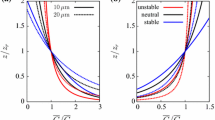
Abstract
The power law and logarithmic law among others are the most commonly well-known theories for equilibrium mean profile of dust concentration in a neutral atmospheric surface layer. However, these theories are based on the assumption of homogeneity in horizontal (streamwise) direction, thereby the horizontal advection term in the transport equation is neglected. In this study, with the help of a self-similar analytical solution of the two-dimensional steady-state dust transport equation (Chamecki and Meneveau, J Fluid Mech 683:1–26, 2011), we examine the applicabilities of the assumption which the one-dimensional theories are based on. In addition, we also propose an empirical fit of the theory, and good agreements with reference data have been obtained. The new approximate profile can be used as an alternative of the one-dimensional theories in practical applications.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RS, Hallet B (1986) Sediment transport by wind: toward a general model. Geol Soc Am Bull 97(5):523–535
Bagnold GA (1941) The physics of blown sand and desert dunes. Methuen, London
Belan S, Lebedev V, Falkovich G (2016) Particle dispersion in the neutral atmospheric surface layer. Bound Layer Meteorol 159(1):1–18
Budd WF (1966) The drifting of nonuniform snow particles. In: Studies in antarctic meteorology, Wiley Online Library, pp 59–70
Chamberlain AC (1967) Transport of lycopodium spores and other small particles to rough surfaces. Proc R Soc Math Phys Eng Sci 296(1444):45–70
Chamecki M (2012) An analytical model for dispersion of biological particles emitted from area sources: inclusion of dispersion in the crosswind direction. Agric For Meteorol 157(2):30–38
Chamecki M, Meneveau C (2011) Particle boundary layer above and downstream of an area source: scaling, simulations, and pollen transport. J Fluid Mech 683:1–26
Chamecki M, Hout RV, Meneveau C, Parlange MB (2007) Concentration profiles of particles settling in the neutral and stratified atmospheric boundary layer. Bound Layer Meteorol 125(1):25–38
Chamecki M, Dufault NS, Isard SA (2012) Atmospheric dispersion of wheat rust spores: a new theoretical framework to interpret field data and estimate downwind dispersion. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 51(3):672–685
Darmenova K, Sokolik IN, Shao Y, Marticorena B, Bergametti G (2009) Development of a physically based dust emission module within the weather research and forecasting (WRF) model: assessment of dust emission parameterizations and input parameters for source regions in central and east asia. J Geophys Res Atmos 114(D14):1159–1171
Freire LS, Chamecki M, Gillies JA (2016) Flux-profile relationship for dust concentration in the stratified atmospheric surface layer. Bound Layer Meteorol 160(2):249–267
Garratt JR (1992) The atmospheric boundary layer. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gillies JA, Berkofsky L (2004) Eolian suspension above the saltation layer, the concentration profile. J Sediment Res 74(2):176–183
Kind RJ (1992) One-dimensional aeolian suspension above beds of loose particlesa new concentration-profile equation. Atmos Environ Part A Gen Top 26(5):927–931
Klose M, Shao Y (2012) Stochastic parameterization of dust emission and application to convective atmospheric conditions. Atmos Chem Phys 12(1):3263–3293
Kok JF (2011) A scaling theory for the size distribution of emitted dust aerosols suggests climate models underestimate the size of the global dust cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(3):1016–1021
Kok JF, Parteli EJ, Michaels TI, Karam DB (2012) The physics of wind-blown sand and dust. Rep Prog Phys 75(10):1660–1669
Kok JF, Mahowald NM, Fratini G, Gillies JA, Ishizuka M, Leys JF, Mikami M, Park MS, Park SU, Van Pelt RS (2014) An improved dust emission model—part 1: model description and comparison against measurements. Atmos Chem Phys 14(23):13023–13041
Lu H, Shao Y (1041) A new model for dust emission by saltation bombardment. J Geophys Res Atmos D14:16827–16842
Marticorena B, Bergametti G (1995) Modeling the atmospheric dust cycle: 1. Design of a soil-derived dust emission scheme. J Geophys Res Atmos 100(D8):16415–16430
Monin AS (1970) The atmospheric boundary layer. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 2(1):225–250
Pan Y, Chamecki M, Isard SA (2013) Dispersion of heavy particles emitted from area sources in the unstable atmospheric boundary layer. Bound Layer Meteorol 146(2):235–256
Prandtl L (1952) Essentials of fluid dynamics. Blackie and Son, London
Rouse H (1937) Modern conceptions of the mechanics or fluid turbulence. Trans Am Soc Civ Eng 102(1):463–505
Schlichting H (1968) Boundary-layer theory. McGraw-Hill, New York
Shao Y (2001) A model for mineral dust emission. J Geophys Res Atmos 106(D17):20239–20254
Shao Y (2004) Simplification of dust emission scheme and comparison with data. J Geophys Res Atmos 109(10):1–6
Shao Y (2008) Physics and modelling of wind erosion. Springer, Berlin
Shao Y, Raupach MR, Findlater PA (1993) Effect of saltation bombardment on the entrainment of dust by wind. J Geophys Res Atmos 98(D7):12719–12726
Shao Y, Ishizuka M, Mikami M, Leys JF (2011) Parameterization of size-resolved dust emission and validation with measurements. J Geophys Res Atmos 116(D8):185–212
Wang G, Zheng X (2016) Very large scale motions in the atmospheric surface layer: a field investigation. J Fluid Mech 802:464–489
Whicker JJ, Breshears DD, Field JP (2014) Progress on relationships between horizontal and vertical dust flux: mathematical, empirical and risk-based perspectives. Aeol Res 14:105–111
Xiao J, Taylor PA (2002) On equilibrium profiles of suspended particles. Bound Layer Meteorol 105(3):471–482
Yang XIA, Sadique J, Mittal R, Meneveau C (2015) Integral wall model for large eddy simulations of wall-bounded turbulent flows. Phys Fluids 27:025112
Zheng X (2009) Mechanics of wind-blown sand movements. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Jie Zhang and Prof. Feng Xu for helpful discussions and suggestions, as well as very insightful comments from the anonymous referees. Financial supports by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11490553, 11502185 and 11362010), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (2016JQ1004) and Key Laboratory of Mechanics on Disaster and Environment in Western China (Klmwde201501) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z., Hu, R., Zheng, X. et al. On dust concentration profile above an area source in a neutral atmospheric surface layer. Environ Fluid Mech 17, 1171–1188 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-017-9542-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-017-9542-z