Abstract
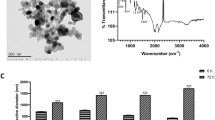
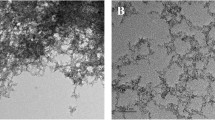
With wide use of nanoparticles, co-exposure of aquatic organisms to nanoparticles and organic pollutants often takes place in the environment. However, the combined effects are still rarely understood. In this study, in order to study the interaction and biological effects of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) and linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS), which acts as a typical surfactant, the freshwater algae Scenedesmus obliquus was exposed to nZVI and LAS individually and in combination for 96 h. According to the inhibition rate of the algae, the toxic effects were investigated by dose-response analysis. Then the combined effect of nZVI and LAS was evaluated using three evaluation models including toxicity unit (TU), additional index (AI), and mixture toxicity index (MTI). The results showed that the 96 h IC50 of nZVI and LAS to Scenedesmus obliquus was 2.464 mmol L−1 and 0.332 mmol L−1, respectively. When nZVI coexisted with LAS at toxic ratio 1:1, the 96 h IC50 value was 1.658 mmol L−1 (shown with nZVI), and the partly additive effect of nZVI mixed with LAS was confirmed. However, when the toxic ratio of nZVI:LAS was 4:1, it showed synergistic effect. In addition, when nZVI mixed with LAS at toxic ratio 1:4, the joint effect is antagonistic effect. In addition, the content of chorophyll in Scenedesmus obliquus, especially the content of chlorophyll a, was decreased with the increase of mixture dose. However, the protein levels did not show significant changes at different mixture doses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson PD, Weber LJ (1975) Proceedings of the International Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment. Institute of Environmental Studies. Toronto
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Baun A, Sorensen SN, Rasmussen RF, Hartmann NB, Koch CB (2008) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of xenobiotic organic compounds in the presence of aqueous suspensions of aggregates of nano-C60. Aquat Toxicol. 86:379–387
Bliss IC (1939) The toxicity of poisons applied jointly. Ann Appl Biol 5:585–615
Brandt KK, Hesselsoe M, Roslev P, Henriksen K, Sorensen J (2001) Toxic effects of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate on metabolic activity, growth rate, and microcolony formation of Nitrosomonas and Nitrosospira strains. Appl Environ Microb 67:2489–2498
Carpenter AW, Laughton SN, Wiesner MR (2015) Enhanced biogas production from nanoscale zero valent iron-amended anaerobic bioreactors. Environ Eng Sci 32:647–655
Chang MC, Kang HY (2009) Remediation of pyrene-contaminated soil by synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. J Environ Sci Health 44:576–582
Chen P, Su C, Tseng C, Tan S, Cheng C (2011) Toxicity assessments of nanoscale zerovalent iron and its oxidation products in medaka (Oryzias latipes) fish. Mar Pollut Bull 63:339–346
Cheng R, Li G, Shi L, Xue X, Kang M, Zheng X (2016) The mechanism for bacteriophage f2 removal by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Res 105:429–435
Diao M, Yao M (2009) Use of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in inactivating microbes. Water Res 43:5243–5251
El-Temsah YS, Joner EJ (2012) Ecotoxicological effects on earthworms of fresh and aged nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) in soil. Chemosphere 89:76–82
Farkas J, Peter H, Ciesielski TM, Thomas KV, Sommaruga R, Salvenmoser W et al. (2015) Impact of TiO2 nanoparticles on freshwater bacteria from three Swedish lakes. Sci Total Environ 535:85–93
Fu F, Dionysiou DD, Liu H (2014) The use of zero-valent iron for groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment: a review. J Hazard Mater 267:194–205
Handy RD, von der Kammer F, Lead JR, Hassellov M, Owen R, Crane M (2008) The ecotoxicology and chemistry of manufactured nanoparticles. Ecotoxiclogy 17:287–314
Hund-Rinke K, Simon M (2006) Ecotoxic effect of photocatalytic active nanoparticles TiO2 on algae and daphnids. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:225–232
Iswarya V, Sharma V, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2017) Impact of tetracycline on the toxic effects of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles towards the freshwater algal species, Scenedesmus obliquus. Aquat Toxicol 193:168–177
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem Phys Pflanzen 167:191–194
Jurado E, Fernandez-Serrano M, Lechuga M, Rios F (2012) Environmental impact of ether carboxylic derivative surfactants. J Surfactants Deterg 15:1–7
Keller AA, Mcferran S, Lazareva A, Suh S (2013) Global life cycle releases of engineered nanomaterials. J Nanopart Res 15:1692
Kong X, Wei Y, Xu S, Liu J, Li H, Liu Y et al. (2016) Inhibiting excessive acidification using zero-valent iron in anaerobic digestion of food waste at high organic load rates. Bioresour Technol 211:65–71
Könemann (1981) Fish toxicity tests with mixtures of more than twochemicals a proposal for a quantitative approach and experimental results. Toxicology 19:229–238
Lechuga M, Fernández-Serrano M, Jurado E, Núñez-Olea J, Ríos F (2016) Acute toxicity of anionic and non-ionic surfactants to aquatic organisms. Ecotox Environ Safe 125:1–8
Lee J, Bartelt-Hunt SL, Li Y, Morton M (2015) Effect of 17 beta-estradiol on stability and mobility of TiO2 rutile nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 511:195–202
Lei C, Zhang L, Yang K, Zhu L, Lin D (2016) Toxicity of iron-based nanoparticles to green algae: effects of particle size, crystal phase, oxidation state and environmental aging. Environ Pollut 218:505–512
Liu D, Liu H, Wang S, Chen J, Xia Y (2018) The toxicity of ionic liquid 1-decylpyridinium bromide to the algae Scenedesmus obliquus: growth inhibition, phototoxicity, and oxidative stress. Sci Total Environ 622-623:1572–1580
Magesky A, Pelletier E (2015) Toxicity mechanisms of ionic silver and polymer-coated silver nanoparticles with interactions of functionalized carbon nanotubes on early development stages of sea urchin. Aquat Toxicol 167:106–123
Marking L (1977) Method for Assessing Additive Toxicity of Chemical Mixtures. Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Evaluation (eds.) F. Mayer and J. Hamelink), ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA. pp.99–108
Marsalek B, Jancula D, Marsalkova E, Mashlan M, Safarova K (2012) Multimodal action and selective toxicity of zerovalent iron nanoparticles against cyanobacteria. Environ Sci Technol 46:2316–2323
Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Oprckal P, Mladenovic A, Vidmar J, Pranjic AM, Milacic R, Scancar J (2017) Critical evaluation of the use of different nanoscale zero-valent iron particles for the treatment of effluent water from a small biological wastewater treatment plant. Chem Eng J 321:20–30
Pineda Flores G, Monterrubio Badillo C, Hernandez Cortazar M, Nolasco Hipolito C, Sanchez Perez R, Garcia Sanchez I (2010) Toxic effects of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate, anthracene and their mixture on growth of a microbial consortium isolated from polluted sediment. Rev Int Contaminación Ambiental. 26:39–46
Rasheed QJ, Pandian K, Muthukumar K (2011) Treatment of petroleum refinery wastewater by ultrasound-dispersed nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. Ultrason Sonochem 18:1138–1142
Segura Y, Martinez F, Antonio Melero J (2016) Simple and efficient treatment of high-strength industrial waste water using commercial zero-valent iron. Chem Pap 70:1059–1065
Sims DA, Gamon JA (2002) Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sens Environ. 81:337–354
Sprague JB, Ramsay BA (1965) Lethal levels of mixed copper-zinc solutions for Juvenile Salmon. J the Fish Res Board of Canada. 22:425–432
Stanley JK, Laird JG, Kennedy AJ, Steevens JA (2016) Sublethal effects of multi-walled carbon nanotube exposure in the invertebrate Daphnia magna. Environ Toxicol Chem 35:200–204
Tao X, Yu Y, Fortner JD, He Y, Chen Y, Hughes JB (2015) Effects of aqueous stable fullerene nanocrystal (nC60) on Scenedesmus obliquus: evaluation of the sub-lethal photosynthetic responses and inhibition mechanism. Chemosphere 122:162–167
Utsunomiya A, Watanuki T, Matsushita K, Tomita I (1997) Toxic effects of linear alkylbenzenesulfonate and quaternary alkylammonium chloride on Dunaliella sp. as measured by H-1-NMR analysis of glycerol. Chemosphere 35:1215–1226
Valko M, Morris H, Cronin M (2005) Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 12:1161–1208
Wang D, Lin Z, Yao Z, Yu H (2014) Surfactants present complex joint effects on the toxicities of metal oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 108:70–75
Wang Z, Quik JTK, Song L, Van den Brandhof E, Wouterse M, Peijnenburg WJGM (2015) Humic substances alleviate the aquatic toxicity of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silver nanoparticles to organisms of different trophic levels. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:1239–1245
Wang Z, Wang S, Peijnenburg WJGM (2016) Prediction of joint algal toxicity of nano-CeO2/nano-TiO2 and florfenicol: independent action surpasses concentration addition. Chemosphere 156:8–13
Wei C, Zhang Y, Guo J, Han B, Yang X, Yuan J (2010) Effects of silica nanoparticles on growth and photosynthetic pigment contents of Scenedesmus obliquus. J Environ Sci 22:155–160
Xia T, Kovochich M, Brant J, Hotze M, Sempf J, Oberley T (2006) Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett. 6:1794–1807
Ye N, Wang Z, Fang H, Wang S, Zhang F (2017) Combined ecotoxicity of binary zinc oxide and copper oxide nanoparticles to Scenedesmus obliquus. Environ Lett 52:555–560
Zhang T, Li X, Lu Y, Liu P, Zhang C, Luo H (2014) Joint toxicity of heavy metals and chlorobenzenes to pyriformis Tetrahymena. Chemosphere. 104:177–183
Zhang X, Wang Z, Wang S, Fang H, Zhang F, Wang D (2017) Impacts of dissolved organic matter on aqueous behavior of nano/micron-titanium nitride and their induced enzymatic/non-enzymatic antioxidant activities in Scenedesmus obliquus. J Environ Sci Health A 52:23–29
Acknowledgements
This paper is to commemorate Professor Shu-Pei Cheng. And this work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51778618), which is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, R., Liu, Yp., Chen, Yh. et al. Combined effect of nanoscale zero-valent iron and linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) to the freshwater algae Scenedesmus obliquus. Ecotoxicology 30, 1366–1375 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02294-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02294-1