Abstract
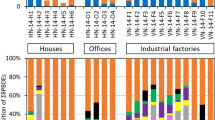
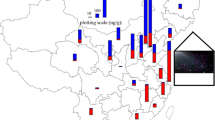
The levels and distributions of hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers (HBCDs) (including α, β, and γ-HBCD) and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) were investigated in indoor dust from bedrooms and offices. HBCDs diastereoisomers were the most abundant compounds in the dust samples, and the concentrations of ∑HBCDs in the bedrooms and offices ranged from 10.6 to 290.1 ng/g and 17.6 to 1521.9 ng/g, respectively. The concentrations of target compounds in the offices were generally higher than those in the bedrooms, probably due to the presence of more electrical equipment in the offices. In this study, highest levels of target compounds were all found in the electronics. In the bedrooms, the highest mean level of ∑HBCDs was found in air conditioning filter dust (118.57 ng/g), while the personal computer table surface dust showed the peak mean concentrations of ∑HBCDs (290.74 ng/g) and TBBPA (539.69 ng/g) in the offices. Interestingly, a significantly positive correlation was observed between the concentrations of ∑HBCDs in windowsills and beddings dust in the bedrooms, suggesting beddings was one of the crucial sources of ∑HBCDs in the bedrooms. The high dust ingestion values of ∑HBCDs and TBBPA were 0.046 and 0.086 ng/kg bw/day for adults, while 0.811 and 0.04 ng/kg bw/day for toddlers, respectively. The high dermal exposure values of ∑HBCDs were 0.026 and 0.226 ng/kg bw/day for adults and toddlers, respectively. Except for dust ingestion, other human exposure pathways (such as the dermal contact with beddings and furniture) should be paid attention.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abafe, O. A., & Martincigh, B. S. (2016). Determination and human exposure assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and tetrabromobisphenol A in indoor dust in South Africa. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 23, 7038–7049.
Abdallah, M. A., & Harrad, S. (2018). Dermal contact with furniture fabrics is a significant pathway of human exposure to brominated flame retardants. Environment International, 118, 26–33.
Abdallah, M.A.-E., Harrad, S., & Covaci, A. (2008a). Hexabromocyclododecanes and tetrabromobisphenol-A in indoor air and dust in Birmingham, UK: Implications for human exposure. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 6855–6861.
Abdallah, M.A.-E., Harrad, S., Ibarra, C., Diamond, M., Melymuk, L., Robson, M., & Covaci, A. (2008b). Hexabromocyclododecanes in indoor dust from Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 459–464.
Barghi, M., Shin, E.-S., Kim, J.-C., Choi, S.-D., & Chang, Y.-S. (2017). Human exposure to HBCD and TBBPA via indoor dust in Korea: Estimation of external exposure and body burden. Science of the Total Environment, 593–594, 779–786.
Besis, A., Christia, C., Poma, G., Covaci, A., & Samara, C. (2017). Legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in interior car dust—Implications for human exposure. Environmental Pollution, 230, 871–881.
Cao, X., Lu, Y., Zhang, Y., Khan, K., Wang, C., & Baninla, Y. (2018). An overview of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDs) in environmental media with focus on their potential risk and management in China. Environmental Pollution, 236, 283–295.
Carignan, C. C., Abdallah, M.A.-E., Wu, N., Heiger-Bernays, W., McClean, M. D., Harrad, S., & Webster, T. F. (2012). Predictors of Tetrabromobisphenol-A (TBBP-A) and hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCD) in milk from Boston mothers. Environmental Science and Technology, 46, 12146–12153.
Chakraborty, P., Zhang, G., Li, J., Sivakumar, A., & Jones, K. C. (2015). Occurrence and sources of selected organochlorine pesticides in the soil of seven major Indian cities: Assessment of air–soil exchange. Environmental Pollution, 204, 74–80.
Davis, J. W., Gonsior, S. J., Markham, D. A., Friederich, U., Hunziker, R. W., & Ariano, J. M. (2006). Biodegradation and product identification of [14C]hexabromocyclododecane in wastewater sludge and freshwater aquatic sediment. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 5395–5401.
Feiteiro, J., Mariana, M., & Cairrao, E. (2021). Health toxicity effects of brominated flame retardants: From environmental to human exposure. Environmental Pollution, 285, 117475.
Fromme, H., Hilger, B., Kopp, E., Miserok, M., & Volkel, W. (2014). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) and “novel” brominated flame retardants in house dust in Germany. Environment International, 64, 61–68.
Gallen, C., Banks, A., Brandsma, S., Baduel, C., Thai, P., Eaglesham, G., Heffernan, A., Leonards, P., Bainton, P., & Mueller, J. F. (2014). Towards development of a rapid and effective non-destructive testing strategy to identify brominated flame retardants in the plastics of consumer products. Science of the Total Environment, 491–492, 255–265.
Geens, T., Roosens, L., Neels, H., & Covaci, A. (2009). Assessment of human exposure to bisphenol-A, triclosan and tetrabromobisphenol-A through indoor dust intake in Belgium. Chemosphere, 76, 755–760.
Germer, S., Piersma, A. H., van der Ven, L., Kamyschnikow, A., Fery, Y., Schmitz, H. J., & Schrenk, D. (2006). Subacute effects of the brominated flame retardants hexabromocyclododecane and tetrabromobisphenol A on hepatic cytochrome P450 levels in rats. Toxicology, 218, 229–236.
Goscinny, S., Vandevijvere, S., Maleki, M., Van Overmeire, I., Windal, I., Hanot, V., & Van Loco, J. (2011). Dietary intake of hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers (α-, β-, and γ-HBCD) in the Belgian adult population. Chemosphere, 84(3), 279–288.
He, R., Li, Y., Xiang, P., Li, C., Zhou, C., Zhang, S., Cui, X., & Ma, L. Q. (2016). Organophosphorus flame retardants and phthalate esters in indoor dust from different microenvironments: Bioaccessibility and risk assessment. Chemosphere, 150, 528–535.
Heeb, N. V., Schweizer, W. B., Mattrel, P., Haag, R., Kohler, M., Schmid, P., Zennegg, M., & Wolfensberger, M. (2008). Regio- and stereoselective isomerization of hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs): Kinetics and mechanism of β-HBCD racemization. Chemosphere, 71, 1547–1556.
Jarosiewicz, M., Duchnowicz, P., Jarosiewicz, P., Huras, B., & Bukowska, B. (2021). An in vitro comparative study of the effects of tetrabromobisphenol a and tetrabromobisphenol s on human erythrocyte membranes-changes in atp level, perturbations in membrane fluidity, alterations in conformational state and damage to proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(17), 9443.
Jeon, J. W., Kim, C. S., Kim, L., Lee, S. E., Kim, H. J., Lee, C. H., & Choi, S. D. (2019). Distribution and diastereoisomeric profiles of hexabromocyclododecanes in air, water, soil, and sediment samples in South Korea: Application of an optimized analytical method. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 181, 321–329.
Kajiwara, N., Noma, Y., & Takigami, H. (2011). Brominated and organophosphate flame retardants in selected consumer products on the Japanese market in 2008. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 1250–1259.
Kajiwara, N., Sueoka, M., Ohiwa, T., & Takigami, H. (2009). Determination of flame-retardant hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers in textiles. Chemosphere, 74, 1485–1489.
Lee, J. G., Jeong, Y., Kim, D., Kang, G. J., & Kang, Y. (2020). Assessment of tetrabromobisphenol and hexabromocyclododecanes exposure and risk characterization using occurrence data in foods. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 137, 111121.
Li, H., Zhang, Z., Sun, Y., Wang, W., Xie, J., Xie, C., Hu, Y., Gao, Y., Xu, X., Luo, X., & Mai, B. (2021). Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecanes in sediments and biota from two typical mangrove wetlands of South China: Distribution, bioaccumulation and biomagnification. Science of the Total Environment, 750, 141695.
Liu, K., Li, J., Yan, S., Zhang, W., Li, Y., & Han, D. (2016). A review of status of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in China. Chemosphere, 148, 8–20.
Liu, X., Cao, Z., Yu, G., Wu, M., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, B., & Huang, J. (2018). Estimation of exposure to organic flame retardants via hand wipe, surface wipe, and dust: Comparability of different assessment strategies. Environmental Science and Technology, 52, 9946–9953.
Lu, J.-F., He, M.-J., Yang, Z.-H., & Wei, S.-Q. (2018). Occurrence of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) and hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) in soil and road dust in Chongqing, western China, with emphasis on diastereoisomer profiles, particle size distribution, and human exposure. Environmental Pollution, 242, 219–228.
Newton, S., Sellstrom, U., & de Wit, C. A. (2015). Emerging flame retardants, PBDEs, and HBCDDs in indoor and outdoor media in Stockholm, Sweden. Environmental Science and Technology, 49, 2912–2920.
Ni, H.-G., & Zeng, H. (2013). HBCD and TBBPA in particulate phase of indoor air in Shenzhen, China. Science of the Total Environment, 458, 15–19.
Nostbakken, O. J., Duinker, A., Rasinger, J. D., Nilsen, B. M., Sanden, M., Frantzen, S., Hove, H. T., Lundebye, A. K., Berntssen, M. H. G., Hannisdal, R., Madsen, L., & Maage, A. (2018). Factors influencing risk assessments of brominated flame-retardants; evidence based on seafood from the North East Atlantic Ocean. Environment International, 119, 544–557.
Pawar, G., Abdallah, M. A., de Saa, E. V., & Harrad, S. (2017). Dermal bioaccessibility of flame retardants from indoor dust and the influence of topically applied cosmetics. Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology, 27, 100–105.
Qian, Z., Xu, Y., Zheng, C., Zhang, A., & Sun, J. (2019). Enhanced emissions of brominated flame retardants from indoor sources by direct contact with dust. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 170.
Ronisz, D., Finne, E. F., Karlsson, H., & Forlin, L. (2004). Effects of the brominated flame retardants hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD), and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA), on hepatic enzymes and other biomarkers in juvenile rainbow trout and feral eelpout. Aquatic Toxicology, 69, 229–245.
Roosens, L., Abdallah, M. A., Harrad, S., Neels, H., & Covaci, A. (2009). Exposure to hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) via dust ingestion, but not diet, correlates with concentrations in human serum: Preliminary results. Environmental Health Perspectives, 117, 1707–1712.
Sahlstrom, L. M., Sellstrom, U., de Wit, C. A., Lignell, S., & Darnerud, P. O. (2015). Estimated intakes of brominated flame retardants via diet and dust compared to internal concentrations in a Swedish mother-toddler cohort. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 218, 422–432.
Schecter, A., Szabo, D. T., Miller, J., Gent, T. L., Malik-Bass, N., Petersen, M., Paepke, O., Colacino, J. A., Hynan, L. S., Harris, T. R., Malla, S., & Birnbaum, L. S. (2012). Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) stereoisomers in U.S. food from Dallas, Texas. Environmental Health Perspectives, 120, 1260–1264.
Shi, Y., Gao, L., Li, W., Wang, Y., Liu, J., & Cai, Y. (2016). Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variation of organophosphate flame retardants and plasticizers in urban surface water in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 209, 1–10.
Shi, Z., Zhang, L., Zhao, Y., Sun, Z., Zhou, X., Li, J., & Wu, Y. (2017). Dietary exposure assessment of Chinese population to tetrabromobisphenol-A, hexabromocyclododecane and decabrominated diphenyl ether: Results of the 5th Chinese total diet study. Environmental Pollution, 229, 539–547.
Sun, J., Chen, Q., Han, Y., Zhou, H., & Zhang, A. (2018a). Emissions of selected brominated flame retardants from consumer materials: The effects of content, temperature, and timescale. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 25, 24201–24209.
Sun, R., Luo, X., Zheng, X., Cao, K., Peng, P., Li, Q. X., & Mai, B. (2018b). Hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) in fish: Evidence of recent HBCD input into the coastal environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 126, 357–362.
Sunday, O. E., Bin, H., Guanghua, M., Yao, C., Zhengjia, Z., Xian, Q., Xiangyang, W., & Weiwei, F. (2022). Review of the environmental occurrence, analytical techniques, degradation and toxicity of TBBPA and its derivatives. Environmental Research, 206, 112594.
Tang, B., Christia, C., Malarvannan, G., Liu, Y. E., Luo, X. J., Covaci, A., Mai, B. X., & Poma, G. (2020). Legacy and emerging organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in indoor microenvironments from Guangzhou South China. Environmental International, 143, 105972.
Tian, C., Liu, L., Ma, J., Tang, J., & Li, Y.-F. (2011). Modeling redistribution of α-HCH in Chinese soil induced by environment factors. Environmental Pollution, 159, 2961–2967.
Waiyarat, S., Boontanon, S. K., Boontanon, N., Fujii, S., Harrad, S., Drage, D. S., & Abdallah, M. A. (2022). Exposure, risk and predictors of hexabromocyclododecane and tetrabromobisphenol-A in house dust from urban, rural and e-waste dismantling sites in Thailand. Chemosphere, 302, 134730.
Wang, J., Wang, Y., Shi, Z., Zhou, X., & Sun, Z. (2018a). Legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in indoor dust from Beijing, China: Occurrence, human exposure assessment and evidence for PBDEs replacement. Science of the Total Environment, 618, 48–59.
Wang, W., Abualnaja, K. O., Asimakopoulos, A. G., Covaci, A., Gevao, B., Johnson-Restrepo, B., Kumosani, T. A., Malarvannan, G., Minh, T. B., Moon, H.-B., Nakata, H., Sinha, R. K., & Kannan, K. (2015). A comparative assessment of human exposure to tetrabromobisphenol A and eight bisphenols including bisphenol A via indoor dust ingestion in twelve countries. Environment International, 83, 183–191.
Wang, X., Hales, B. F., & Robaire, B. (2021). Effects of flame retardants on ovarian function. Reproductive Toxicology, 102, 10–23.
Wang, X., Yuan, X., Yang, S., & Zhao, Y. (2018b). Concentrations, distributions, and risk assessment of HBCD in sediment in the Weihe river basin in Northwest China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 2340.
Xu, Y., Li, J., Zheng, Q., Pan, S., Luo, C., Zhu, H., Nizzetto, L., & Zhang, G. (2015). Polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) in Chinese forest soil: Will combustion become a major source? Environmental Pollution, 204, 124–132.
Yamada-Okabe, T., Sakai, H., Kashima, Y., & Yamada-Okabe, H. (2005). Modulation at a cellular level of the thyroid hormone receptor-mediated gene expression by 1, 2, 5, 6, 9, 10-hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD), 4,4’-diiodobiphenyl (DIB), and nitrofen (NIP). Toxicology Letters, 155, 127–133.
Zhang, Y., Lu, Y., Wang, P., & Shi, Y. (2018). Biomagnification of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) in a coastal ecosystem near a large producer in China: Human exposure implication through food web transfer. Science of the Total Environment, 624, 1213–1220.
Zheng, Q., Mo, K., Lou, Y., Ru, S., Wang, J., Zheng, X., & Xie, Q. (2023). Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecanes from interior and surface dust of personal computers: Implications for sources and human exposure. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30, 44316–44324.
Zheng, Q., Nizzetto, L., Li, J., Mulder, M. D., Sáňka, O., Lammel, G., Bing, H., Liu, X., Jiang, Y., Luo, C., & Zhang, G. (2015a). Spatial distribution of old and emerging flame retardants in Chinese forest soils: Sources, trends and processes. Environmental Science and Technology, 49, 2904–2911.
Zheng, X., Qiao, L., Covaci, A., Sun, R., Guo, H., Zheng, J., Luo, X., Xie, Q., & Mai, B. (2017a). Brominated and phosphate flame retardants (FRs) in indoor dust from different microenvironments: Implications for human exposure via dust ingestion and dermal contact. Chemosphere, 184, 185–191.
Zheng, X., Sun, R., Qiao, L., Guo, H., Zheng, J., & Mai, B. (2017b). Flame retardants on the surface of phones and personal computers. Science of the Total Environment, 609, 541–545.
Zheng, X., Xu, F., Chen, K., Zeng, Y., Luo, X., Chen, S., Mai, B., & Covaci, A. (2015b). Flame retardants and organochlorines in indoor dust from several e-waste recycling sites in South China: Composition variations and implications for human exposure. Environment International, 78, 1–7.
Zhou, H., Yin, N., & Faiola, F. (2020). Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA): A controversial environmental pollutant. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 97, 54–66.
Acknowledgements
This work was finally supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41603086), Guangdong Science and Technology Program (2021B1212040008, Open Fund No. 20211001), and Basic and Applied Basic Research Project of Guangzhou (202201010685).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jing Wang: Validation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing. Yueshang Lou: Methodology, Formal analysis. Kexin Mo: Methodology, Formal analysis. Xiaobo Zheng: Sample collection, Formal analysis, Writing - review & editing. Qian Zheng: Conceptualization, Writing - review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no known competitive financial interests or personal relationships, which may affect the work reported in this article. All authors were directly involved in the execution and/or analysis of this study. The contents of this manuscript have not been previously copyrighted or published. We declare that we have no commercial or affiliated interests that represent a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Lou, Y., Mo, K. et al. Occurrence of hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) and tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in indoor dust from different microenvironments: levels, profiles, and human exposure. Environ Geochem Health 45, 6043–6052 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01620-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01620-w