Abstract
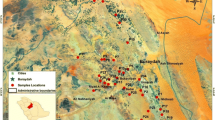
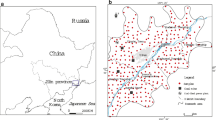
Surface agricultural soil samples obtained from Dexing Pb/Zn mining area in Jiangxi province were analyzed for trace metals to assess their pollution status and potential ecological risk. The spatial distributions and the major trace metals pollution sources were described and identified with the combination of chemical measures and geographic information systems technology. The level of pollution in seven metals is decreasing in the following order: zinc (Zn 128.9 mg/kg) > chromium (Cr 64.1 mg/kg) > lead (Pb 58.4 mg/kg) > arsenic (As 45.3 mg/kg) > copper (Cu 41.9 mg/kg) > nickel (Ni 31.3 mg/kg) > cadmium (Cd 1.5 mg/kg). Trace metal spatial distribution maps established by geographic information system techniques displayed two high-pollution zones around mining sites in the study area. Multivariate statistical analyses were also applied, and the results demonstrated that Cd, As, Pb, Cu and Zn in the soils originated from mining activities, whereas Cr and Ni primarily originated from natural sources. The values of pollution index ranged from 4.79 to 71.59, and the values of modified pollution index ranged from 1.98 to 24.69. Moreover, the potential ecological risk values ranged from 264.0 to 3263.5, which indicated considerable ecological risk to very high ecological risk. The potential ecological risk values and other soil contamination indices showed similar patterns that the high-risk areas were around Dexing Pb/Zn mining site. The surface agricultural soil in study area is heavily to extremely polluted , with Cd that made the most dominant contribution.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahim, G. M., & Parker, R. J. (2008). Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 136, 227–238.
Aslan, A. (2009). Determination of heavy metal toxicity of finished leather solid waste. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 82, 633–638.
Boteva, S., Radeva, G., Traykov, I., & Kenarova, A. (2016). Effects of long-term radionuclide and heavy metal contamination on the activity of microbial communities, inhabiting uranium mining impacted soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 23, 5644–5653.
Brady, J. P., Ayoko, G. A., Martens, W. N., & Goonetilleke, A. (2015). Development of a hybrid pollution index for trace metals in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 306–319.
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. (1990). Chinese soil element background value. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press.
Du, P., Xie, Y. F., Wang, S. J., Zhao, H. H., Zhang, Z., Wu, B., et al. (2015). Potential sources of and ecological risks from heavy metals in agricultural soils, Daye City, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 3498–3507.
Duan, Q., Lee, J., Liu, Y., Chen, H., & Hu, H. (2016). Distribution of trace metal pollution in surface soil samples in China: A graphical review. Bulletin of Environment Contamination and Toxicology, 97, 303–309.
Fang, T., Liu, G., Zhou, C., & Lu, L. (2015). Lead in soil and agricultural products in the Huainan Coal Mining Area, Anhui, China: levels, distribution, and health implications. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 152–161.
Guo, G., Yuan, T., Wang, W., Li, D., Cheng, J., Gao, Y., et al. (2011). Bioavailability, mobility, and toxicity of Cu in soils around the Dexing Cu mine in China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33, 217–224.
Haris, H., Looi, L. J., Aris, A. Z., Mokhtar, N. F., Ayob, N. A. A., Yusoff, F. M., et al. (2017). Geo-accumulation index and contamination factors of heavy metals (Zn and Pb) in urban river sediment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39(6), 1259–1271.
Hinojosa, M. B., Carreira, J. A., Garcia-Ruiz, R., & Dick, R. P. (2005). Microbial response to heavy metal-polluted soils: community analysis from phospholipid-linked fatty acids and ester-linked fatty acids extracts. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 1789–1800.
Hofmann, J., Venohr, M., Behrendt, H., & Opitz, D. (2010). Integrated water resources management in central Asia: nutrient and heavy metal emissions and their relevance for the Kharaa River Basin, Mongolia. Water Science and Technology, 62, 353–363.
Ihedioha, J. N., Ukoha, P. O., & Ekere, N. R. (2017). Ecological and human health risk assessment of trace metal contamination in soil of a municipal solid waste dump in Uyo, Nigeria. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39, 497–515.
Jayawardena, U. A., Angunawela, P., Wickramasinghe, D. D., Ratnasooriya, W. D., & Udagama, P. V. (2017). Heavy metal-induced toxicity in the Indian green frog: Biochemical and histopathological alterations. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 36, 2855–2867.
Kapusta, P., & Sobczyk, L. (2015). Effects of heavy metal pollution from mining and smelting on enchytraeid communities under different land management and soil conditions. Science of the Total Environment, 536, 517–526.
Kaur, R., & Rani, R. (2006). Spatial characterization and prioritization of heavy metal contaminated soil-water resources in peri-urban areas of National Capital Territory (NCT), Delhi. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 123, 233–247.
Kim, H. S., Kim, Y. J., & Seo, Y. R. (2015). An overview of carcinogenic heavy metal: Molecular toxicity mechanism and prevention. Journal of Cancer Prevention, 20, 232–240.
Kistemann, T., Dangendorf, F., & Schweikart, J. (2002). New perspectives on the use of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) in environmental health sciences. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 205, 169–181.
Li, Z. Y., Ma, Z. W., Kuijp, T. J. V. D., Yuan, Z. W., & Huang, L. (2014). A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 468, 843–853.
Li, J., Xie, Z. M., Xu, J. M., & Sun, Y. F. (2006). Risk assessment for safety of soils and vegetables around a lead/zinc mine. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28, 37–44.
Lim, S. R., & Schoenung, J. M. (2010). Human health and ecological toxicity potentials due to trace metal content in waste electronic devices with flat panel displays. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177, 251–259.
Lopez, B. N., Man, Y. B., Zhao, Y. G., Zheng, J. S., Leung, A. O., Yao, J., et al. (2011). Major pollutants in soils of abandoned agricultural land contaminated by e-waste activities in Hong Kong. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 61, 101–114.
Loska, K., & Wiechuła, D. (2003). Application of principle component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemo, 51, 723–733.
Ma, R. M., Cai, C. F., Li, Z. X., Wang, J. G., Xiao, T. Q., Peng, G. Y., et al. (2015). Evaluation of soil aggregate microstructure and stability under wetting and drying cycles in two Ultisols using synchrotron-based X-ray micro-computed tomography. Soil & Tillage, 149, 1–11.
Mazurek, R., Kowalska, J., Gąsiorek, M., Zadrozny, P., & Józefowska, A. (2016). Assessment of trace metals contamination in surface layers of Roztocze National Park forest soils (SE Poland) by indices of pollution. Chemosphere, 168, 839–850.
Motta, I. S., Volpato, G. T., Damasceno, D. C., Sinzato, Y. K., Vesentini, G., Rudge, C. V., et al. (2016). Contamination index. A novel parameter for metal and pesticide analyses in maternal blood and umbilical cord. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira, 31, 490–497.
Muller, A., & Geyer, G. (1969). Submicroscopic heavy metal localization in the prosecreta of the Paneth cells of the mouse. Gegenbaurs Morphologisches Jahrbuch, 113, 70–77.
Nemerow, N. L. (1991). Stream, lake, estuary and ocean pollution. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Peng, H., Geng, W., Yong-quan, W., Mao-teng, L., Jun, X., & Long-jiang, Y. (2010). Effect of trace metal stress on emerging plants community constructions in wetland. Water Science and Technology, 62, 2459–2466.
Shafie, N. A., Aris, A. Z., Zakaria, M. P., Haris, H., Lim, W. Y., & Isa, N. M. (2013). Application of geoaccumulation index and enrichment factors on the assessment of heavy metal pollution in the sediments. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A, Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 48(2), 182–190.
Sun, C., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Sun, L., & Yu, H. (2013). Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of trace metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere, 92, 517–523.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment associated heavy metals in an urban stream, Oahu Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39, 611–627.
Uwizeyimana, H., Wang, M., Chen, W., & Khan, K. (2017). The eco-toxic effects of pesticide and trace metal mixtures towards earthworms in soil. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 55, 20–29.
Verma, R., Xu, X., Jaiswal, M. K., Olsen, C., Mears, D., Caretti, G., et al. (2011). In vitro profiling of epigenetic modifications underlying heavy metal toxicity of tungsten-alloy and its components. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 253, 178–187.
Wang, A. Y., Li, R. P., & Ni, S. Q. (2014). Relationship between heavy metal accumulation of rice field topsoils along the Le’an River and the Dexing ore concentration area, northeast Jiangxi Province. Geological Bulletin of China (in Chinese), 33, 1213–1219.
Wang, Y. Q., Yang, L. Y., Kong, L. H., Liu, E. F., Wang, L. F., & Zhu, J. R. (2015). Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. CATENA, 125, 200–205.
Wong, S. C., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., Qi, S. H., & Min, Y. S. (2002). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environmental Pollution, 119, 33–44.
Wu, J. Y., Zhou, J. L., Liu, Z. T., Wang, X. N., & Gao, A. F. (2014). Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Liao River. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(6N), 268–273.
Yang XL (2011) The geological characteristics of Dexing Yinshan copper-lead-zinc deposit, mining exploration and evaluation work of deep resources. Central South University (in chinese) (pp. 23–45).
Zhang, H., Jiang, Y., Ding, M., & Xie, Z. (2017). Level, source identification, and risk analysis of Heavy metal in surface sediments from river-lake ecosystems in the Poyang Lake, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 24, 21902–21916.
Zhuang, P., Shu, W., Li, Z., Liao, B., Li, J., & Shao, J. (2009). Removal of metals by sorghum plants from contaminated land. Journal of Environmental Science (in chinese), 21, 1432–1437.
Zoller, W. H., Gladney, E. S., Gordon, G. E., & Bors, J. J. (1974). Emissions of trace elements from coal fired power plants. In D. D. Hemphill (Ed.), Trace substances in environmental health (8) (pp. 167–172). Rolla: University of Missouri, Colombia.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the start fund of high-level talent researcher for Dongguan University of Technology (GC200109-17) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC-81273127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal right statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, J., Lin, B., Yuan, M. et al. Trace metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in agricultural soil in Dexing Pb/Zn mining area, China. Environ Geochem Health 41, 967–980 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0193-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0193-x