Abstract
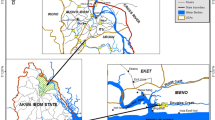
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are an important group of compounds of major environmental concern, which are in the class of persistent organic pollutants. Therefore, the key purpose of this research was to analyze seasonal fluctuations and to determine the probability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coastal sediments of the Iranian Marine Resource Center based on the evaluation of 16 US-EPA important PAH compounds. These compounds have been collected from intertidal sediments located in the marine resources of southern Iran in different seasons. These samples of the surficial sediment were collected at the PSEEZ area using a stainless steel grab sampler in four seasons, from depths between 0.5 and 30 m. Surface sediment samples were removed by spoons and carefully placed in an aluminum foil; they were taken to the laboratory on ice and held at 20° C until their study. After extraction, by using a rotary evaporator apparatus, samples were condensed. The assay was added to roughly 2 g of activated copper flasks in the refrigerator for 36 h for desulfurization. Among different seasons, the highest concentration was observed in winter, with a mean of 281.3 ng g−1. According to ecological risk assessment (concentrations of possible effects, low effect range, degree of threshold effects, and median effect range), PAH risks in surface sediments of PSEEZ were lower than the threshold results levels (TEL), possible effects levels (PEL), low range of effects (ERL), and median range of effects (ERM), indicating that a biological effect would rarely occur. The dry weight scale of the concentration of ∑PAHs ranges from 145.7 to 348.42 ng g−1 with a mean quantity of 260.52 ng g−1. Therefore, according to the amount of ∑PAH concentration, the sediments in the PSEEZ area indicated moderate to heavy pollutions. In this way, the sedimentary surface ecosystems of the Persian Gulf were considered as moderately polluted compared with other ecosystems worldwide. Our study highlighted some of the research gaps in PAH contamination studies and the level of PAH contamination. Therefore, this study will provide a scientific background, planning, and policies for PAH pollution control and environmental protection in Iran and similar regions around the world.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. Also, the datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abatemarco, D., Perera, S., Bao, S. H., et al. (2018). Training augmented intelligent capabilities for pharmacovigilance: Applying deep-learning approaches to individual case safety report processing. Pharmaceutical Medicine, 32, 391–401.
Abbasi, S., Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., et al. (2019). Geochemistry and environmental effects of potentially toxic elements, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and microplastics in coastal sediments of the Persian Gulf. Environmental Earth Science, 78, 492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8420-z
Abdel-Shafy, H. I., & Mansour, M. S. (2016). A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 25(1), 107–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2015.03.011
Abdollahi, S., Raoufi, Z., Faghiri, I., Savari, A., Nikpour, Y., & Mansouri, A. (2013). Contamination levels and spatial distributions of heavy metals and PAHs in surface sediment of Imam Khomeini Port, Persian Gulf. Iran. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 71(1–2), 336–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.01.025
Abeysirigunawardena, D., Jeffries, M., Morley, M. G., Bui, A. O., & Hoeberechts, M. (2015). Data quality control and quality assurance practices for Ocean Networks Canada observatories. In OCEANS 2015-MTS/IEEE Washington (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Adeniji, A. O., Okoh, O. O., & Okoh, A. I. (2018). Analytical methods for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their global trend of distribution in water and sediment: a review. Recent insights in petroleum science and engineering, 10.
Adeyeye, S. A. Q. (2020). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in foods a critical review. Current Nutrition and Food Science, 16(6), 866–873.
Agah, H., Elskens, M., Fatemi, S. M. R., Owfi, F., Baeyens, W., & Leermakers, M. (2009). Mercury speciation in the Persian Gulf sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 157(1–4), 363–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0541-x
Akhbarizadeh, R., Moore, F., & Keshavarzi, B. (2019). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and potentially toxic elements in seafood from the Persian gulf Presence, trophic transfer, and chronic intake risk assessment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41, 2803–2820.
Amos-Tautua, B. M. W., Inengite, A. K., Abasi, C. Y., & Amirize, G. C. (2013). Evaluation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and some heavy metals in roasted food snacks in Amassoma. Niger Delta Nigeria, 7(10), 961–966. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJEST2013.1545
Baklanov, A., Hänninen, O., Slørdal, L. H., Kukkonen, J., Bjergene, N., Fay, B., Finardi, S., Hoe, S. C., Jantunen, M., Karppinen, A., & Rasmussen, A. (2007). Integrated systems for forecasting urban meteorology. Air Pollution and Population Exposurehttps://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-855-2007
Baltrėnas, P., & Baltrėnaitė, E. (2020). Sustainable Natural Materials and Their Importance for Waste Management and Stabilization of Soil Pollution. Sustainable Environmental Protection Technologies (pp. 93–141). Cham: Springer.
Barhoumi, B., LeMenach, K., Devier, M. H., Ameur, W. B., Etcheber, H., Budzinski, H., Cachot, J., & Driss, M. R. (2014). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments from the Bizerte Lagoon, Tunisia Levels, sources, and toxicological significance. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(5), 2653–2669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3569-5
Bauer, A. K., Velmurugan, K., Plöttner, S., et al. (2018). Environmentally prevalent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons can elicit co-carcinogenic properties in an in vitro murine lung epithelial cell model. Archives of Toxicology, 92, 1311–1322.
Baumard, P., Budzinski, H., Michon, Q., Garrigues, P., Burgeot, T., & Bellocq, J. (1998). Origin and bioavailability of PAHs in the Mediterranean Sea from mussel and sediment records. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 47(1), 77–90. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.1998.0337
Baumard, P., Budzinski, H., Garrigues, P., Dizer, H., & Hansen, P. D. (1999). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in recent sediments and mussels (Mytilus edulis) from the Western Baltic Sea Occurrence, bioavailability and seasonal variations. Marine Environmental Research, 47(1), 17–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(98)00105-6
Bellasi, A., Binda, G., Pozzi, A., Galafassi, S., Volta, P., & Bettinetti, R. (2020). Microplastic contamination in freshwater environments A review, focusing on interactions with sediments and benthic organisms. Environments, 7, 30.
Birch, G. F. (1996). Sediment-bound metallic contaminants in Sydney’s estuaries and adjacent offshore, Australia. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 42(1), 31–44. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.1996.0003
CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment), 2002. Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life. Summary tables. Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines.
Chen, C. F., Chen, C. W., Dong, C. D., & Kao, C. M. (2013). Assessment of toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor. Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 463, 1174–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.101
Ciarkowska, K., Gambus, F., Antonkiewicz, J., & Koliopoulos, T. (2019). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and heavy metal contents in the urban soils in southern Poland. Chemosphere, 229, 214–226.
Collivignarelli, M. C., Abbà, A., Benigna, I., Sorlini, S., & Torretta, V. (2018). Overview of the main disinfection processes for wastewater and drinking water treatment plants. Sustainability, 10, 86.
Cowger, W., & Gray, A. (2020). Critical review of processing and classification techniques for images and spectra in microplastic research. Applied Spectroscopy, 74(9), 989–1010.
D’Amore, F., Bencardino, M., Cinnirella, S., Sprovieri, F., & Pirrone, N. (2015). Data quality through a web-based QA/QC system: implementation for atmospheric mercury data from the global mercury observation system (p. 8). Processes and Impacts.
Darılmaz, E., Kontaş, A., Uluturhan, E., Akçalı, İ, & Altay, O. (2013). Spatial variations in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons concentrations at surface sediments from the Cyprus (Eastern Mediterranean): relation to ecological risk assessment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 75(1–2), 174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.07.042
Davoodi, H., Gharibreza, M., Negarestan, H., Mortazavi, M. S., & Lak, R. (2017). Ecological risk assessment of the Assaluyeh and Bassatin estuaries (northern Persian Gulf) using sediment quality indices. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 192, 17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2017.05.003
de León-Gómez, H., Martin del Campo-Delgado, M. A., Esteller-Alberich, M. V., et al. (2020). Assessment of nitrate and heavy metal contamination of groundwater using the heavy metal pollution index case study of Linares. Mexico. Environmental Earth Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09164-3
de Magalhães, L., Noyma, N. P., Furtado, L. L., et al. (2019). Managing eutrophication in a tropical brackish water lagoon Testing lanthanum-modified clay and coagulant for internal load reduction and cyanobacteria bloom removal. Estuaries and Coasts, 42, 390–402.
Dimashki, M., Lim, L. H., Harrison, R. M., & Harrad, S. (2001). Temporal trends, temperature dependence, and relative reactivity of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environmental Science and Technology, 35(11), 2264–2267. https://doi.org/10.1021/es000232y
Edokpayi, J. N., Odiyo, J. O., & Durowoju, O. S. (2017). Impact of wastewater on surface water quality in developing countries: a case study of South Africa. Water quality, 401–416.
Etats-Unis. Environmental Protection Agency (UEP), 1997 The incidence and severity of sediment contamination in surface waters of the United States. United States environmental protection agency. EPA-823-R-007, Washington, DC.
Fabião, J. P. F., Rodrigues, M. F. G., Fortunato, A. B., et al. (2016). Water exchanges between a multi-inlet lagoon and the ocean The role of forcing mechanisms. Ocean Dynamics, 66, 173–194.
Gagnon, C., & Fisher, N. S. (1997). The bioavailability of sediment-bound Cd Co, and Ag to the mussel Mytilus edulis. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 54(1), 147–156. https://doi.org/10.1139/f96-256
Gevao, B., Boyle, E. A., Carrasco, G. G., Ghadban, A. N., Zafar, J., & Bahloul, M. (2016). Spatial and temporal distributions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Northern Arabian Gulf sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 112(1–2), 218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.08.016
Gilliom, R. J. (2007). Pesticides in US streams and groundwater. Environmental Science & Technology. 3408–3414.
Grandclément, C., Seyssiecq, I., Piram, A., Wong-Wah-Chung, P., Vanot, G., Tiliacos, N., & Doumenq, P. (2017). From the conventional biological wastewater treatment to hybrid processes, the evaluation of organic micropollutant removal: a review. Water research, 111, 297–317.
Gune, M. M., Ma, W. L., Sampath, S., Li, W., Li, Y. F., Udayashankar, H. N., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in air and soil surrounding a coal-fired thermal power plant in the south-west coast of India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(22), 22772–22782.
Guo, W., He, M., Yang, Z., Lin, C., Quan, X., & Wang, H. (2007). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Daliao River watershed. China. Chemosphere, 68(1), 93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.072
Guzzella, L., & De Paolis, A. (1994). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Adriatic Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 28(3), 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(94)90392-1
Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M., Ahmed, M. K., Hossain, A., & Masunaga, S. (2019). Distribution, source apportionment, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the surficial sediments from the coastal areas of Bangladesh. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 76(2), 178–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-018-0571-5
Heiri, O., Lotter, A. F., & Lemcke, G. (2001). Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. Journal of Paleolimnology, 25(1), 101–110. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008119611481
Hoepner, T. (1999). A procedure for environmental impact assessments (EIA) for seawater desalination plants. Desalination, 124(1–3), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(99)00083-1
Hu, N., Shi, X., Huang, P., Mao, J., Liu, J., Liu, Y., & Ma, D. (2011). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments of Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea. China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 18(2), 163–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-010-0359-2
Hu, N. J., Huang, P., Liu, J. H., Ma, D. Y., Shi, X. F., Mao, J., & Liu, Y. (2014). Characterization and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments in the Yellow River Estuary. China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(2), 873–883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2490-0
Huang, W., Wang, Z., & Yan, W. (2012). Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments from Zhanjiang Bay and Leizhou Bay. South China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(9), 1962–1969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.05.023
Hull, S. L., Oty, U. V., & Mayes, W. M. (2014). Rapid recovery of benthic invertebrates downstream of hyperalkaline steel slag discharges. Hydrobiologia, 736, 83–97.
Jakovljević, I., Pehnec, G., Vađić, V., Čačković, M., Tomašić, V., & Jelinić, J. D. (2018). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM 10, PM 2.5 and PM 1 particle fractions in an urban area. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 11(7), 843–854.
Jaward, F. M., Alegria, H. A., Galindo Reyes, J. G., & Hoare, A. (2012). Levels of PAHs in the waters, sediments, and shrimps of Estero de Urias, an estuary in Mexico, and their toxicological effects. The Scientific World Journal, 2012.
Karbalaei, S., Hanachi, P., Walker, T. R., et al. (2018). Occurrence, sources, human health impacts and mitigation of microplastic pollution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 36046–36063.
Karyab, H., Yunesian, M., Nasseri, S., Mahvi, A. H., Ahmadkhaniha, R., Rastkari, N., & Nabizadeh, R. (2013). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in drinking water of Tehran. Iran. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 11(1), 1–7.
Katsoyiannis, A., & Breivik, K. (2014). Model-based evaluation of the use of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons molecular diagnostic ratios as a source identification tool. Environmental Pollution, 184, 488–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.09.028
Keshavarzifard, M., Zakaria, M. P., Hwai, T. S., Mustafa, S., Vaezzadeh, V., Magam, S. M., Masood, N., Alkhadher, S. A., & Abootalebi-Jahromi, F. (2014). Baseline distributions and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the surface sediments from the Prai and Malacca Rivers. Peninsular Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 88(1–2), 366–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.08.014
Keshavarzifard, M., Zakaria, M. P., & Hwai, T. S. (2017). Bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) to short-neck clam (Paphia undulata) from sediment matrices in mudflat ecosystem of the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39, 591–610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9835-z
Kim, K. H., Jahan, S. A., Kabir, E., & Brown, R. J. (2013). A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environment International, 60, 71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.07.019.
Kim, S. K., & Chae, D. H. (2016). Seasonal variation in diffusive exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons across the air–seawater interface in coastal urban area. Marine pollution bulletin, 109(1), 221–229.
Konstantinova, E., Minkina, T., Sushkova, S., et al. (2020). Levels, sources, and toxicity assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban topsoils of an intensively developing Western Siberian city. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42, 325–341.
Kucuksezgin, F., Pazi, I., Gonul, L. T., & Duman, M. (2013). Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Cilician Basin shelf sediments (NE Mediterranean). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 71(1–2), 330–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.01.026
Kucuksezgin, F., Pazi, I., Gonul, L. T., & Duman, M. (2016). Organochlorine compounds in surface sediments from the northern coast of Cyprus, Eastern Mediterranean: Levels, possible sources and potential risk. Marine pollution bulletin, 109(1), 591–596.
Kuppusamy, S., Maddela, N. R., Megharaj, M., & Venkateswarlu, K. (2020). Ecological Impacts of Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons. Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (pp. 95–138). Cham: Springer.
Laffoley, D., Baxter, J. M., et al. (2019). Eight urgent, fundamental and simultaneous steps needed to restore ocean health, and the consequences for humanity and the planet of inaction or delay. Aquatic Conservation, 30(1), 194–208.
Larsson, P. (1985). Contaminated sediments of lakes and oceans act as sources of chlorinated hydrocarbons for release to water and atmosphere. Nature, 317(6035), 347–349. https://doi.org/10.1038/317347a0
Li, T., Sun, G., Ma, S., Liang, K., Yang, C., Li, B., & Luo, W. (2016). Inferring sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments from the western Taiwan Strait through end-member mixing analysis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 112(1–2), 166–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.08.024
Lima, A. L. C., Eglinton, T. I., & Reddy, C. M. (2003). High-resolution record of pyrogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon deposition during the 20th century. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(1), 53–61. https://doi.org/10.1021/es025895p
Lin, C., Weng, C. E., Yuan, C. S., Lee, C. W., Hung, C. H., Bui, X. T., & Lin, J. X. (2018). Vertical stratification of volatile organic compounds and their photochemical product formation potential in an industrial urban area. Journal of environmental management, 217, 327–336.
Liu, L. Y., Wang, J. Z., Wei, G. L., Guan, Y. F., & Zeng, E. Y. (2012). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in continental shelf sediment of China: implications for anthropogenic influences on coastal marine environment. Environmental Pollution, 167, 155–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.03.038
Loh, M., Sarigiannis, D., Gotti, A., Karakitsios, S., Pronk, A., Kuijpers, E., Annesi-Maesano, I., Baiz, N., Madureira, J., Oliveira Fernandes, E., Jerrett, M., & Cherrie, J. W. (2017). How Sensors Might Help Define the External Exposome. International Journal of Environmental Research Public Health, 14(4), 434.
Long, E. R., Macdonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19(1), 81–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02472006
Lu, L., Luo, T., Zhao, Y., Cai, C., Fu, Z., & Jin, Y. (2019). Interaction between microplastics and microorganism as well as gut microbiota A consideration on environmental animal and human health. Science of The Total Environment, 667, 94–100.
Lübeck, J. S., Poulsen, K. G., Knudsen, S. B., Soleimani, M., Furbo, S., Tomasi, G., & Christensen, J. H. (2016). Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments from Khuzestan province. Iran. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 110(1), 584–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.05.057
Macdonald, D. D., Carr, R. S., Calder, F. D., Long, E. R., & Ingersoll, C. G. (1996). Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology, 5(4), 253–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00118995
Magi, E., Bianco, R., Ianni, C., & Di Carro, M. (2002). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of the Adriatic Sea. Environmental Pollution, 119(1), 91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00321-9
Malarut, J., & Vangnai, K. (2020). Influence of wood types on quality and carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) of smoked sausages. Food Control, 85, 98–106.
Mandalakis, M., Gustafsson, Ö., Alsberg, T., Egebäck, A. L., Reddy, C. M., Xu, L., Klanova, J., Holoubek, I., & Stephanou, E. G. (2005). Contribution of biomass burning to atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at three European background sites. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(9), 2976–2982. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048184v
Manneh, R., Ghanem, C. A., Khalaf, G., Najjar, E., El Khoury, B., Iaaly, A., & El Zakhem, H. (2016). Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Lebanese surficial sediments A focus on the regions of Tripoli, Jounieh, Dora, and Tyre. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 110(1), 578–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.05.058
McCubbin, F. M., Herd, C. D. K., Yada, T., et al. (2019). Advanced curation of astromaterials for planetary science. Space Science Reviews, 215, 48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-019-0615-9
Mehr, M. R., Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., Fooladivanda, S., Sorooshian, A., & Biester, H. (2020). Spatial distribution, environmental risk and sources of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments-northwest of Persian Gulf. Continental Shelf Research, 193, 104036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2019.104036
Mocq, J., & Hare, L. (2018). Influence of Acid Mine Drainage, and Its Remediation, on Lakewater Quality and Benthic Invertebrate Communities. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 229, 28.
Mostafa, A. R., Wade, T. L., Sweet, S. T., Al-Alimi, A. K. A., & Barakat, A. O. (2009). Distribution and characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments of Hadhramout coastal area, Gulf of Aden. Yemen. Journal of Marine Systems, 78(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2009.02.002
Neff, J. M. (1979). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the aquatic environment: sources, fates and biological effects. Applied Science Publishers.
Neira, C., Cossaboon, J., Mendoza, G., Hoh, E., & Levin, L. A. (2017). Occurrence and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of San Diego Bay marinas. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 114(1), 466–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.10.009
Neşer, G., Kontas, A., Ünsalan, D., Altay, O., Darılmaz, E., Uluturhan, E., Küçüksezgin, F., Tekoğul, N., & Yercan, F. (2012). Polycyclic aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons pollution at the coast of Aliağa (Turkey) ship recycling zone. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(5), 1055–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.02.019
Nowak, P., Kucharska, K., & Kamiński, M. (2019). Ecological and health effects of lubricant oils emitted into the environment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16, 3002.
Ofori, S. A., Cobbina, S. J., & Doke, D. A. (2020). The occurrence and levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in African environments—a systematic review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 32389–32431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09428-2
Ohkouchi, N., Kawamura, K., & Kawahata, H. (1999). Distributions of three-to seven-ring polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons on the deep sea floor in the central Pacific. Environmental Science and Technology, 33(18), 3086–3090. https://doi.org/10.1021/es981181w
Olenycz, M., Sokołowski, A., Niewińska, A., Wołowicz, M., Namieśnik, J., Hummel, H., & Jansen, J. (2015). Comparison of PCBs and PAHs levels in European coastal waters using mussels from the Mytilus edulis complex as biomonitors. Oceanologia, 57(2), 196–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceano.2014.12.001
Oracz, J., & Zyzelewicz, D. (2019). In vitro antioxidant activity and ftir characterization of high-molecular weight melanoidin fractions from different types of cocoa beans. Antioxidants, 8, 560.
Ozaki, N., Yamauchi, T., Kindaichi, T., & Ohashi, A. (2019). Stormwater inflow loading of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons into urban domestic wastewater treatment plant for separate sewer system. Water Science and Technology, 79(7), 1426–1436.
Porter, J. H., Hanson, P. C., & Lin, C. C. (2012). Staying afloat in the sensor data deluge. Trends in ecology and evolution., 27(2), 121–129.
Qiao, M., Wang, C., Huang, S., Wang, D., & Wang, Z. (2006). Composition, sources, and potential toxicological significance of PAHs in the surface sediments of the Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake. China. Environment International, 32(1), 28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2005.04.005
Ramzi, A., Rahman, K. H., Gireeshkumar, T. R., Balachandran, K. K., Jacob, C., & Chandramohanakumar, N. (2017). Dynamics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments of Cochin estuary. India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 114(2), 1081–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.10.015
Ravindra, K., Sokhi, R., & Van Grieken, R. (2008). Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmospheric Environment, 42(13), 2895–2921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.12.010
Readman, J. W., Fillmann, G., Tolosa, I., Bartocci, J., Villeneuve, J. P., Catinni, C., & Mee, L. D. (2002). Petroleum and PAH contamination of the Black Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44(1), 48–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00189-8
Reddy, M. S., Basha, S., Joshi, H. V., & Ramachandraiah, G. (2005). Seasonal distribution and contamination levels of total PHCs, PAHs and heavy metals in coastal waters of the Alang-Sosiya ship scrapping yard, Gulf of Cambay. India. Chemosphere, 61(11), 1587–1593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.04.093
Sany, S. B. T., Hashim, R., Salleh, A., Safari, O., Mehdinia, A., & Rezayi, M. (2014). Risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the West Port semi-enclosed basin (Malaysia). Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(10), 4319–4332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2826-9
Sarti, E., Pasti, L., Scaroni, I., Casali, P., Cavazzini, A., & Rossi, M. (2017). Determination of n-alkanes, PAHs and nitro-PAHs in PM2. 5 and PM1 sampled in the surroundings of a municipal waste incinerator. Atmospheric Environment, 149, 12–23.
Savvides, C., Papadopoulos, A., Haralambous, K. J., & Loizidou, M. (1995). Sea sediments contaminated with heavy metals: metal speciation and removal. Water Science and Technology, 32(9–10), 65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1223(96)00077-7
Sharma, S., & Chatterjee, S. (2017). Microplastic pollution, a threat to marine ecosystem and human health: a short review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 21530–21547.
Siemering, G. S., & Thiboldeaux, R. (2020). Background concentration, risk assessment and regulatory threshold development: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in Milwaukee. Wisconsin surface soils. Environmental Pollution, 268, 115772.
Smith, M., Love, D. C., Rochman, C. M., et al. (2018). Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Current Environmental Health Reports, 5, 375–386.
soil pollution and remediation. (2019). Sakshi, Singh, S.K. & Haritash, A.K. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16, 6489–6512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02414-3
Sun, Y., Wu, S., & Gong, G. (2019). Trends of research on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food: A 20-year perspective from 1997 to 2017. Trends in Food Science and Technology, 83, 86–98.
Sverdrup, L. E., Nielsen, T., & Krogh, P. H. (2002). Soil ecotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in relation to soil sorption, lipophilicity, and water solubility. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(11), 2429–2435. https://doi.org/10.1021/es010180s
Szopińska, M., Szumińska, D., Bialik, R. J., Dymerski, T., Rosenberg, E., & Polkowska, Ż. (2019). Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and other organic pollutants in freshwaters on the western shore of Admiralty Bay (King George Island, Maritime Antarctica). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(18), 18143–18161.
Taghvaee, S., Sowlat, M. H., Hassanvand, M. S., Yunesian, M., Naddafi, K., & Sioutas, C. (2018). Source-specific lung cancer risk assessment of ambient PM2. 5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in central Tehran. Environment International, 120, 321–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.08.003
Tobiszewski, M., & Namieśnik, J. (2012). PAH diagnostic ratios for the identification of pollution emission sources. Environmental Pollution, 162, 110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.10.025
Tolosa, I., De Mora, S. J., Fowler, S. W., Villeneuve, J. P., Bartocci, J., & Cattini, C. (2005). Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in marine biota and coastal sediments from the Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(12), 1619–1633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.06.029
Tongo, I., Ogbeide, O., & Ezemonye, L. (2017). Human health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in smoked fish species from markets in Southern Nigeria. Toxicology Reports, 4, 55–61.
Truskewycz, A., Gundry, T. D., Khudur, L. S., Kolobaric, A., Taha, M., Aburto-Medina, A., Ball, A. S., & Shahsavari, E. (2019). Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contamination in Terrestrial Ecosystems—Fate and Microbial Responses. Molecules, 24, 3400.
U. S. Integrated, "Manual for Real-Time Quality Control of Ocean Optics Data: A guide to quality control and quality assurance of coastal and oceanic optics observations", Ocean Observing System 2015, pp. 46.
Vagge, G., Cutroneo, L., Castellano, M., Canepa, G., Bertolotto, R. M., & Capello, M. (2018). The effects of dredging and environmental conditions on concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the water column. Marine pollution bulletin, 135, 704–713.
Vijayan, A., Österlund, H., Marsalek, J., et al. (2019). Laboratory melting of late-winter urban snow samples: The Magnitude and dynamics of releases of heavy metals and PAHs. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 230, 182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4201-2
Wang, C., Wang, W., He, S., Du, J., & Sun, Z. (2011). Sources and distribution of aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Yellow River Delta Nature Reserve. China. Applied Geochemistry, 26(8), 1330–1336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.05.006
Wang, B., Zeng, C., Chu, K. H., Wu, D., Yip, H. Y., Ye, L., & Wong, P. K. (2017). Enhanced biological hydrogen production from Escherichia coli with surface precipitated cadmium sulfide nanoparticles. Advanced Energy Materials, 7(20), 1700611. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201700611
Wu, K., Huang, J., Yi, J., Liu, X., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., & Xia, Y. (2020). Recent advances in polymer electrolytes for zinc ion batteries: Mechanisms, properties, and perspectives. Advanced Energy Materials. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201903977
Yan, J., Liu, J., Li, Y., & Lang, S. (2014). Effect of water current on the distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, heavy metals and benthic diatom community in sediments of Haihe estuary. China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(20), 12050–12061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3145-8
Yun, X., Yang, Y., Liu, M., Zhang, M., & Wang, J. (2016). Distribution, seasonal variations, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the East Lake. China. CLEAN Soil Air Water, 44(5), 506–514. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201400187
Yunker, M. B., Macdonald, R. W., Vingarzan, R., Mitchell, R. H., Goyette, D., & Sylvestre, S. (2002). PAHs in the Fraser River basin A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Organic Geochemistry, 33(4), 489–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-6380(02)00002-5
Zakaria, M. P., Takada, H., Tsutsumi, S., Ohno, K., Yamada, J., Kouno, E., & Kumata, H. (2002). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rivers and estuaries in Malaysia A widespread input of petrogenic PAHs. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(9), 1907–1918. https://doi.org/10.1021/es011278+
Zeng, S., Zeng, L., Dong, X., & Chen, J. (2013). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in river sediments from the western and southern catchments of the Bohai Sea, China Toxicity assessment and source identification. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(5), 4291–4303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2869-5
Zha, D., Li, Y., Yang, C., et al. (2018). Assessment of organophosphate flame retardants in surface water and sediment from a freshwater environment (Yangtze River, China). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6587-5
Zhang, J. D., Wang, Y. S., Cheng, H., Jiang, Z. Y., Sun, C. C., & Wu, M. L. (2015). Distribution and sources of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of the Pearl River estuary. China. Ecotoxicology, 24(7–8), 1643–1649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1503-z
Zhang, P., Pan, X., Wang, Q., et al. (2020). Toxic effects of heavy metals on the freshwater benthic organisms in sediments and research on quality guidelines in Poyang Lake, China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 20, 3779–3792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02700-5
Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Tan, F., Yang, Y., Wu, X., Wang, W., & Liu, D. (2020). Tidal variability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organophosphate esters in the coastal seawater of Dalian. China. Science of The Total Environment, 708, 134441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134441
Zheng, H., Xing, X., & Hu, T. (2018). Biomass burning contributed most to the human cancer risk exposed to the soil-bound PAHs from Chengdu Economic Region, western China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 159, 63–70.
Yusuf, K. A., Ezechukwu, L. N., Fakoya, K. A., Akintola, S. L., Agboola, J. I., & Omoleye, T. O. (2015). Influence of fish smoking methods on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons content and possible risks to human health. African Journal of Food Science, 9(3), 126–135.
Zambianchi, M., Durso, M., Liscio, A., Treossi, E., Bettini, C., Capobianco, M. L., & Melucci, M. (2017). Graphene oxide doped polysulfone membrane adsorbers for the removal of organic contaminants from water. Chemical Engineering Journal, 326, 130–140.
Funding
This work was supported by Iranian Fisheries Science Research Institute and Mohsen Mirzaei also supported by the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) (Grant Greement: 98018616).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Masoud Hatami Manesh wrote the paper and observed scientific content of the paper, Arash Haghshenas edited, funding acquisition and supervised the form of the paper, Mohsen Mirzaei performed the calculus, methodology, designed experiments, wrote the initial version of the paper and managed, and Hossein Azadi and Safar Marofi7edited and observed the scientific content of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
All authors have read and agreed with their participating.
Consent to publish
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatami Manesh, M., Haghshenas, A., Mirzaei, M. et al. Seasonal variations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coastal sediments of a marine resource hot spot: the case of pars special economic energy zone, Iran. Environ Geochem Health 43, 3897–3919 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00863-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00863-9