sugihara, Y. (2022a). Insights into boron removal from water using Mg-Al-LDH: Reaction parameters optimization & 3D-RSM modeling. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 46(102608), 1–13.
Eljamal, R., Maamoun, I., Bensaida, K., Yilmaz, G., Sugihara, Y., & Eljamal, O. (2022b). A novel method to improve methane generation from waste sludge using iron nanoparticles coated with magnesium hydroxide. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 158(112192), 1–13.
Eren, Z., & Acar, F. N. (2006). Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 from an aqueous solution: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Desalination, 194(1–3), 1–10.
Falyouna, O., Idham, M. F., Maamoun, I., Bensaida, K., Ashik, U. P. M., Sugihara, Y., & Eljamal, O. (2022a). Promotion of ciprofloxacin adsorption from contaminated solutions by oxalate modified nanoscale zerovalent iron particles. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 359(119323), 1–20.
Falyouna, O., Bensaida, K., Maamoun, I., Ashik, U. P. M., Tahara, A., Tanaka, K., Aoyagi, N., Sugihara, Y., & Eljamal, O. (2022b). Synthesis of hybrid magnesium hydroxide/magnesium oxide nanorods [Mg (OH) 2/MgO] for prompt and efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 342(130949), 1–15.
Feng, Q., Lin, Q., Gong, F., Sugita, S., & Shoya, M. (2004). Adsorption of lead and mercury by rice husk ash. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 278(1), 1–8.
Field, J. L., Keske, C. M. H., Birch, G. L., Defoort, M. W., & Cotrufo, M. F. (2013). Distributed biochar and bioenergy coproduction: A regionally specific case study of environmental benefits and economic impacts. Gcb Bioenergy, 5(2), 177–191.
GB/T 50123-2019, 2019. Standard for geotechnical testing method. Beijing: China Planning Press.
Hsu, T. C. (2009). Experimental assessment of adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution by oyster shell powder. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171(1–3), 995–1000.
Inyang, M., Gao, B., & Ding, W. (2011). Enhanced lead sorption by biochar derived from anaerobically digested sugarcane bagasse. Separation Science and Technology, 46(12), 1950–1956.
Jayasundara, R. B. C. D., Udayagee, K. P. P., Karunarathna, A. K., Manage, P. M., Nugara, R. N., & Abhayapala, K. M. R. D. (2023). Permeable reactive barriers as an in situ groundwater remediation technique for open solid waste dumpsites: A review and prospect. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 234(1), 50.
Jeon, D. Y., Lee, K. S., & Shin, H. M. (2006). Adsorption characteristics of heavy metals for waste sludge and oyster shell. Journal of Environmental Science International, 15(11), 1053–1059.
Jeong, S. H., Lim, J. E., & Lee, S. S. (2013). Evaluation on remediation efficiency on acid-spilled soil using oyster shell and biochar. Journal of Agricultural, Life and Environmental Sciences, 25(2), 1–10.
Kenney, T. C., Lau, D., & Ofoegbu, G. I. (1984). Permeability of compacted granular materials. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 21(4), 726–729.
Kim, W. K., Shim, T., & Kim, Y. S. (2013). Characterization of cadmium removal from aqueous solution by biochar produced from a giant Miscanthus at different pyrolytic temperatures[J]. Bioresource Technology, 138, 266–270.
Kobya, M., Demirbas, E., & Senturk, E. (2005). Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from apricot stone. Bioresource Technology, 96(13), 1518–1521.
Kuh, S. E., & Kim, D. S. (2000). Removal characteristics of cadmium ion by waste egg shell. Environmental Technology, 21(8), 883–890.
Laird, D., Fleming, P., Wang, B., Horton, R., & Karlen, D. (2010). Biochar impact on nutrient leaching from a Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma, 158(3–4), 436–442.
Lim, A. P., & Aris, A. Z. (2014). Continuous fixed-bed column study and adsorption modeling: Removal of cadmium (II) and lead (II) ions in aqueous solution by dead calcareous skeletons. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 87, 50–61.
Liu, Z., & Zhang, F. S. (2009). Removal of lead from water using biochars prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167(1–3), 933–939.
Maamoun, I., Falyouna, O., Eljamal, R., Bensaida, K., Tanaka, K., Tosco, T., Sugihara, Y., & Eljamal, O. (2022a). Multi-functional magnesium hydroxide coating for iron nanoparticles towards prolonged reactivity in Cr (VI) removal from aqueous solutions. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3), 107431.
Maamoun, I., Bensaida, K., Eljamal, R., Falyouna, O., Tanaka, K., Tosco, T., Sugihara, Y., & Eljamal, O. (2022b). Rapid and efficient chromium (VI) removal from aqueous solutions using nickel hydroxide nanoplates (nNiHs). Journal of Molecular Liquids, 358(119216), 1–17.
Mao Y., Lin F., Fang J., Fang J., Li J., Du M., 2019. Bivalve production in China. Goods and services of marine bivalves, 51–72.
McLaren, A. C., McLaren, S. G., McLemore, R., & Vernon, B. L. (2007). Particle size of fillers affects permeability of polymethylmethacrylate. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 2007(461), 64–67.
Mohan, D., Rajput, S., Singh, V. K., Steele, P., & Pittman, C. (2011). Modeling and evaluation of chromium remediation from water using low cost bio-char, a green adsorbent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 188(1–3), 319–333.
Obiri, N. F., Grajales, M. S. J., & Malina, G. (2014). An overview of permeable reactive barriers for in situ sustainable groundwater remediation. Chemosphere, 111, 243–259.
Ok, Y. S., Lim, J. E., & Moon, D. H. (2011). Stabilization of Pb and Cd contaminated soils and soil quality improvements using waste oyster shells. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(1), 83–91.
Osama, E., Junya, O., & Kazuaki, H. (2012). Removal of phosphorus from water using marble dust as sorbent material. Journal of Environmental Protection, 3(8), 709–714.
Otero, M., Rozada, F., Calvo, L. F., & Moran, A. (2003). Kinetic and equilibrium modelling of the methylene blue removal from solution by adsorbent materials produced from sewage sludges. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 15(1), 59–68.
Powell, R. M., Blowes, D. W., Gillham, R. W., Schultz, D., Sivavec, T., Puls, R. W., Vogan, J. L., Powell, P. D., & Landis, R. (1998). Permeable reactive barrier technologies for contaminant remediation. US EPA, 600, 1–94.
Pratiwi, E. P. A., & Shinogi, Y. (2016). Rice husk biochar application to paddy soil and its effects on soil physical properties, plant growth, and methane emission. Paddy and Water Environment, 14(4), 521–532.
Putro, J. N., Santoso, S. P., & Ismadji, S. (2017). Investigation of heavy metal adsorption in binary system by nanocrystalline cellulose–bentonite nanocomposite: Improvement on extended Langmuir isotherm model[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 246, 166–177.
Qiao, J., Zhu, Y., Jia, X., Shao, M., Niu, X., & Liu, J. (2019). Distributions of arsenic and other heavy metals, and health risk assessments for groundwater in the Guanzhong Plain region of China. Environmental Research, 181(7), 108957.
Rashid, A., Aziemah, N., & Abustan, I. (2015). Effect of particle size distribution to remove contaminants in groundwater at Dengkil, Selangor. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 773, 1158–1162.
Roehl, K. E., Meggyes, T., Simon, F. G., & Stewart, D. I. (2005). Long-term performance of permeable reactive barriers (pp. 1–19). Gulf Professional Publishing.
Shim, Y. S., Kim, Y. K., Kong, S. H., Rhee, S. W., & Lee, W. K. (2003). The adsorption characteristics of heavy metals by various particle sizes of MSWI bottom ash. Waste Management, 23(9), 851–857.
Shin, W. S., Kang, K., & Kim, Y. K. (2014). Adsorption characteristics of multi-metal ions by red mud, zeolite, limestone, and oyster shell. Environmental Engineering Research, 19(1), 15–22.
Smail, F. A., & Aris, A. Z. (2013). Experimental determination of Cd2+ adsorption mechanism on low-cost biological waste. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 7(3), 356–364.
Song, T., & Gao, Y. J. (2013). 2013, Removal of Heavy Metals from Synthetic Landfill Leachate Using Oyster Shells Adsorbent. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 25(15), 8533–8536.
Song, J., Zou, W., Bian, Y., Su, F., & Han, R. (2011). Adsorption characteristics of methylene blue by peanut husk in batch and column modes. Desalination, 265(1–3), 119–125.
Tudor, H. E. A., Gryte, C. C., & Harris, C. C. (2006). Seashells: De-toxifying agents for metal-contaminated waters. Environmental Pollution, 173, 209–242.
Vilvanathan, S., & Shanthakumar, S. (2017). Column adsorption studies on nickel and cobalt removal from aqueous solution using native and biochar form of Tectona grandis. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 36(4), 1030–1038.
Wang, F., Pan, Y., & Cai, P. (2017). Single and binary adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using sugarcane cellulose-based adsorbent[J]. Bioresource Technology, 241, 482–490.
Wilson, S. D. (1964). Suggested Method of Test for Moisture-Density Relations of Soils Using Harvard Miniature Compaction Apparatus. Procedures for Testing Soils, 1964, 160–162.
Wong, Y. C., Szeto, Y. S., & Cheung, W. H. (2008). Effect of temperature, particle size and percentage deacetylation on the adsorption of acid dyes on chitosan. Adsorption, 14(1), 11–20.
Wu, Q., Chen, J., & Clark, M. (2014). Adsorption of copper to different biogenic oyster shell structures. Applied Surface Science, 311, 264–272.
Wu, H., Gao, X., Wu, M., Zhu, Y., & Ye, S. (2020). The efficiency and risk to groundwater of constructed wetland system for domestic sewage treatment - a case study in Xiantao. China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 277(123384), 1–11.
Xie, T., Dang, Z., Zhang, J., Zhang, Q., & Lu, G. N. (2021). Decontamination of dense nonaqueous-phase liquids in groundwater using pump-and-treat and in situ chemical oxidation processes: A field test. RSC Advances, 11(7), 4237–4246.
Yoon, Y. H., & Nelson, J. H. (1984). Application of gas adsorption kinetics-II. A theoretical model for respirator cartridge service life and its practical applications. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 45(8), 517–524.
Zhang, T., Tu, Z., & Lu, G. (2017). Removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage using chicken eggshells in column mode. Journal of Environmental Management, 188, 1–8.
Zhong, G., Liu, Y., & Tang, Y. (2020). Oyster shell powder for Pb(II) immobilization in both aquatic and sediment environments. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(5), 1891–1902.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51978438) (No.52281340410); Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi, China (No.202103021223122); School Foundation of Taiyuan University of Technology (No.2022QN044).
Funding
This research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51978438) (No.52281340410); Natural Science Foundation for Young Scientists of Shanxi Province, China (No.202103021223122); Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China (2023-060); School Foundation of Taiyuan University of Technology (No.2022QN044). This research was supported by Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Geomechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grant NO.SKLGME022012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. XL did experiments, image rendering, data analysis, writing—original draft; XD was involved in supervision, validation, and review; SC done sample analyses, data interpretation and presentation; XX and JL performed methodology and sample collection; HP reviewed and edited the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Dong, X., Chang, S. et al. Remediation of lead-contaminated groundwater by oyster shell powder–peanut shell biochar mixture. Environ Geochem Health 45, 9599–9619 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01756-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01756-9