Abstract
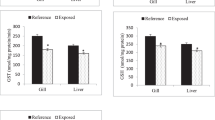
Environmental contaminant-induced aquatic pollution threatens the aquatic biota and causes oxidative stress in the aquatic organisms. Mahananda River, the lifeline of Malda district, West Bengal, India is presently experiencing environmental crisis due to increasing level of contaminants which deteriorate the water quality along with its biota. Puntius sarana is an economically important edible fish species in the River Mahananda that seems to be declining, owing to environmental pollution. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the health status of Puntius sarana by evaluating different oxidative stress biomarkers. The sampling sites were selected according to population density and possible anthropogenic activities around the River Mahananda. Significantly higher concentration of Zn2+ (p < 0.01), Cu2+ (p < 0.05) in different sampling sites has been observed, compared to the control site. Results of the water quality index and water pollution index confirmed the pollution status of different sampling sites. Significant decreases were observed in superoxide dismutase and catalase activity, compared to the control. The decreased values of reduced and oxidized glutathione ratio also indicate the increased oxidative stress of Puntius sarana. The principal component analysis showed that total hardness, calcium hardness, nitrate, manganese, zinc, copper, iron and arsenic were the main descriptors of the aquatic pollution. Therefore, findings of the present study demonstrate the ecotoxicological impacts of various anthropogenic activities which necessitates the need for continuous monitoring of the fresh water resources and its ecosystem from further contamination.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [Subhrajyoti Roy], upon reasonable request.
References
Abdel-Tawwab M, Sharafeldin KM, Mosaad MNM, Ismaiel NEM (2015) Coffee bean in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. diets: effect on growth performance, biochemical status, and resistance to waterborne zinc toxicity. Aquaculture 448:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.06.010
Amoatey P, Baawain MS (2019) Effects of pollution on freshwater aquatic organisms. Water Environ Res 91(10):1272–1287. https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1221
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Ahmed I, Sheikh ZA (2019) Hematological and serum biochemical parameters of five freshwater snow trout fish species from river Jhelum of Kashmir Himalaya, India. Comp Clin Pathol 28(3):771–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-02909-y
Bentsen H (2017) Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids, brain function and mental health. MicrobEcol Health Dis 28(sup1). https://doi.org/10.1080/16512235.2017.1281916
Brix KV, de Boeck G, Baken S, Fort DJ (2022) Adverse outcome pathways for chronic copper toxicity to fish and amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5483, PMID 36148934. 10.1002/etc.5483
Bureau of Indian Standards (2012). In: Drinking water—specification. http://cgwb.gov.in/Documents/WQ-standards.pdf. Accessed 13 September 2022
Central Pollution Control Board (2007). In: Guidelines for water quality monitoring. https://www.mpcb.gov.in/sites/default/files/water-quality/standardsprotocols/GuidelinesforWQMonitoring%5B1%5D.pdf. Accessed10 September 2022
Drasovean R, Murariu G (2021) Water quality parameters and monitoring soft surface water quality using statistical approaches. In: Moujdin IA, Summers JK (ed) promising techniques for wastewater treatment and water quality assessment. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.97372
Dubovskiy IM, Martemyanov VV, Vorontsova YL, Rantala MJ, Gryzanova EV, Glupov VV (2008) Effect of bacterial infection on antioxidant activity and lipid peroxidation in the midgut of Galleria mellonella L. larvae (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 148(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.02.003
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Gioda CR, Lissner LA, Pretto A et al. (2007) Exposure to sublethal concentrations of Zn(II) and Cu(II) changes biochemical parameters in Leporinus obtusidens. Chemosphere 69(1):170–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.008
Griffith OW (1980) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem 106(1):207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(80)90139-6
Hematyar N, Rustad T, Sampels S, Kastrup Dalsgaard T (2019) Relationship between lipid and protein oxidation in fish. Aquac Res 50(5):1393–1403. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14012
Hore M, Bhattacharyya S, Chowdhury H, Roy S (2022) Assessment of water quality index and some oxidative stress biomarkers in Labeo rohita as the indicator of aquatic pollution in different ponds of Malda, West Bengal, India. Fundam Appl Limnol. https://doi.org/10.1127/fal/2022/1443
Hossain MAR, Nahiduzzaman Md, Saha D (2010) Threatened fishes of the world: puntius sarana (Hamilton 1822) (Cyprinidae). Environ Biol Fish 87(3):197–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-010-9579-z
Hossain M, Patra PK (2020) Water pollution index – A new integrated approach to rank water quality. Ecol Indic 117:106668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106668
Ishchenko V (2019) Heavy metals in municipal waste: the content and leaching ability by waste fraction. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 54(14):1448–1456. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2019.1655369
IUCN (2022) IUCN red list of threatened species. https://www.iucnredlist.org/search?query=puntius%20sarana&searchType=species. Accessed 8 September 2022
Kohen R, Nyska A (2002) Oxidation of biological systems: oxidative stress phenomena, antioxidants, redox reactions, and methods for their quantification. Toxicol Pathol 30(6):620–650. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230290166724
Kono Y, Fridovich I (1982) Superoxide radical inhibits catalase. J Biol Chem 257(10):5751–5754. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)83842-5
Kumari K, Khare A, Dange S (2014) The applicability of oxidative stress biomarkers in assessing chromium induced toxicity in the fish Labe orohita. BioMed Res Int 2014:782493. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/782493
Kuppu R, Manoharan S, Uthandakalaipandian R (2018) A study on the impact of water quality on the murrel fish Channa striata and Channa punctata from three major Southern Tamil Nadu rivers, India. RSC Adv 8(21):11375–11387. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA13583A
Li M, Hu C, Zhu Q, Chen L, Kong Z, Liu Z (2006) Copper and zinc induction of lipid peroxidation and effects on antioxidant enzyme activities in the microalga Pavlova viridis (Prymnesiophyceae). Chemosphere 62(4):565–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.06.029
Lionetto MG, Caricato R, Calisi A, Giordano ME, Schettino T (2013) Acetylcholinesterase as a biomarker in environmental and occupational medicine: new insights and future perspectives. BioMed Res Int 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/321213
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the FOLIN phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6
Melegari SP, Perreault F, Costa RHR, Popovic R, Matias WG (2013) Evaluation of toxicity and oxidative stress induced by copper oxide nanoparticles in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat Toxicol 142-143:431–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.09.015
Mishra S, Kumar A, Shukla P (2021) Estimation of heavy metal contamination in the Hindon River, India: an environmetric approach. Appl Water Sci 11(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01331-y
Mohan SV, Nithila P, Reddy SJ (1996) Estimation of heavy metals in drinking water and development of heavy metal pollution index. J Environ Sci Health A Environ Sci Eng Toxicol 31(2):283–289. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529609376357
Muhammad OI, Mahmoud UM, Fazio F, Sayed AE-DH (2018) SDS-PAGE technique as biomarker for fish toxicological studies. Toxicol Rep 5:905–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.08.020
Nayak S, Patnaik L (2021) Acetylcholinesterase, as a potential biomarker of naphthalene toxicity in different tissues of freshwater teleost, Anabas testudineus. J Environ Eng Landsc Manag 29(4):403–409. https://doi.org/10.3846/JEELM.2021.15808
Olivares-Rubio HF, Espinosa-Aguirre JJ (2021) Acetylcholinesterase activity in fish species exposed to crude oil hydrocarbons: a review and new perspectives. Chemosphere 264(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128401
Patil I (2019) Lipid profile in freshwater fish puntius sarana sarana (Hamilton-Buchanan) from industrial polluted river Pawana, Maharashtra, India. IJRAR 6(1):163–169
Pourahmad J, O’Brien PJ (2000) A comparison of hepatocyte cytotoxic mechanisms for Cu2+ and CD2+. Toxicol 143(3):263–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-483X(99)00178-X
Rahman I, Kode A, Biswas SK (2006) Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method. Nat Protoc 1(6):3159–3165. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.378
Rani L, Srivastav AL, Kaushal J, Grewal AS, Madhav S (2022) Heavy metal contamination in the river ecosystem. In: Madhav S, Kanhaiya S, Srivastav A, Singh V, Singh P (ed) Ecological significance of river ecosystems. Elsevier, pp 37-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85045-2.00016-9.
Rani S, Gupta RK, Yadav J (2017) Heavy metal induced alterations in acetylcholinesterase activity of Indian major carps. J Entomol Zool Stud 5(4):818–821
Rimet F (2012) Recent views on river pollution and diatoms. Hydrobiologia 683(1):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0949-0
Rodríguez-Fuentes G, Rubio-Escalante FJ, Noreña-Barroso E, Escalante-Herrera KS, Schlenk D (2015) Impacts of oxidative stress on acetylcholinesterase transcription, and activity in embryos of zebrafish (Danio rerio) following chlorpyrifos exposure. Comp BiochemPhysiol C ToxicolPharmacol172-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CBPC.2015.04.003
Usmani Z, Kumar V (2017) Metal bioaccumulation in tissues of puntius sarana and Labeorohita and its associated risk status: a case study of Damodar River, India. DWT 76:196–211. https://doi.org/10.5004/DWT.2017.20719
Varó I, Navarro JC, Amat F, Guilhermino L (2002) Characterisation of cholinesterases and evaluation of the inhibitory potential of chlorpyrifos and dichlorvos to artemia salina and artemia parthenogenetica. Chemosphere 48(6):563–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00075-9
Winterbourn CC, Metodiewa D (1994) The reaction of superoxide with reduced glutathione. Arch Biochem Biophys 314(2):284–290. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1994.1444
Zhang Z, Zheng Z, Cai J et al. (2017) Effect of cadmium on oxidative stress and immune function of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) by transcriptome analysis. Aquat Toxicol 192(September):171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.09.022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mayukh Hore & Subhrajyoti Roy have developed the research idea and design. Mayukh Hore, Riya Saha, Sanchita Bhaskar, Shreya Mandal and Shubham Bhattacharyya have collected the samples and helped in research work. Mayukh Hore, Riya Saha, Sanchita Bhaskar, Shreya Mandal have done the research work. Mayukh Hore wrote first draft. Subhrajyoti Roy has supervised, analyzed the data statistically and edited the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hore, M., Saha, R., Bhaskar, S. et al. Oxidative stress responses in Puntius sarana collected from some environmentally contaminated areas of River Mahananda, Malda, West Bengal. Ecotoxicology 32, 211–222 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02630-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02630-1