Abstract
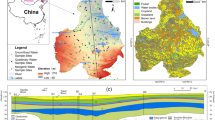
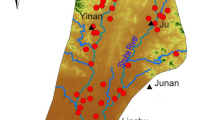
In this study, the formation mechanism and water quality of groundwater in the northwest of Nansi Lake Catchment (NNLC) were analyzed through mathematical statistics, hydrochemical analysis and entropy weighted water quality index (EWQI), and the human health risk of nitrate was also evaluated. To this end, 89 wells in the NNLC were sampled, and the groundwater samples were divided into three groups (I, II, and III) according to cluster analysis results and spatial distribution. The main results are as follows: Topographically, Groups I, II, and III correspond to the alluvial plains, apron plain, and low hills and its front margin, respectively. According to the Piper diagram, the hydrochemical types of Groups I and II groundwater are Na–SO4·Cl and Ca·Mg–HCO3, respectively, and that of Group III is more concentrated, mostly corresponding to the Ca–HCO3 type. Hydrochemical analysis indicated that the development of groundwater hydrochemistry is mainly attributable to water–rock interactions, with the primary process being the dissolution of minerals such as calcite, dolomite, gypsum, and albite. Evaporation exhibited an increasing trend from the northeast to the southwest. Groups I and III presented obvious effects of human activities, with Group I showing sulfate pollution and Group III mainly showing nitrate pollution. Analysis of the characteristics and causes of the groundwater hydrochemistry revealed the proposed approach has excellent performance for classification in areas with complex hydrogeological conditions. The results of EWQI showed that the overall water quality was good, following the order Group III > Group II > Group I. The overall human health risk of nitrate in groundwater was low, but the risk was slightly higher for children than for adults. Therefore, the effects of nitrate contamination should be considered when exploiting hilly and peri-urban groundwater for drinking water.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Wahab, D., Adomako, D., Abass, G., Adotey, D. K., Anornu, G., & Ganyaglo, S. (2021). Hydrogeochemical and isotopic assessment for characterizing groundwater quality and recharge processes in the Lower Anayari catchment of the Upper East Region, Ghana. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00815-w
Adimalla, N., & Qian, H. (2020). Geospatial distribution and potential noncarcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate contaminated groundwater in southern India: a case study. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-020-00762-7
Adimalla, N., & Qian, H. (2021). Groundwater chemistry, distribution and potential health risk appraisal of nitrate enriched groundwater: A case study from the semi-urban region of South India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental, 207, 111277.
Amiri, V., Kamrani, S., Ahmad, A., Bhattacharya, P., & Mansoori, J. (2020). Groundwater quality evaluation using Shannon information theory and human health risk assessment in Yazd province, central plateau of Iran. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10362-6
Barzegari, M., Sepaskhah, A. R., & Ahmadi, S. H. (2017). Irrigation and nitrogen manage: Ments affect nitrogen leaching and root yield of sugar beet. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 108(2), 211–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-017-9853-y
Drever, J. I. (1997). The geochemistry of natural waters Jersey. Journal of Environmental Quality, 27(1), 245–246. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1998.00472425002700010037x
Gao, Z., et al. (2019b). Hydrochemical characteristics and temporal variations of geothermal water quality in Tangtou, Shandong, China. Water, 11(8), 1643.
Gao, Z., et al. (2019c). Factors that influence the chemical composition and evolution of shallow groundwater in an arid region: A case study from the middle reaches of the Heihe River China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(14), 390.
Gao, Z., Liu, J., Feng, J., Wang, M., & Wu, G. (2019a). Hydrogeochemical characteristics and the suitability of groundwater in the alluvial-diluvial plain of southwest Shandong Province China. Water, 11(8), 1577.
Geng, X., Fukuda, S., Moritaka, M., Zhou, Y., & Li, Q. (2013). A Study on Interpersonal relationships, market orientation and performance of Chinese garlic farmers. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture Kyushu University, 58(2), 439–447.
He, Z., Han, D., Song, X., & Yang, S. (2020). Impact of human activities on coastal groundwater pollution in the Yang-Dai River plain, northern China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 27(30), 37592–37613.
Ion, I., Ion, A. C., Calin, M. R., Radulescu, I., & Bogdan, D. (2019). Assessment of chemical parameters and natural radionuclides concentrations in carbonated natural mineral water and contribution to radiation dose. Romanian Journal of Physics, 64(1–2), 804.
Jandu, A., Malik, A., & Dhull, S. B. (2021). Fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of rural habitations of semiarid region of northern Rajasthan, India: A hydrogeochemical, multivariate statistical, and human health risk assessment perspective. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00882-6.
Ji, Y., Wu, J., Wang, Y., Elumalai, V., & Subramani, T. (2020). Seasonal variation of drinking water quality and human health risk assessment in Hancheng city of Guanzhong Plain China. Exposure and Health, 12(3), 469–485.
Karunanidhi, D., et al. (2020). Groundwater quality evolution based on geochemical modeling and aptness testing for ingestion using entropy water quality and total hazard indexes in an urban-industrial area (Tiruppur) of Southern India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10724-0
Kim, K. H., Yun, S. T., Yu, S., Choid, B. Y., Kim, M. J., & Leeb, K. J. (2020). Geochemical pattern recognitions of deep thermal groundwater in South Korea using self-organizing map: Identified pathways of geochemical reaction and mixing. Journal of Hydrology, 589, 125202.
Kou, Li., & Hua, Li. (2019). Hydrochemical characteristics, controlling factors, and solute sources of streamflow and groundwater in the Hei River Catchment China. Water, 11(11), 2293.
Li, P., Li, X., Meng, X., Li, M., & Zhang, Y. (2016). Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a Semiarid region of Northwest China. Expos Health, 8(3), 361–379.
Liu, F., Zhao, Z., Yang, L., Ma, Y., Xu, Y., Gong, L., & Liu, H. (2020). Geochemical characterization of shallow groundwater using multivariate statistical analysis and geochemical modeling in an irrigated region along the upper Yellow River, Northwestern China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 215, 106565.
Liu, J., Peng, Y., Li, C., Gao, Z., & Chen, S. (2020a). Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei Plain, Northern China, as well as an assessment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health. Environmental Pollution, 268, 115947.
Liu, J., Peng, Y., Li, C., Gao, Z., & Chen, S. (2021). A characterization of groundwater fluoride, influencing factors and risk to human health in the southwest plain of Shandong Province North China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 207, 111512.
Liu, X., et al. (2020b). Impact of land use on shallow groundwater quality characteristics associated with human health risks in a typical agricultural area in Central China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10492-x
Liu, Y., Yang, L., & Jiang, W. (2020c). Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal dynamic evolution between social economy and water environmental quality - A case study from Nansi Lake catchment. China. Ecological Indicators, 119, 106870.
Liu, Y., Yang, L., & Jiang, W. (2020d). Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the relationship between water pollution and economic growth: A case study in Nansi Lake catchment China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(4), 4008–4020.
Madhav, S., Raju, N. J., & Ahamad, A. (2020). A study of hydrogeochemical processes using integrated geochemical and multivariate statistical methods and health risk assessment of groundwater in Trans-Varuna region Uttar Pradesh. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00928-2
Mandal, R., Das, A., Sudheer, A. K., Kumar, S., Verma, S., Gaddam, M., & Deshpande, R. D. (2021). Sources, controls, and probabilistic health risk assessment of fluoride contamination in groundwater from a semi-arid region in Gujarat, Western India: An isotope-hydrogeochemical perspective. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00894-2.
Sener, S., Sener, E., & Varol, S. (2020). Hydro-chemical and microbiological pollution assessment of irrigation water in Kızılırmak Delta (Turkey). Environmental Pollution, 266(1), 115214.
Sohrabi, M., Mehrjerdi, M. Z., Karimi, S., & Tavallali, V. (2020). Using gypsum and selenium foliar application for mineral biofortification and improving the bioactive compounds of garlic ecotypes. Industrial Crops and Products, 154(7), 112742.
Tardy, Y. (1971). Characterization of the principal weathering types by the geochemistry of waters from some European and African crystalline massifs. Chemical Geology, 7(253), 271. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(71)90011-8
Vaiphei, S. P., Kurakalva, R. M., & Sahadevan, D. K. (2020). Water quality index and GIS-based technique for assessment of groundwater quality in Wanaparthy watershed, Telangana India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(36), 45041–45062.
Valappil, N. K. M., Viswanathan, P. M., & Hamza, V. (2020). Seasonal hydrochemical dynamics of surface water in the Limbang River, Northern Borneo-evaluating for spatial and temporal trends. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13(19), 980.
Vlachou, C., Hofstädter, D., Rauscher-Gabernig, E., Griesbacher, A., Fuchs, K., & König, J. (2020). Probabilistic risk assessment of nitrates for Austrian adults and estimation of the magnitude of their conversion into nitrites. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 145, 111719.
Wang, L., He, Z., & Li, J. (2020). Assessing the land use type and environment factors affecting groundwater nitrogen in an arid oasis in northwestern China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 27(32), 40061–40074.
Wu, J., Bian, J., Wan, H., Ma, Y., & Sun, X. (2021). Health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Songnen Plain. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 207, 111245.
Wu, J., & Sun, Z. (2015). Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities Mid-West China. Exposure and Health, 8(3), 311–329.
Xu, S., Cui, Y., Yang, C., Wei, S., Dong, W., Huang, L., Liu, C., Ren, Z., & Wang, W. (2021). The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation (FCE) and the principal component analysis (PCA) model simulation and its applications in water quality assessment of Nansi Lake Basin China. Environmental Engineering Research, 26(2), 222–232.
Yan, H., Xiao, J., Liu, T., & Liu, Y. (2020). Evaluation of groundwater geochemical characteristics and quality in the central and Northern Shaanxi Province China. Acta Geochimica, 39(5), 733–740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-020-00427-1
Zhang, Q., Xu, P., Qian, H., & Yang, F. (2020a). Hydrogeochemistry and fluoride contamination in Jiaokou Irrigation District, Central China: Assessment based on multivariate statistical approach and human health risk. Science of the Total Environment, 741, 140460.
Zhang, Y., Wu, J., & Xu, B. (2018). Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Jinghui canal irrigation area of the loess region, northwest China. Environment and Earth Science, 77(7), 273.
Zhang, Y., Yang, J. S., Yao, R. J., Wang, X. P., & Xie, W. P. (2020b). Short-term effects of biochar and gypsum on soil hydraulic properties and sodicity in a saline-alkali soil. Pedosphere, 30(5), 694–702.
Zhu, B., Wang, X., & Rioual, P. (2017). Multivariate indications between environment and ground water recharge in a sedimentary drainage basin in northwestern China. Journal of Hydrology, 549, 92–113.
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous reviewers and Editor for their useful comments, which helped improve the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41772257; 41472216), the Research Project of Shandong Province Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (No. KY2018003; KY201933), the Shandong Provincial Geological Environment Exploration Project (2016) No.3 and the 68th batch of general projects of the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M682207).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZG contributed to formal analysis and writing—original draft. CH contributed to formal analysis, software, and methodology. SY was involved in formal analysis, software, and methodology. JL contributed to conceptualization, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. YP contributed to funding acquisition and resources. CL contributed to investigation, resources, and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethics approval was not required for this research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Han, C., Yuan, S. et al. Assessment of the hydrochemistry, water quality, and human health risk of groundwater in the northwest of Nansi Lake Catchment, north China. Environ Geochem Health 44, 961–977 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01011-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01011-z