Abstract
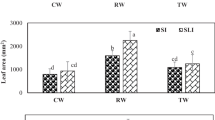
Water deficiency, especially in the arid and semi-arid areas, necessitates the proper water use and recycling. The objective was to investigate the effects of deficit irrigation as well as treated wastewater on the biochemical properties of Rosmarinus officinalis L., grown in the arid area of Iranshahr, Iran. A split-split plot design on the basis of a complete randomized block design with three replicates was conducted in 2017. Irrigation water treatments of (I1 = 100% of field capacity, FC), 75% of FC (I2), and 50% of FC (I3) as main plots, reduced (S1), and partial irrigation (S2), as sub-plots, and well water (Q1), treated wastewater (Q2), and the combination of Q1 and Q2 (Q3, 50% + 50%), as sub-sub plots, were tested. Plant biochemical properties including proline (Pr), soluble sugars (SS), and essential oil volume (V) and yield (Y) as well as water use efficiency (WUE) were determined. The I2, treatment, compared with I1, increased Pr, SS, V, Y and WUE by 34.4, 31.9, 52.6, 34.3, and 48.1%, respectively. The S2 treatment also increased plant biochemical properties more than 45% related to S1, and Q2 significantly enhanced the measured parameters compared with Q1 and Q3. Treated wastewater improved the essential oil yield of the plant in water deficit conditions. Accordingly, under deficit water conditions, treatment I2S2, and in the case of unfavorable water sources and deficit water conditions, treatment I2Q2 are recommendable to alleviate water stress and improve the biochemical properties of Rosmarinus officinalis L. in the arid areas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasnia, A., Yousefi, N., Mahvi, A. H., Nabizadeh, R., Radfard, M., Yousefi, M., & Alimohammadi, M. (2019). Evaluation of groundwater quality using water quality index and its suitability for assessing water for drinking and irrigation purposes: Case study of Sistan and Baluchistan province (Iran). Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 25, 988–1005.
Albergaria, E. T., Oliveira, A. F. M., & Albuquerque, U. P. (2020). The effect of water deficit stress on the composition of phenolic compounds in medicinal plants. South African Journal of Botany, 131, 12–17.
Alhaithloul, H. A., Soliman, M. H., Ameta, K. L., El-Esawi, M. A., & Elkelish, A. (2020). Changes in ecophysiology, osmolytes, and secondary metabolites of the medicinal plants of Mentha piperita and Catharanthus roseus subjected to drought and heat stress. Biomolecules, 10, 43.
Bagheri, M., Javanmard, H. R., & Naderi, M. R. (2021). Soil cadmium and lead affecting biochemical properties of Matricaria chamomilla L. at different growth stages in the greenhouse and field. BioMetals, 34, 881–893.
Bakhshian, M., Naderi, M. R., Javanmard, H. R., & Bahreininejad, B. (2022). The growth of summer savory (Satureja hortensis) affected by fertilization and plant growth regulators in temperature stress. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 43, 102371.
Balkhair, K., El-Nakhlawi, F., Ismail, S., & Al-Solimani, S. (2013). Treated wastewater use and its effect on water conservation, vegetative yeild, yield components and water use efficiency of some vegetable crops grown under two different irrigation systems in western region, Saudi Arabia. European Scientific Journal, 9(21), 24.
Bates, L. S., Waldren, R. P., & Teare, I. D. (1973). Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant and Soil, 39, 205–207.
Elansary, H. O., El-Ansary, D. O., & Al-Mana, F. A. (2019). 5-Aminolevulinic acid and soil fertility enhance the resistance of rosemary to Alternaria dauci and Rhizoctonia solani and modulate plant biochemistry. Plants, 8(12), 585.
Elansary, H., Mahmoud, E., El-Ansary, D., & Mattar, M. (2020). Effects of water stress and modern biostimulants on growth and quality characteristics of mint. Agronomy, 10, 6.
Farhadkhani, M., Nikaeen, M., Yadegarfar, G., Hatamzadeh, M., Pourmohammadbagher, H., Sahbaei, Z., & Rahmani, H. R. (2018). Effects of irrigation with secondary treated wastewater on physicochemical and microbial properties of soil and produce safety in a semi-arid area. Water Research, 144, 356–364.
Ghahremani, A., Pirbalouti, A. G., Mozafari, H., Habibi, D., & Sani, B. (2020). Phytochemical and morpho-physiological traits of mullein as a new medicinal crop under different planting pattern and soil moisture conditions. Industrial Crops and Products, 145, 111976.
Gomez, L., Rubio, E., & Auge, M. (2002). A new procedure for extraction and measurement of soluble sugars in ligneous plants. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 82, 360–369.
Hassan, F. A. S., Bazaid, S., & Ali, E. F. (2013). Effect of deficit irrigation on growth, yield and volatile oil content on Rosmarinus officinalis. L. plant. Journal of Medicinal Plant Studies, 1, 12–21.
Kamali, S., & Mehraban, A. (2020). Effects of Nitroxin and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the agro-physiological traits and grain yield of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) under drought stress conditions. PLoS ONE, 15, e0243824.
Kazemi, E., Ganjali, H. R., Mehraban, A., & Ghasemi, A. (2022). Yield and biochemical properties of grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) affected by nano-fertilizer under field drought stress. Cereal Research Communications, 50, 397–405.
Khalafi, A., Mohsenifar, K., Gholami, A., & Barzegari, M. (2021). Corn (Zea mays L.) Growth, Yield and Nutritional Properties Affected by Fertilization Methods and Micronutrient Use. International Journal of Plant Production, 15, 589–597.
Khorasaninejad, S., Mousavi, A., Soltanloo, H., Hemmati, K., & Khalighi, A. (2011). The effect of drought stress on growth parameters, essential oil yield and constituent of Peppermint (Mentha piperita L.). Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 5, 5360–5365.
Miransari, M., Adham, S., Miransari, M., & Miransari, A. (2022). The physicochemical approaches of altering growth and biochemical properties of medicinal plants in saline soils. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 106, 1895–19041.
Miransari, M., Bahrami, H. A., Rejali, F., & Malakouti, M. J. (2008). Using arbuscular mycorrhiza to alleviate the stress of soil compaction on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40, 1197–1206.
Miransari, M., Mahdavi, S., & Smith, D. (2021). The biological approaches of altering the growth and biochemical properties of medicinal plants under salinity stress. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 105, 7201–7213.
Miransari, M., & Smith, D. L. (2014). Plant hormones and seed germination. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 99, 110–121.
Miransari, M., & Smith, D. (2019). Sustainable wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) production in saline fields: A review. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 39, 999–1014.
Mola Ali Abasiyan, S., Nasiri Sour, A., Mokhtari, A., Dashbolaghi, F., & Sabzi, M. (2022). Preparation of chitosan/sodium alginate/nano cellulose composite for the efficient removal of cadmium (II) cations from wastewater and soil systems. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 44, 1259–1275.
Peña-Guerrero, M. D., Nauditt, A., Muñoz-Robles, C., Ribbe, L., & Meza, F. (2020). Drought impacts on water quality and potential implications for agricultural production in the Maipo River Basin, Central Chile. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 65, 1005–1021.
Rigi Karvandri, A., Mehraban, A., Ganjali, H. R., Miri, K. H., & Mobser, H. R. (2020a). Effect of quantity and quality of irrigation on quantitative traits of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Iranian Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 14, 402–413. Abstract in English.
Rigi Karvandri, A., Mehraban, A., Ganjali, H. R., Miri, K. H., & Mobser, H. R. (2020b). Evaluation of growth traits of Rosmarinus Officinalis L. under deficit irrigation. Journal of Water and Soil Science (abstract in English), 4, 329–339.
Rodrigues, J., Inzé, D., Nelissen, H., & Saibo, N. J. (2019). Source–sink regulation in crops under water deficit. Trends in Plant Science, 24, 652–663.
Selmar, D., & Kleinwächter, M. (2013). Stress enhances the synthesis of secondary plant products: The impact of stress-related over-reduction on the accumulation of natural products. Plant and Cell Physiology, 54, 817–826.
Shokuhifar, Y., Mohammadi Ghahsareh, A., Shahbazi, K., Tehrani, M.M., Besharati, H. (2021). Biochar and wheat straw affecting soil chemistry and microbial biomass carbon countrywide. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery (in press).
Walkley, A., & Black, I. A. (1934). An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37, 29–38.
Wang, C., Shu, L., Zhou, S., Yu, H., & Zhu, P. (2019). Effects of alternate partial root-zone irrigation on the utilization and movement of nitrates in soil by tomato plants. Scientia Horticulturae, 243, 41–47.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank very much the International Publisher, AbtinBerkeh Scientific Ltd. Company (https://AbtinBerkeh.com), inclduing AbtinBerkeh Academy (https://Academy.AbtinBerkeh.com), Isfahan, Iran, for editing the manuscript and revising it according to the journal format.
Funding
There was not any funding for the present research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AR conducted the experiments, collected, and analyzed data, AM supervised the research and wrote the first draft, HG, KM, and HM co-supervised the research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rigi Karvandri, A., Mehraban, A., Ganjali, H.R. et al. The biochemical properties of Rosmarinus officinalis L. affected by irrigation water amount and quality. Environ Geochem Health 45, 6903–6913 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01584-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01584-x