Abstract
Personalized education—the systematic adaptation of instruction to individual learners—has been a long-striven goal. We review research on personalized education that has been conducted in the laboratory, in the classroom, and in digital learning environments. Across all learning environments, we find that personalization is most successful when relevant learner characteristics are measured repeatedly during the learning process and when these data are used to adapt instruction in a systematic way. Building on these observations, we propose a novel, dynamic framework of personalization that conceptualizes learners as dynamic entities that change during and in interaction with the instructional process. As these dynamics manifest on different timescales, so do the opportunities for instructional adaptations—ranging from setting appropriate learning goals at the macroscale to reacting to affective-motivational fluctuations at the microscale. We argue that instructional design needs to take these dynamics into account in order to adapt to a specific learner at a specific point in time. Finally, we provide some examples of successful, dynamic adaptations and discuss future directions that arise from a dynamic conceptualization of personalization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
The personalization of education has been a desired goal in educational science and practice for more than 200 years. Educators and policymakers alike are putting their hopes in personalization as a panacea for achievement gaps, lack of student motivation, and more effective instruction in general. Broadly construed, personalized education refers to the adaptation of instruction to a specific learner and is juxtaposed with “traditional” instruction that is targeted at entire groups of learners. By changing the mode, content, or rate of instruction in accordance with some characteristic of the learner, it is suggested that individual shortcomings of learners can be addressed and their resources leveraged (Dockterman 2018).
A key argument for the efficacy of personalization can be drawn from empirical demonstrations that learning gains in one-on-one tutoring are up to two standard deviations higher than in conventional classroom instruction (Bloom 1984). This phenomenon and the subsequent desire to scale up the relevant instructional components to larger groups of learners became known as the 2-sigma-problem in educational psychology (e.g., Barrows et al. 1986; Corbett 2001). Although later studies reported less extreme effect size differences (e.g., Vanlehn 2011), scaling up the benefits of one-on-one tutoring to larger groups of learners has remained one of the driving forces behind research on personalization.
Bloom (1984) explained the considerable effect of one-on-one tutoring in his studies by arguing that a personal tutor is better able to assess the individual characteristics of the specific learner and to select appropriate instructional methods and materials—such as identifying the zone of proximal development (Rieber and Carton 1988) and choosing tasks that are located within it. Other benefits of tutoring include fluent adaptations of the instructional method during the tutoring process and dynamic reactions to fluctuations in affective or motivational states of the learner (Lehman et al. 2008).
More recently, Bloom’s explanations have been supported by the emergence of intelligent tutoring systems (ITS), which have been shown to greatly increase learning gains when compared with regular instruction (Ma et al. 2014; Steenbergen-Hu and Cooper 2014). ITS have two defining features: (1) student modeling, i.e., the assessment of several specific learner characteristics through direct measures (e.g., correct or incorrect responses to tasks) or indirect measures (e.g., logfiles of clicking behavior) and (2) the subsequent adaptation of instruction. The success of these tutors can therefore be conceptualized as a success of personalized education. The benefits of personalization can not only be seen in digital environments, however. Even in a conventional classroom context, there is mounting evidence for increased learning gains through personalized instruction across a wide range of settings and subjects (Connor et al. 2007; Connor et al. 2009; Jung et al. 2018; Slavin and Karweit 1985; Stecker et al. 2005; Waxman et al. 1985).
This paper is not intended as a comprehensive review of the expansive literature on personalized education. Instead, we aim to scope out a new direction that adopts a dynamic, person-centered perspective on the subject while still maintaining a systematic and data-based approach. By taking intraindividual dynamics into account, it is possible to adapt instruction not only to a specific learner but also to that learner at a specific point in time. To achieve this, we first look at three different environments in which personalized education has been studied: laboratory research, digital learning environments, and traditional classroom environments. We then highlight commonalities that underlie effective personalization across all three environments—dynamic assessment and subsequent data-driven adaptations of instruction and/or assistance. We conclude that, for personalized education to be effective, dynamic student modeling is needed. A student model is considered dynamic if it accounts for potential changes in relevant learner characteristics that may occur during the instructional process. Teaching agents need knowledge on which learner characteristics are relevant for the learning process at different timescales and on the different ways in which these can vary—between individuals, within individuals over time, and in response to interventions.
In the last part of this manuscript, we present a dynamic framework of personalized education that offers a systematic classification of different learner dynamics over different timescales, as well as a broad characterization of the corresponding instructional adaptations. Since our focus lies on the dynamic modeling of learner characteristics, we only briefly touch upon these adaptations by providing some promising examples and some references for further reading.
What Is Personalized Education?
We define personalized education as the data-based adjustment of any aspect of instructional practice to relevant characteristics of a specific learner. Relevant learner characteristics are defined as all variables that explain (or are assumed to explain) variance in learning outcomes. By instruction, we mean any interaction between learning and teaching agent that has (or is assumed to have) direct or indirect relevance for the learning process.
In the personalized education literature, there are several related terms that are used sometimes interchangeably, sometimes carrying slightly different connotations. For the purpose of this article, we are using “adaptive” as an umbrella term for all educational approaches that adjust some aspect of instruction based on a measured or predicted characteristic of a learner or group of learners. We are using “personalization” synonymous with “individualization,” meaning that the adjustment of instructional practice is targeted at a specific learner and thus implying some form of assessment or modeling. This is in contrast to “differentiation,” which we use for any practices that adjust instruction to different groups of learners.
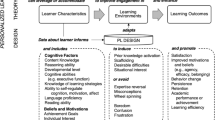
Figure 1 details the loop that we deem necessary for effective personalization.
This loop consists of the following sequence of steps:
-
Step 1—Initial assessment of learner characteristics: identifying those learner characteristics that are relevant for the specific learning process and assessing them in order to establish a student model.
-
Step 2—Instructional design: designing an instructional unit that forms or facilitates the next step towards the overarching learning goal.
-
Step 3—Progress assessment: using the information from task performance and embedded assessment to update the student model based on the progress in the to-be-learned material.
These data- or system-driven personalization endeavors represent one end of a continuum. The other end of this continuum puts the focus on learner participation in goal setting and task selection, allowing learners to personalize their own learning path. The predominantly learner-driven approach is quite prevalent in educational science and teacher education (e.g., Crosby and Fremont 1960) and in e-learning programs (McLoughlin and Lee 2009). The assumption behind these learner-driven approaches is that learners will generally know best what is best for them. Psychological research on metacognition, however, shows that this is not necessarily the case and learners do not always select the most appropriate tasks (Nugteren et al. 2018; Son and Metcalfe 2000). We posit that simply shifting control to the learner is not sufficient for personalized instruction. Rather, the amount of learner control should be carefully selected in accordance with the learning prerequisites and with the learning goals. For an exemplary model of such a dynamic allocation of control, see Corbalan et al. (2006).
Existing Research on Personalized Education
In the following three sections, we will briefly review existing research in the field of personalized education. We will begin with research on aptitude-treatment interactions, which form the basis for effective personalization. We will then examine different approaches to personalize learning in a classroom setting, before moving on to personalized education in digital learning environments.
Aptitude-Treatment Interactions
The main paradigm under which psychology has studied personalization is called aptitude-treatment interactions (ATI). The concept was established by Lee Cronbach, who saw in it the synthesis of correlational (aptitudes) and experimental (treatment) psychology (Cronbach 1957). Using methods of correlational psychology, interindividual differences in relevant characteristics (aptitudes) are assessed and used to group people with similar values together. Then, relying on experimental psychology, people from these groups get randomly assigned to different treatments. If a disordinal interaction is found (group A learns best under treatment A, group B under treatment B), there is evidence for the efficacy of providing learners with different treatments, based on that particular aptitude. The existence of these interactions is a necessary prerequisite for any form of personalization to show direct effects on learning. Without the existence of ATIs, some learners may learn better than others and some instructional parameters may foster learning better than others but there would be no advantage of adapting instruction to specific learners.
Over the following 40 years, a lot of research was carried out using this paradigm—with remarkably sparse robust results (see Tobias 1989). While a few disordinal interactions between aptitude measures and different treatments have been found (see Cronbach 1975), the vast majority of ATI studies found no or only ordinal interactions (both groups learn better under treatment A, but the difference between treatments is bigger for one group). Cronbach and Snow’s (1977) exhaustive review of the early literature on ATI studies concluded that “no aptitude by treatment interactions is so well confirmed that they can be used directly as guides to instruction” (page 492). Several more recent reviews also reached the same conclusion, speculating on different reasons for this apparent failure, including a focus on laboratory experiments (Shapiro 1975), factorially complex aptitude measures (Bracht 1968), a focus on the surface structure of treatment (Tobias 1989), and low specificity of to-be-learned content (Driscoll 1987). Besides these mainly conceptual shortcomings, there exists also a series of methodological concerns that may lead to a reduced prevalence of demonstrable ATIs, chief among them a disregard for multilevel structure of data, a lack of statistical power (Preacher and Sterba 2019), and a focus on linear modeling, which may lead to biased or false-negative results when the true relationships between aptitudes and treatments are nonlinear (Bauer and Cai 2009; Dumas et al. 2020).
Of note, none of the reviews on ATIs has reached the conclusion that they simply do not, or only in very rare circumstances, exist. The concept has such a high face validity that it seemed more reasonable to assume that researchers just had not yet looked in the right places (Tobias 1989), or in the correct way (Shapiro 1975). The demonstrated efficacy of data-based individualization also strongly implies some kind of ATIs existing; no other mechanism has been proposed so far to be responsible for these effects.
A special case of ATI is the expertise reversal effect (Kalyuga 2007). The expertise reversal effect is present if a certain instructional parameter leads to increased learning gain in novices, but decreased learning gains in experts. This effect is particularly interesting in the context of this paper as it highlights the need for a dynamic conceptualization of aptitudes. Instructional parameters that prove effective at the beginning of a learning process (low expertise) can actively impede learning as expertise grows. Even an intervention as simple as reading a short text can drastically alter the effectiveness of subsequent instruction (Rey and Fischer 2013).
Interim Conclusion: Aptitude-Treatment Interactions
If ATIs exist, why are they so hard to find even when researchers are actively looking for them? We believe that the aptitude concept used in most ATI studies, which stems from differential/correlational psychology, does not suffice to answer questions about differential effectiveness of treatments. Instead, a dynamic perspective is needed for the following reason. By design, ATI research focuses on average differences between groups of students and from there tries to draw conclusions about the learning processes of individual students. Since learning processes are always intraindividual processes, trying to approach them by analyzing interindividual differences is suboptimal. Many different combinations of long-term (e.g., maturational and environmental) and short-term (e.g., affective-motivational) processes can lead to the same value on a scale of interindividual differences (Borsboom et al. 2009) but can indicate completely different instructional practices (Bracht 1970). Researchers usually operationalize aptitudes via single measurement points. Learners and their specific aptitudes vary considerably in their general stability, their developmental trajectories, and their responsiveness to instruction. An initial measure of, for example, metacognitive skills can capture learners at the upper or lower end of their intraindividual distributions, at the beginning or the end of a developmental process, and directly before or after an intervention that completely changes the value. Research in developmental psychology, however, suggests that learners and their aptitudes are dynamic entities that (a) change over time, (b) are sensitive to different interventions, and (c) fluctuate (for a similar distinction, see Nesselroade 1991).
Personalized Learning in Digital Learning Environments
One of the most common forms of personalization in digital learning environments is the adaptation of instructional materials to fit the “learning style” of the learner (Kumar and Ahuja 2020; Truong 2016; Yang et al. 2013). Despite its widespread prevalence (not just in e-learning) and some empirical studies reporting increased learning gains through consideration of the individual learning styles, the validity of the concept and the robustness of the evidence have been heavily disputed (Kirschner 2017; Pashler et al. 2008). Other personalization strategies include adapting to the users “intelligence profile,” “media preferences,” prior knowledge, or motivation level. These adaptations are usually based on a single initial assessment of the characteristic in question which is then used to sort the learner in one of several discrete groups (Essalmi et al. 2015).
Despite those personalization strategies, a meta-analysis on the effectiveness of e-learning programs for nurses found no benefit compared with regular instruction (Lahti et al. 2014). Similarly, Sitzmann et al. (2006) found no advantage of e-learning over classroom instruction in their meta-analysis, as long as the same instructional methods were used in both conditions.
In contrast, the research tradition of intelligent tutoring systems (ITS), a subfield of e-learning, has taken a much more dynamic approach to personalization. ITS are, by definition, computer programs that model learners’ psychological states to provide personalized instruction (Ma et al. 2014). These so-called student models allow personalization over and above adjusting the difficulty of the next task based on the performance in the current one or assigning the user-specific content based on static pretest measures. Several meta-analyses have shown the effectiveness of these systems across different domains and contexts (Corbett 2001; Ma et al. 2014; Steenbergen-Hu and Cooper 2014), leading to the conclusion that dynamic student modeling and subsequent adaptations are an effective mechanism for promoting learning gains.
While this line of research does not allow statements about isolated interaction effects of specific treatment variables with specific aptitudes, it does provide some empirical evidence regarding the efficacy of adapting to specific characteristics. Characteristics that have been successfully adapted to, over and above prior knowledge, include metacognitive skills (Azevedo et al. 2009), current affect (D’Mello et al. 2012; Lehman et al. 2013), and motivation (Walkington 2013; for a comprehensive overview of different adaptations in ITS see Aleven et al. 2017).
Interim Conclusion: Personalization in Digital Learning Environments
The discrepancy between the null effects found for many forms of e-learning and the convincing evidence for the efficacy of ITS further strengthens the point that the success of ITS cannot just be traced back to them being computer-based (and thus flexible and delocalized). Instead, it seems plausible to conclude that they are caused by the dynamic assessment and subsequent instructional adaptations that set ITS apart from other forms of e-learning. While most e-learning systems claim some form of “individualization” or “personalization” of content based on some form of pretest, the lack of significant effects on learning gains of these adaptations suggests that dynamic assessment likely is a necessary precursor for effective personalization.
To conclude, while digital learning environments offer the potential for new ways to personalize instruction, the empirical evidence indicates that just because something is personalized, it does not mean that it automatically fosters learning. Adapting to learner characteristics that are not strongly connected to learning processes (such as learning styles) or using static modeling as a basis for adaptations can be seen as potential culprits for ineffective personalization attempts. In contrast, using dynamic modeling to assess and adapt to relevant learner characteristics can lead to learning gains only rivaled by one-on-one human tutoring (Corbett 2001; Vanlehn 2011).
Personalized Learning in the Classroom
The most basic approach to data-based personalization in classroom contexts is ability grouping—the grouping of students with similar ability (usually measured once at the start of the program) either in different classes or within a class in order to present different materials or progress content at a different pace for the separate groups (Slavin 1987). While still a far cry from true personalization, the appeal of these methods lies in their practicability. Administering a single test to measure ability in broad categories is already part of most school systems and providing specific instruction to 2–3 different groups of students is much less daunting a task than doing so for 20–30 individual students. In their field study on individualized mathematics instruction, Slavin and Karweit (1985) found a clear benefit of ability grouping vs. conventional whole-class teaching and a clear benefit of a completely personalized model (team-assisted individualization) vs. ability grouping on student achievement.
Formative assessment, also known as learning progress assessment or curriculum-based measurement, is the most widespread approach to systematically personalize education in classrooms. Black and William (2009, p. 5) have put forward the following definition of formative assessment: “Practice in a classroom is formative to the extent that evidence about student achievement is elicited, interpreted, and used by teachers, learners, or their peers, to make decisions about the next steps in instruction that are likely to be better, or better founded, than the decisions they would have taken in the absence of the evidence that was elicited.” This stands in contrast to summative assessment, which is not meant to directly inform further instruction but rather provide a summary of the knowledge or skill level of the learner at the end of a predefined period (Harlen and James 1997).
The concept of formative assessment originated in the field of special education, and was thought of as an advancement upon Bloom’s mastery learning (Deno 1990; Fuchs 2004; Wesson et al. 1984). In the classical mastery learning approach (Bloom 1968), students are repeatedly tested on the content they are currently trying to learn—upon reaching a certain proficiency they advance to the next content (and are tested on that). In the formative assessment approach, the students regularly complete parallel tests on the content they should have mastered by the end of the year/semester. This allows the teaching agent to continuously monitor progress on a single scale and to adapt the instruction in case of stagnation. In the beginning of the twenty-first century, this concept began to gain a lot more traction internationally and in general educational sciences and the evidence for its effectiveness grew (Black and Wiliam 2009; Förster and Souvignier 2014; Klauer 2011; Stecker et al. 2005; Waxman et al. 1985).
Even though different formative assessment procedures vary significantly in several parameters (type of feedback, learner- or teacher-driven, one- or multidimensional, etc.), they all incorporate some dynamic assessment of learning progress on an individual basis and they all seem to have at least some positive effects on learning, compared with a business-as-usual control group. This has been shown in several meta-analyses reporting effect sizes of d = 0.32 in regular classrooms (Kingston and Nash 2011), and higher ones for students with special educational needs (Jung et al. 2018).
Interim Conclusion: Personalization in the Classroom
The effectiveness of formative assessment procedures compared with regular classroom instruction also highlights the advantages of dynamic modeling through repeated measurements during the learning process. Usually, formative assessment is only used to track (multidimensional) domain knowledge, but using similar techniques to also measure progress in characteristics such as metacognitive skills or strategy knowledge to identify and address shortcomings could be a worthwhile endeavor.
A challenge that formative assessment poses to scientists researching personalized education is that the actual instructional adaptations are usually left up to the practitioners. Their dynamic nature makes it quite hard to reliably assess or prescribe them. While the abovementioned success of these practices shows that many teachers are able to draw meaningful conclusions from the assessment data, the absence of information concerning the instructional adaptations still poses a significant obstacle to furthering our understanding about personalization in detail.
Synthesis
An overall conclusion that can be drawn from the research discussed thus far is that personalization seems to be more successful when it takes the dynamic nature of learning processes into account. Dynamic means that the constituting factors of successful learning can change during and in interaction with the instructional process.
Evidence for this conclusion can be drawn from the surprising lack of clear ATIs using static aptitude measures and from the success stories of ITS and formative assessment, both of which use dynamic assessment procedures to create and update student models, allowing the teaching agents to continuously adapt their instruction to a developing learner. We argue that the success of these practices is a direct consequence of this dynamic approach to student modeling.
Generally speaking, a student model is any abstract representation of a learner that is being held by a teaching agent (Holt et al. 1994). These student models can be formal, such as the placement on a distribution of test scores, or informal, such as a teacher believing someone to be a fast learner, as well as high-level, such as an aggregated grade over a whole school year in a specific subject, or low-level, such as a specific mistake a student made twice in a row. Static student models get established once, usually to compare the student either to a comparable sample or to a specific criterium. Their underlying conceptualization is deterministic, i.e., knowledge about the learning prerequisites and the specific instructional parameters is deemed sufficient to determine learning progress over a longer period of time. While we do not want to dispute that this is theoretically possible when knowing all relevant prerequisites, it does not seem to be a realistic proposition. Dynamic modeling deals with this lack of information by leaving room for differing individual trajectories. Repeated measurements can be used to correct mistaken assumptions and better determine future learning.
Not only do static characterizations potentially lead to an aptitude-treatment mismatch, they can also deprive the learner of the opportunity to acquire the lacking aptitudes. An example of this can be seen in a study in which learning gains increased for low-engagement students when presented with material which did not correspond to their preferred learning style (Kelly and Tangney 2006). Another (hypothetical) example would be a teaching agent measuring the metacognitive skills of a learner and concluding from a low value that the learner needs a lot of explicit feedback and guidance in task selection. This in turn drastically reduces the learning opportunities for the student to actually improve in judging their own learning and selecting appropriate tasks—a phenomenon known as part of the assistance dilemma (see Koedinger et al. 2008).
A dynamic modeling approach is not a new invention in research on learning. Developmental psychology has been using so-called microgenetic methods (consisting of highly frequent measurements during times of interesting developmental processes) since the 1920s to better understand the development of cognitive competencies in early childhood (Catán 1986). Recently, there has also been a rise of studies employing measurement-intensive longitudinal designs and recognizing the potential of within-person analyses and dynamic measurement models in educational research (Dumas et al. 2020; Murayama et al. 2017). Even for presumably stable traits, such as intelligence, dynamic testing procedures have been shown to produce educationally relevant information beyond that produced by static tests (Resing et al. 2009; Vogelaar et al. 2020). The underlying assumption behind dynamic assessment is that learners change during and in interaction with the instructional process. If the characteristics of learners were stable entities that completely predicted learning outcomes under specific treatment conditions (as assumed in the early days of ATI research), there would be no need for dynamic modeling and thus no measurable advantage in employing it. Since the evidence clearly points to increased learning gains as a result of dynamic modeling (and subsequent adaptations), we will now turn to the different ways learners and their characteristics can change, as well as the educational relevance of these changes.
Learner Dynamics
Leaning on the conceptualization of Hertzog and Nesselroade (2003), we propose that there are three main ways in which relevant characteristics of a learner can vary: along an individual developmental trajectory, in response to an intervention, as well as in short-term fluctuations.
Figure 2 depicts the fictional change of a single aptitude of two learners over time. This aptitude could, for example, be learners’ metacognitive control skills. In the uppermost graph, we can see the development over several months. Both learners show a gradual increase that changes in steepness over time with certain periods of more pronounced development. We can also see that there are clear differences between the learners in the measured level of the aptitude at most time points.
As soon as we zoom in on a particular point in time and look at the development from day to day, we can see that the value for the aptitude of both learners also shows a systematic trend—this can be caused by instructional input or some other intervention, such as changes in the environment of the learners. Learners react quite differently to the same instruction and already simple interventions can have far-reaching consequences for the development of specific aptitudes. These changes operate on a much smaller timescale than the developmental processes outlined above (and need to be accompanied by regular assessment to be correctly modeled).
By zooming in even further and looking at the processes within a specific day, we can see that the value for the aptitude of both learners fluctuates. Even though one of them shows a higher average performance, on specific tasks, he or she may perform far below the other. We can also see that the amplitude and frequency of these fluctuations differ between people. A high amplitude in intraindividual fluctuations of relevant aptitudes can lead to very unstable performance patterns and indicates a need for instructional adaptations.
As can be seen in Fig. 2, obtaining an aptitude measure at a single point in time may be influenced by all three dynamics, making it difficult to infer appropriate instructional adaptations. By using repeated measures at different timescales, the teaching agent can identify if a performance is typical, if an intervention was successful for a specific learner, or if a learner needs additional assistance on a specific day. Particularly, if dynamics at the different time levels are nonlinear (as in Fig. 2), a sufficiently dense temporal resolution of measurements is necessary to capture them. In the following sections, we will have a closer look at how knowledge about learner dynamics on different timescales can be used to inform instructional decision-making.
Learner Dynamics on the Macroscale
We define the macroscale as the timescale of months to years. The main driver behind learner dynamics on the macroscale is developmental processes. Developmental processes are changes in relevant learner characteristics that are part of the regular development of students. These can be caused by maturation of brain structures, common environmental influences (such as the onset of schooling), and potential interactions between them. The attainment of mastery in a certain domain can also be conceptualized as a developmental process. These developmental trajectories differ from person to person (and from characteristic to characteristic) in their intercepts, slopes, and general shapes.
The performance on working memory tasks is a prime example of a developmental trend. It is increasing rapidly roughly up to the age of nine for simple tasks and roughly up to the age of thirteen for complex tasks (Luciana et al. 2005). Other characteristics show flatter developmental trajectories. This is the case for most affective-motivational factors, which remain relatively stable across the lifespan despite showing remarkable short-term variability (e.g., Röcke and Brose 2013).
In a learning context, the macroscale is the scale of higher-order goals, such as mastery and skill acquisition. The most obvious example of instructional decision-making on the macroscale is the grade-based school system. In most educational systems, students get sorted into groups according to their age, which then get assigned to specific curricula that are assumed to be suitable for that specific age group. The underlying theory behind this grouping is that most relevant differences between learners are developmental differences and that the shape of the trajectories is relative consistent across learners. Some assumed cases of accelerated or protracted development can easily be addressed by assigning children to slightly higher or lower age groups (Dockterman 2018). The decision as to which skill or content to master is often out of control of the single teaching agent, but the specific individual learning goal and the optimal learning path towards that goal still need to be determined.
Most digital learning environments also try to guide learners to a specific, preset learning goal and only come into play after the to-be-mastered content has been selected.
In laboratory settings, there also exists evidence for differential effectiveness of treatments based on the age of the learner (see Breitwieser and Brod 2020).
Learner Dynamics on the Mesoscale
We define the mesoscale as the timescale of days to weeks. The main driver behind learner dynamics on the mesoscale is intervention-induced changes. Intervention-induced changes describe any changes in relevant learner characteristics that result directly from an intervention. Under a broad definition, every instructional unit can be conceptualized as an intervention intended to modify the domain knowledge of the learner. In a more specific sense, the fact that some characteristics respond to targeted small-scale interventions opens up leverage points for teaching agents. Instead of adapting instruction to a specific characteristic, teaching agents can choose to modify it to have a better basis for subsequent instruction. A prime example of a characteristic that shows strong intervention-induced changes is the strategy knowledge of learners (e.g., Ryan et al. 2008). With short strategy trainings, learners can expand their repertoire of available learning strategies, which can lead to increased learning gains at the domain level.
In a learning context, the mesoscale is the scale of instructional units—bundles of tasks, explanations, examples etc. that can be processed in one session. Each instructional unit should present the next logical step towards the overarching learning goal and the difficulty should be adapted to the learning progress of the particular student. If a particular skill or knowledge component that would be required to proceed towards the learning goal is found to be missing, an instructional unit targeting that component should be presented.
Most ITS track multidimensional domain knowledge in order to generate appropriate instructional units (Nwana 1990), but there are also several examples of small-scale interventions that are targeted at other characteristics that are identified as relevant for learning, such as metacognitive skills (Aleven, Mclaren, Roll, & Koedinger, 2006; D’Mello et al. 2012) or epistemic emotions (Lehman et al. 2013). Formative assessment is also primarily operating on the mesoscale—the learning progress caused by the previous instruction gets measured in order to better inform subsequent instruction. This includes simple adaptations of difficulty and addressing specific gaps in knowledge or skills of individual learners. Finally, there is a long tradition of laboratory research showing the potential of utilizing the malleability of characteristics such as metacognition (Eslami Sharbabaki 2013) or strategy knowledge (Ryan et al. 2008) to increase domain-level learning gains.
Learner Dynamics on the Microscale
We define the microscale as the timescale of minutes to hours. The main driver behind learner dynamics on the microscale is short-term fluctuations in relevant characteristics. An obvious example of a characteristic fluctuating in value is the affective state of a learner. The way we feel can change from moment to moment. But even characteristics that are traditionally assumed to be stable traits, such as working memory capacity, have been shown to manifest substantial intraindividual variance, not just from day to day but even from moment to moment (Dirk and Schmiedek 2016). These fluctuations happen over larger timescales as well, but their relevance for educational decision-making mainly lies in the microscale.
This relevance is partially shown in classroom education, where the concept of assessing and modifying students affective and motivational states on a day-to-day (or even moment-to-moment) basis forms part of what has been called the “supportive climate” dimension of good teaching (Fauth, Decristan, Rieser, Klieme, & Büttner, 2014). Teaching that fosters a supportive climate has been linked to increased student engagement and achievement (Reyes, Brackett, Rivers, White, & Salovey, 2012).
There is also a growing base of research attempting to automate affect detection in classrooms via facial recognition systems (Bosch et al. 2016; Dragon et al. 2008). Studies on human one-on-one tutoring have likewise shown that expert tutors monitor the affective states of their tutees and engage in pedagogical moves such as off-topic conversation or positive feedback to counteract significant negative affect (Lehman et al. 2008).
Additionally, there are several examples of ITS fine-tuning some part of their content on a moment-by-moment basis, based on intraindividual fluctuations in affective, cognitive, or process variables. GazeTutor is using eye-tracking to detect boredom and disengagement in learners and tries to reengage them via dialog/animation and has been shown to increase learning gains compared with an equivalent system without affect modeling (D’Mello et al. 2012). Help Tutor und Meta-Tutor are tracking difficulties in metacognitive monitoring/control that the learner exhibits (such as inefficient help seeking) and offering prompts aimed at improving these behaviors (Aleven et al. 2016; Azevedo et al. 2009). Most ITS are also providing feedback during task processing that adapts to the specific errors and/or the solution path the student has chosen (Koedinger et al. 2013; Vanlehn 2011).
A Dynamic Framework of Personalized Education
Taking into account these different learner dynamics and their relevance for learning processes on the different timescales, Fig. 3 provides an updated version of Fig. 1 and highlights the relevant instructional decision-making processes and opportunities for adaptations at each of the different timescales.
In order for personalized learning to be effective, the general learning prerequisites (which are influenced by the individual developmental trajectory and the current age) over all relevant characteristics should be assessed as they inform the instructional decision-making on all timescales. Information from this initial assessment can be supplemented and adjusted by repeated measurements throughout the learning process.
The elements colored in red show the macroscale of personalization. The main instructional decision to be made on that scale is the selection of an appropriate higher-order learning goal. Progress towards mastery of that goal can be continuously measured and in case of stagnation, instructional change can be implemented. This cycle of assessing the learner prerequisites, setting a reasonable learning goal, and employing summative assessment practices to check whether mastery was achieved (which influences the learning goals for the next cycle) is the backbone of personalized instruction at the macroscale. As described above, decisions on the macro level are often predetermined by context and thus difficult to truly personalize. Nevertheless, adapting to student characteristics on the macroscale was historically one of the first steps from homogenous ability grouping towards truly personalized instruction (Dockterman 2018; Lee and Park 2008).
Designing an instructional unit that falls in the zone of proximal development of the learner and fits their individual learning prerequisites is the main instructional adaptation of relevance on the mesoscale (colored in purple). As posited in Bloom’s mastery learning approach (Bloom 1968), the teaching agent needs to measure the success of the instructional unit before proceeding with the next one. Upon completion of the unit, there needs to be some assessment of the learning gains and subsequent selection/design of the next unit (located in the zone of proximal development and presenting a logical next step on the way to the high-level learning goal). This cycle of presenting an instructional unit, measuring the learning progress with formative assessment procedures, and then using that information to design the next instructional unit is the main way to personalize instruction at the mesoscale. An integral part of designing personalized instructional units is “efficient” task selection. Personalizing task selection based on predicted efficiency and learner preference has been shown to increase training and transfer performance, respectively, when compared with yoked control groups (Salden et al. 2006).
If we take a closer look at the processes within an instructional unit (colored in blue), we can see that the main way that a teaching agent can adapt on this scale is by selectively giving or withholding assistance. We define assistance as any action a teaching agent takes that facilitates progress in the current task (e.g., error specific feedback, scaffolding, hints). It is important to note here that quicker or easier task progress does not necessarily translate to increased learning gains. Studies on the assistance dilemma (Koedinger et al. 2008) generally imply an inverted U-shaped relationship between task difficulty (after assistance) and learning progress, where too little assistance can leave the learner unable to make progress on the task, and too much assistance does not require the learner to engage in the cognitive processes necessary for deep processing (and thus robust learning). Studies on the expertise reversal effect (Kalyuga et al. 2003) also imply that, generally speaking, extensive assistance should be provided if a task is new and difficult and then should be gradually reduced as the learner gains expertise in that specific task. Besides this general trend, assistance should also be given or withheld reactively, depending on fluctuations in relevant characteristics. This means that if a learner is experiencing frustration, it might be advisable to increase the amount of assistance for that specific task-step, regardless of the general amount of expertise displayed. Assessing fluctuations in task performance or affective-motivational factors “on-line” (parallel to the task progress) and reacting by giving or withholding assistance is the main personalization lever at the microscale.
These adaptations of provided assistance can take many different forms, ranging from affective-motivational (e.g., D’Mello et al. 2012) over metacognitive support (e.g., Azevedo et al. 2009) to the provision of hints or error specific feedback (Koedinger et al. 2013; Vanlehn 2011).
Conclusion
This article summarized the key findings from three mostly distinct research traditions on personalized education, synthesizing them into a comprehensive framework of personalized instruction and highlighting the need for dynamic assessment. While there are examples of successful personalization based on relatively stable pretest measures, empirical evidence and conceptual considerations strongly point towards an advantage of dynamic modeling, at least for those characteristics that show substantial intraindividual variance.
Assessing such characteristics at a high frequency throughout the learning process provides a variety of relevant information. It allows to separate individual characteristics at the macro, meso, and micro levels. This way, estimates of presumably stable trait characteristics (e.g., aptitudes) may be measured with increasing precision as more observations are collected. Also, individual differences in characteristics of observed learning curves, like learning rates or asymptotes, may be parameterized, estimated, and used as prognostic information for further learning processes that follow. Furthermore, the amount of intraindividual variability around average levels or trends may provide useful information. For example, sustained strong variability in task performance can give hints to instructors that the performance bottleneck lies in a highly volatile characteristic, such as affect, motivation, or metacognitive control, rather than in a stable (or monotonously increasing) characteristic such as domain knowledge. Finally, information on how different relevant variables that show such variation are coupled (i.e., correlated at the within-person level) within learners across time may be of diagnostic value. For example, Neubauer et al. (2019) report that within-child fluctuations (within and across days) in working memory performance are coupled with different dimensions of affect for different groups of children. Inferring such learner characteristics directly from process data may aid the on-line adaptation of learning circumstances to individual learners’ needs.
Other fields already lead the way towards dynamic modeling. In the field of clinical psychology, there has been a similar push towards dynamic intraindividual patient models instead of basing personalization attempts on interindividual difference scores (Fisher and Boswell 2016). These allow a much better fit of the treatment to the needs of the patient, as well as an easier adaptation of treatment parameters to changes in the process. We argue that a dynamic conceptualization is also needed to bring the science of personalized education (and ATI) forward.
This dynamic conceptualization undoubtedly brings with it an additional load for teaching agents. They not only need to regularly assess relevant parameters but also have to use this information to inform subsequent instructional decisions. This load can be partially constrained by knowledge about which characteristics can be reasonably expected to vary over which timescale and the educational relevance of this variance. The presented framework serves as a starting point for such considerations. By mapping out the decision space for teaching agents, we identified relevant kinds of learner parameters on each timescale and provided some rough classification of the different levels of instructional practice that can be adapted: goal setting, design of instructional units/task selection, and assistance. The proposed framework further constrains the selection of both learner parameters and instructional parameters to those that are actually relevant on the specific timescale. It also provides a frame of reference for the localization of future research questions regarding personalized education by systematically differentiating between different kinds of learner dynamics, the learner characteristics they apply to, and the instructional levers that can be manipulated.
There has been substantial progress in research on personalized education in recent years, not just towards more precise measurement and conceptualization of aptitudes, but also towards a systematic classification of instructional adaptations. Nevertheless, we are still a long way off from being able to reliably describe adaptations at different timescales based on learner characteristics. In most formative assessment studies, the instructional adaptations are left up to the practitioners, providing almost no mechanistical information regarding causes of the observed benefit. Most classical ATI studies only define the treatment in very broad categories (learner vs. teacher driven, high vs. low structure material) and thus fail to account for the complex nature of instructional practice. Most ITS studies are designed to only evaluate a complete “package” of adaptations (e.g., a system that tracks and interacts with affect vs. one that does not), providing evidence for or against the usage of that system but containing little information about specific adaptations. Future research needs to better isolate specific treatment variables in order to study their effects on specific learners at specific points in the learning process. Only then can we move to a truly evidence-based practice of personalized education, be it in the classroom, the laboratory, or in a digital learning environment.
References
Aleven, V., McLaughlin, E. A., Glenn, R. A., & Koedinger, K. R. (2017). Instruction based on adaptive learning technologies. Handbook of Research on Learning and Instruction, 522–560. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315736419.ch24.
Aleven, V., McLaren, B., Roll, I., & Koedinger, K. (2006). Toward Meta-cognitive Tutoring: A Model of Help Seeking with a Cognitive Tutor. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 16(2), 101–128.
Aleven, V., Roll, I., McLaren, B. M., & Koedinger, K. R. (2016). Help helps, but only so much: research on help seeking with intelligent tutoring systems. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 26, 205–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-015-0089-1, 1.
Azevedo, R., Witherspoon, A., Chauncey, A., Burkett, C., & Fike, A. (2009). MetaTutor: A MetaCognitive tool for enhancing self-regulated learning. AAAI Fall Symposium - Technical Report, FS-09-02, 14–19.
Barrows, H. S., Myers, A., Williams, R. G., & Moticka, E. J. (1986). Large group problem-based learning: a possible solution for the “2 sigma problem.”. Medical Teacher, 8(4), 325–331. https://doi.org/10.3109/01421598609028991.
Bauer, D. J., & Cai, L. (2009). Consequences of unmodeled nonlinear effects in multilevel models. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 34, 97–114. https://doi.org/10.3102/1076998607310504, 1.
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (2009). Developing the theory of formative assessment. 5–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11092-008-9068-5.
Bloom, B. (1968). Learning for mastery. Evaluation Comment, 1(4), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed063p318.
Bloom, B. S. (1984). The 2 sigma problem: the search for methods of group instruction as effective as one-to-one tutoring. Educational Researcher, 13(6), 4–16. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X013006004.
Borsboom, D., Kievit, R. A., Cervone, D., & Hood, S. B. (2009). The two disciplines of scientific psychology, or: the disunity of psychology as a working hypothesis. In Dynamic Process Methodology in the Social and Developmental Sciences (pp. 67–97). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-95922-1_4.
Bosch, N., D’Mello, S. K., Baker, R. S., Ocumpaugh, J., Shute, V., Ventura, M., … Zhao, W. (2016). Detecting student emotions in computer-enabled classrooms. IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2016-Januar, 4125–4129.
Bracht, G. H. (1970). Experimental Factors Related to Aptitude-Treatment Interactions. Review of Educational Research, 40(5), 627.
Breitwieser, J., & Brod, G. (2020). Cognitive prerequisites for generative learning: why some learning strategies are more effective than others. Child Development, cdev.13393. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13393.
Catán, L. (1986). The dynamic display of process: historical development and contemporary uses of the microgenetic method. Human Development, 29(5), 252–263. https://doi.org/10.1159/000273062.
Connor, C. M. D., Morrison, F. J., Fishman, B. J., Schatschneider, C., & Underwood, P. (2007). Algorithm-guided individualized reading instruction. Science, 315(5811), 464–465. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1134513.
Connor, C. M., Piasta, S. B., Glasney, S., Schatschneider, C., Fishman, B. J., Underwood, P. S., & Morrison, F. J. (2009). Individualizing student instruction precisely: effects of child-by-instruction interactions on students’ literacy. Child Development, 80(1), 77–100.
Corbalan, G., Kester, L., & Van Merriënboer, J. J. G. (2006). Towards a personalized task selection model with shared instructional control. Instructional Science, 34(5), 399–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-005-5774-2.
Corbett, A. (2001). Cognitive computer tutors: solving the two-sigma problem. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 2109, 137–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44566-8_14.
Cronbach, L. J. (1957). The two disciplines of scientific psychology. American Psychologist, 12(11), 671–684. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0043943.
Cronbach, L. J. (1975). Beyond the two disciplines of scientific psychology. American Psychologist, 30(2), 116–127. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0076829.
Cronbach, L. J., & Snow, R. E. (1977). Aptitudes and instructional methods: A handbook for research on interactions. Irvington.
Crosby, G., & Fremont, H. (1960). Individualized algebra. The Mathematics Teacher, 53, 109–112. https://doi.org/10.2307/27956078.
D’Mello, S., Olney, A., Williams, C., & Hays, P. (2012). Gaze tutor: a gaze-reactive intelligent tutoring system. International Journal of Human Computer Studies, 70(5), 377–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2012.01.004.
Deno, S. L. (1990). Individual differences and individual difference. The Journal of Special Education, 24(2), 160–173. https://doi.org/10.1177/002246699002400205.
Dirk, J., & Schmiedek, F. (2016). Fluctuations in elementary school children’s working memory performance in the school context. Journal of Educational Psychology, 108(5), 722–739. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000076.
Dockterman, D. (2018). Insights from 200+ years of personalized learning. Npj Science of Learning, 3(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41539-018-0033-x.
Dragon, T., Arroyo, I., Woolf, B. P., Burleson, W., el Kaliouby, R., & Eydgahi, H. (2008). Viewing student affect and learning through classroom observation and physical sensors. In LNCS (Vol. 5091, pp. 29–39). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69132-7_8.
Driscoll, M. P. (1987). Aptitude-treatment interaction research revisited. In the annual meeting of the Association for Educational Communications and Technology (pp. 171–182).
Dumas, D., McNeish, D., & Greene, J. A. (2020). Dynamic measurement: a theoretical–psychometric paradigm for modern educational psychology. Educational Psychologist, 55(2), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2020.1744150.
Eslami Sharbabaki, H. H. V. (2013). The effect of metacognitive strategy training on social skills and problem - solving performance. Journal of Psychology & Psychotherapy, 03(04), 4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0487.1000121.
Essalmi, F., Ayed, L., Ben, J., Jemni, M., Graf, S., & Kinshuk. (2015). Generalized metrics for the analysis of E-learning personalization strategies. Computers in Human Behavior, 48, 310–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.12.050.
Fauth, B., Decristan, J., Rieser, S., Klieme, E., & Büttner, G. (2014). Grundschulunterricht aus Schüler-, Lehrer- und Beobachterperspektive: Zusammenhänge und Vorhersage von Lernerfolg*. Zeitschrift für Pädagogische Psychologie, 28(3), 127–137.
Fisher, A. J., & Boswell, J. F. (2016). Enhancing the personalization of psychotherapy with dynamic assessment and modeling. Assessment, 23(4), 496–506. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191116638735.
Förster, N., & Souvignier, E. (2014). Learning progress assessment and goal setting: effects on reading achievement, reading motivation and reading self-concept. Learning and Instruction, 32, 91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2014.02.002.
Fuchs, L. S. (2004). The past, present, and future of curriculum-based measurement research. School Psychology Review, 33, 188–192.
Harlen, W., & James, M. (1997). Assessment and learning: differences and relationships between formative and summative assessment. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 21, 365–379. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969594970040304, 3.
Hertzog, C., & Nesselroade, J. R. (2003). Assessing psychological change in adulthood: an overview of methodological issues. Psychology and Aging, 18, 639–657. https://doi.org/10.1037/0882-7974.18.4.639, 4.
Holt, P., Dubs, S., Jones, M., & Greer, J. (1994). The state of student modelling. In Student Modelling: The Key to Individualized Knowledge-Based Instruction (pp. 3–35). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-03037-0_1.
Jung, P.-G., McMaster, K. L., Kunkel, A. K., Shin, J., & Stecker, P. M. (2018). Effects of data-based individualization for students with intensive learning needs: a meta-analysis. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 33, 144–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/ldrp.12172, 3.
Kalyuga, S. (2007). Expertise reversal effect and its implications for learner-tailored instruction. Educational Psychology Review, 19(4), 509–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-007-9054-3.
Kalyuga, S., Ayres, P., Chandler, P., & Sweller, J. (2003). The expertise reversal effect. Educational Psychologist, 38(1), 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15326985EP3801_4.
Kelly, D., & Tangney, B. (2006). Adapting to intelligence profile in an adaptive educational system. Interacting with Computers, 18(3), 385–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intcom.2005.11.009.
Kingston, N., & Nash, B. (2011). Formative assessment: a meta-analysis and a call for research. Educational Measurement: Issues and Practice, 30, 28–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-3992.2011.00220.x, 4.
Kirschner, P. A. (2017). Stop propagating the learning styles myth. Computers and Education, 106, 166–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.12.006.
Klauer, K. J. (2011). Lernverlaufsdiagnostik – Konzept, Schwierigkeiten und Möglichkeiten. Empirische Sonderpädagogik, 207–224.
Koedinger, K. R., Brunskill, E., Baker, R. S. J. D., McLaughlin, E. A., & Stamper, J. (2013). New potentials for data-driven intelligent tutoring system development and optimization. AI Magazine, 34(3), 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1609/aimag.v34i3.2484.
Koedinger, K. R., Pavlik, P., McLaren, B. M., & Aleven, V. (2008). Is it better to give than to receive? The assistance dilemma as a fundamental unsolved problem in the cognitive science of learning and instruction. Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society, 2155–2160.
Kumar, A., & Ahuja, N. J. (2020). An adaptive framework of learner model using learner characteristics for intelligent tutoring systems. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput., 989, 425–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8618-3_45.
Lahti, M., Hätönen, H., & Välimäki, M. (2014). Impact of e-learning on nurses’ and student nurses knowledge, skills, and satisfaction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Nursing Studies, Vol. 51, pp. 136–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2012.12.017, 1.
Lee, J., & Park, O. (2008). Adaptive instructional systems. Handbook of research on educational communications and. Handbook of research on educational communications and technology, 469–484.
Lehman, B., Matthews, M., D’Mello, S., & Person, N. (2008). What are you feeling? Investigating student affective states during expert human tutoring sessions. In Intelligent Tutoring Systems (pp. 50–59). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69132-7_10.
Lehman, B., Mello, S. D., Strain, A., Mills, C., Gross, M., Dobbins, A., et al. (2013). Inducing and tracking confusion with contradictions during complex learning. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 22, 85–105. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAI-130025.
Luciana, M., Conklin, H. M., Hooper, C. J., & Yarger, R. S. (2005). The development of nonverbal working memory and executive control processes in adolescents. Child Development, 76, 697–712. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2005.00872.x, 3.
Ma, W., Nesbit, J. C., & Liu, Q. (2014). Intelligent tutoring systems and learning outcomes: a meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 106, 901–918. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0037123.supp.
McLoughlin, C., & Lee, M. J. W. (2009). Personalised learning spaces and self-regulated learning: global examples of effective pedagogy. ASCILITE 2009 - The Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education, 639–645.
Murayama, K., Goetz, T., Malmberg, L.-E., Pekrun, R., Tanaka, A., & Martin, A.-J. (2017). Within-person analysis in educational psychology: importance and illustrations. In British Journal of Educational Psychology Monograph Series II: Psychological Aspects of Education --- Current Trends: The role of competence beliefs in teaching and learning (Vol. 12, pp. 71–87).
Nesselroade, J. R. (1991). The warp and the woof of the developmental fabric. In R. M. Downs, L. S. Liben, & D. S. Palermo (Eds.), Visions of aesthetics, the environment & development: The legacy of Joachim F. Wohlwill (pp. 213–240).
Neubauer, A. B., Dirk, J., & Schmiedek, F. (2019). Momentary working memory performance is coupled with different dimensions of affect for different children: a mixture model analysis of ambulatory assessment data. Developmental Psychology, 55, 754–766. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000668, 4.
Nugteren, M. L., Jarodzka, H., Kester, L., & Van Merriënboer, J. J. G. (2018). Self-regulation of secondary school students: self-assessments are inaccurate and insufficiently used for learning-task selection. Instructional Science, 46, 357–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-018-9448-2, 3.
Nwana, H. S. (1990). Intelligent tutoring systems: an overview. Artificial Intelligence Review, 4(4), 251–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168958.
Pashler, H., McDaniel, M., Rohrer, D., & Bjork, R. (2008). Learning styles concepts and evidence. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, Supplement, 9(3), 105–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6053.2009.01038.x.
Preacher, K. J., & Sterba, S. K. (2019). Aptitude-by-Treatment Interactions in Research on Educational Interventions. Exceptional Children, 85(2), 248–264.
Resing, W. C. M., de Jong, F. M., Bosma, T., & Tunteler, E. (2009). Learning during dynamic testing: variability in strategy use by indigenous and ethnic minority children. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 8(1), 22–37. https://doi.org/10.1891/1945-8959.8.1.22.
Rey, G. D., & Fischer, A. (2013). The expertise reversal effect concerning instructional explanations. Instructional Science, 41(2), 407–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-012-9237-2.
Reyes, M. R., Brackett, M. A., Rivers, S. E., White, M., & Salovey, P. (2012). Classroom emotional climate, student engagement, and academic achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104(3), 700–712.
Rieber, R. W., & Carton, A. S. (1988). The collected works of L. S. Vygotsky. Boston, MA: Springer.
Röcke, C., & Brose, A. (2013). Intraindividual variability and stability of affect and well-being. GeroPsych, 26(3), 185–199. https://doi.org/10.1024/1662-9647/a000094.
Ryan, E. B., Short, E. J., & Weed, K. A. (2008). The role of cognitive strategy training in improving the academic performance of learning disabled children. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 19, 521–529. https://doi.org/10.1177/002221948601900902, 9.
Salden, R. J. C. M., Paas, F., & Van Merrienboer, J. J. G. (2006). Personalised adaptive task selection in air traffic control. Learning and Instruction, 16, 350–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2006.07.007, 4.
Shapiro, K. R. (1975). An overview of problems encountered in aptitude-treatment interaction (ATI) research for instruction. Educational Communication and Technology Journal, 23(2), 227–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02768380.
Slavin, R. E. (1987). Ability grouping and student achievement in elementary schools: a best-evidence synthesis. Review of Educational Research, 57, 293–336. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543057003293, 3.
Slavin, R. E., & Karweit, N. L. (1985). Effects of whole class, ability grouped, and individualized instruction on mathematics achievement. In American Educational Research Journal Fall, 22). http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.3102/00028312022003351(3), 351–367.
Son, L. K., & Metcalfe, J. (2000). Metacognitive and control strategies in study-time allocation. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning Memory and Cognition, 26(1), 204–221. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.26.1.204.
Stecker, P M, Fuchs, L. S., & Fuchs, D. (2005). Using curriculum-based measurement to improve student achievement: review of research. Psychology in the Schools, 42, 795–819. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.20113, 8.
Steenbergen-Hu, S., & Cooper, H. (2014). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of intelligent tutoring systems on college students’ academic learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 106(2), 331–347. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034752.
Sitzmann, T., Kraiger, K., Stewart, D., & Wisher, R. (2006). The comparative effectiveness of web‐based and classroom instruction: A meta‐analysis. Personnel psychology, 59(3), 623–664.
Tobias, S. (1989). Another look at research on the adaptation of instruction to students characteristics. Educational Psychologist, 24(3), 213–227. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep2403_1.
Truong, H. M. (2016). Integrating learning styles and adaptive e-learning system: current developments, problems and opportunities. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, 1185–1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.02.014.
Vanlehn, K. (2011). The relative effectiveness of human tutoring, intelligent tutoring systems, and other tutoring systems. Educational Psychologist, 46(4), 197–221. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2011.611369.
Vogelaar, B., Resing, W. C. M., & Stad, F. E. (2020). Dynamic testing of children’s solving of analogies: differences in potential for learning of gifted and average-ability children. Journal of Cognitive Education and Psychology, 19(1), 43–64. https://doi.org/10.1891/jcep-d-19-00042.
Walkington, C. A. (2013). Using adaptive learning technologies to personalize instruction to student interests: the impact of relevant contexts on performance and learning outcomes. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(4), 932–945. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0031882.
Waxman, H. C., Wang, M. C., Anderson, K. A., Herbert, J., Waxman, C., Wang, M. C., & Anderson, K. A. (1985). Adaptive education and student outcomes : a quantitative synthesis. 78, 228–236.
Wesson, C. L., King, R. P., & Deno, S. L. (1984). Direct and frequent measurement of student performance: if it’s good for us, why don’t we do it? Learning Disability Quarterly, 7, 45–48. https://doi.org/10.2307/1510260.
Yang, T.-C., Hwang, G.-J., & Yang, S. J.-H. (2013). Development of an adaptive learning system with multiple perspectives based on students’ learning styles and cognitive styles. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, Vol. 16, pp. 185–200. https://doi.org/10.2307/jeductechsoci.16.4.185.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. Research was supported by the Stiftung Mercator GmbH. GB was supported by a Jacobs Foundation Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Not Applicable
Consent to Participate
Not Applicable
Consent for Publication
Not Applicable
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Tetzlaff, L., Schmiedek, F. & Brod, G. Developing Personalized Education: A Dynamic Framework. Educ Psychol Rev 33, 863–882 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09570-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09570-w