Abstract
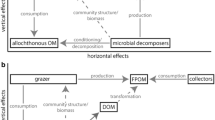
Biofilms are a consortium of communities of organisms that live in syntrophic relationships and present a higher organization level than that of individual cells. Biofilms dominate microbial life in streams and rivers, enable crucial ecosystem processes, contribute to global biogeochemical flows and represent the main active bacterial life form. Epilithic biofilms are the main biomass found in rivers; their exposure to contaminants can lead to changes in their structure and composition. The composition of these communities is influenced by physicochemical factors, temperature, light and prior exposure to pollutants, among other factors, and it can be used for water quality monitoring purposes. The heterogenous composition of biofilms enables them to accumulate compounds in an integrative manner. Moreover, the availability of several sorption sites and their likely saturation can contribute to bioaccumulation. In aquatic environments, biofilms are also susceptible to the acquisition of antibiotic resistance genes and participate in their dissemination. Anthropic pressure intensification processes continuously expose water resources and, consequently, biofilm communities to different contamination sources. Therefore, the use of biofilms to indicate environmental pollution is reinforced by the progress of studies on the subject. Biofilm communities’ response to pollutants in aquatic environments can be mainly influenced by the presence of different organisms, which may change due to community development or age. The current research aims to review studies about biofilm contamination and highlight the importance of biofilm use to better evaluate and maintain the quality of water bodies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khazrajy OSA, Boxall ABA (2016) Impacts of compound properties and sediment characteristics on the sorption behaviour of pharmaceuticals in aquatic systems. J Hazard Mater 317:198–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.065
Almakki A, Jumas-Bilak E, Marchandin H, Licznar-Fajardo P (2019) Antibiotic resistance in urban runoff. Sci Total Environ 667:64–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.183
Ancion P-Y, Lear G, Neale M, Roberts K, Lewis GD (2014) Using biofilm as a novel approach to assess stormwater treatment efficacy. Water Res 49:406–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.023
Atterby C, Ramey AM, Hall GG, Järhult J, Börjesson S, Bonnedahl J (2016) Increased prevalence of antibiotic-resistant E. coli in gulls sampled in Southcentral Alaska is associated with urban environments. Infect Ecol Epidemiol 6:32334. https://doi.org/10.3402/iee.v6.32334
Aubertheau E, Stalder T, Mondamert L, Ploy M, Dagot C, Labanowski J (2017) Impact of wastewater treatment plant discharge on the contamination of river biofilms by pharmaceuticals and antibiotic resistance. Sci Total Environ 579:1387–1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.136
Aubertot JN, Barbier JM, Carpentier A, Grill JJ, Guichard L, Lucas P, Savary S, Savini I, Voltz M (éditeurs) (2005) Pesticides, agriculture et environnement. Réduire l’utilisation des pesticides et limiter leurs impacts environnementaux. Expertise scientifique collective, synthèse du rapport, INRA et Cemagref, France, p 64
Augspurger C, Küsel K (2010) Flow velocity and primary production influences carbon utilization in nascent epilithic stream biofilms. Aquat Sci 72(2):237–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-009-0126-y
Barra Caracciolo A, Topp E, Grenni P (2015) Pharmaceuticals in the environment: biodegradation and effects on natural microbial communities. A review. J Pharm Biomed Anal 106:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2014.11.040
Bastos MC, Santos DR, Castro Lima JAM, Le Guet T, Santos MAS, Zanella R, Aubertheau, E, Mondamert L, Caner L, Labanowski J (2018) Presence of anthropogenic markers in water: a case study of the Guaporé River watershed, Brazil. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 46(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201700019
Battin TJ, Besemer K, Bengtsson MM, Romaní AM, Packmann AI (2016) The ecology and biogeochemistry of stream biofilms. Nat Rev Microbiol 14(4):251–263. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.15
Bauman RW (2008) Microbiology with diseases by body system: books a la carte. Benjamin-Cummings, Prentice Hall, Hoboken, New Jersey
Bergeron S, Boopathy R, Nathaniel R, Corbin A, LaFleur G (2015) Presence of antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes in raw source water and treated drinking water. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 102:370–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.04.017
Bhattacharyya A, Haldar A, Bhattacharyya M, Ghosh A (2019) Anthropogenic influence shapes the distribution of antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) in the sediment of Sundarban estuary in India. Sci Total Environ 647:1626–1639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.038
Bielen A, Šimatović A, kosić-vukšić J et al. (2017) Negative environmental impacts of antibiotic-contaminated effluents from pharmaceutical industries. Water Res 126:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.09.019
Bîrluţiu RM, Bîrluţiu V, Cismasiu RS, Mihalache P, Mihalache M (2017) Bacterial biofilm: a mini-review of an emerging life form of bacteria. Acta Med Transilvanica 22(4):68–71
Bonnineau C, Artigas J, Chaumet B, Dabrin A, Faburé J, Ferrari BJD, Lebrun JD, Margoum C, Mazzella N, Miège C, Morin S, Uher E, Babut M, Pesce S (2020) Role of biofilms in contaminant bioaccumulation and trophic transfer in aquatic ecosystems: current state of knowledge and future challenges. In: Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (Continuation of Residue Reviews). Springer, New York, pp 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/398_2019_39
Bradac P, Wagner B, Kistler D, Traber J, Behra R, Sigg L (2010) Cadmium speciation and accumulation in periphyton in a small stream with dynamic concentration variations. Environ Pollut 158:641–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.10.031
Bricheux G, Le Moal G, Hennequin C, Coffe G, Donnadieu F, Portelli C, Bohatier J, Forestier C (2013) Characterization na devolution of natural aquatic biofilm communities exposed in vitro to herbicides. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 88:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.11.003
Caixeta DS, Scarpa TH, Brugnera DF, Freire DO, Alves E, Abreu LR, Piccoli RH (2012) Chemical sanitizers to control biofilms formed by two Pseudomonas species on stainless steel surface. Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos 32(1):142–150. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612012005000008
Carles L, Gardon H, Joseph L, Sanchís J, Farré M, Artigas J (2019) Meta-analysis of glyphosate contamination in surface waters and dissipation by biofilms. Environ Int 124:284–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.064
Chaumet B, Morin S, Boutry S, Mazzella N (2019a) Diuron sorption isotherms in freshwater biofilms. Sci Total Environ 651:1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.286
Chaumet B, Morin S, Hourtané O, Artigas J, Delest B, Eon M, Mazzella N (2019b) Flow conditions influence diuron toxico kinetics and toxico dynamics in fresh water biofilms. Sci Total Environ 652:1242–1251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.265
Chonova T, Labanowski J, Cournoyer B, Chardon C, Keck F, Laurent E, Mondamert L, Vasselon V, Wiest L, Bouchez A (2018) River biofilm community changes related to pharmaceutical loads emitted by a wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(10):9254–0264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0024-0
Clasen B, Loro VL, Murussi CR, Tiecher TL, Moraes B, Zanella R (2018) Bioaccumulation and oxidative stress caused by pesticides in Cyprinus carpio reared in a rice-fish system. Sci Total Environ 626:737–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.154
Corcoll N, Casellas M, Huerta B, Guasch H, Acuña V, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Serra-Compte A, Barceló D, Sabater S (2015) Effects of flow intermittency and pharmaceutical exposure on the structure and metabolism of stream biofilms. Sci Total Environ 503-504:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.093
Corsaro D, Pages GS, Catalan V, Loret J, Greub G (2010) Biodiversity of amoebae and amoeba-associated bacteria in water treatment plants. Int J Hyg Environ Health 213:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2010.03.002
de Castro Lima JAM, Labanowski J, Bastos MC et al. (2020) “Modern agriculture” transfers many pesticides to watercourses: a case study of a representative rural catchment of southern Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:10581–10598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06550-8
Dias C, Borges A, Oliveira D, Martinez-Murcia A, Saavedra MJ, Simões M (2018) Biofilms and antibiotic susceptibility of multidrug-resistant bacteria from wild animals. Peer J 6:e4974. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4974
Dobor J, Varga M, Záray G (2012) Biofilm controlled sorption of selected acidic drugs on river sediments characterized by different organic carbon content. Chemosphere 87:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.11.067
Dorigo U, Leboulanger C, Berard A, Bouchez A, Humbert J-F, Montuelle B (2007) Lotic biofilm community structure and pesticide tolerance along a contamination gradient in a vineyard area. Aquat Microb Ecol 50:91–102. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame01133
Duong TT, Morin S, Coste M, Herlory O, Feurtet-Mazel A, Boudou A (2010) Experimental toxicity and bioaccumulation of cadmium in freshwater periphytic diatoms in relation with biofilm maturity. Sci Total Environ 408:552–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.015
Duong TT, Morin S, Herlory O, Feurtet-Mazel A, Coste M, Boudou A (2008) Seasonal effects of cadmium accumulation in periphytic diatom communities of freshwater biofilms. Aquat Toxicol 90:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.07.012
Džidić S, Šušković J, Kos B (2008) Antibiotic resistance mechanisms in bacteria: biochemical and genetic aspects. Food Technol Biotechnol 46(1):11–21
Edwards SJ, Kjellerup BV (2013) Applications of biofilms in bioremediation and biotransformation of persistent organic pollutants, pharmaceuticals/personal care products, and heavy metals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9909–9921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5216-z
Faburé J, Dufour M, Autret A, Uher E, Fechner LC (2015) Impact of an urban multi-metal contamination gradient: Metal bioaccumulation and tolerance of river biofilms collected in different seasons. Aquat Toxicol 159:276–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.12.014
Fernandes G, Aparicio V, Bastos MC, Geronimo E, Labanowski J, Prestes OD, Zanella R, Rheinheimer DS (2019) Indiscriminate use of glyphosate impregnates river epilithic biofilms in southern Brazil. Sci Total Environ 651:1377–1387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.292
Findlay S (2010) Stream microbial ecology. J North Am Benthological Soc 29:170–181. https://doi.org/10.1899/09-023.1
Finley RL, Collignon P, Larsson DG, Mcewen SA, Li XZ, Gaze WH, Reid-Smith R, Timinouni M, Graham DW, Topp E (2013) The scourge of antibiotic resistance: the important role of the environment. Clin Infect Dis 57:704–710. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit355
Flemming H-C, Leis A (2002) In: Bitton G (ed) In encyclopedia of environmental microbiology, vol. 5. Wiley-Interscience, p 2958–2967
Flemming H-C, Wingender J (2001) Relevance of microbial extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs)—part I: Structural and ecological aspects. Water Sci Technol 43:1–8. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2001.0326
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2415
Flemming HC, Wingender J, Szewzyk U, Steinberg P, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S (2016) Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:563–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.94
Gaylarde PM, Gaylarde CC (2000) Algae and cyanobacteria on painted buildings in Latin America. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 46:93–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0964-8305(00)00074-3
Geiszinger A, Bonnineau C, Faggiano L, Guasch H, Lopez-Doval JC, Proia L, Ricart M, Ricciardi F, Romani A, Rotter S, Munoz I, Schmitt-Jansen M, Sabater S (2009) The relevance of the community approach linking chemical and biological analyses in pollution assessment. Trends Anal Chem 28:619–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2009.02.012
Glassmeyer ST, Furlong ET, Kolpin DW et al. (2005) Transport of chemical and microbial compounds from known wastewater discharges: potential for use as indicators of human fecal contamination. Environ Sci Technol 39:5157–5169. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048120k
Guo X, Yang Y, Lu D, Niu Z, Feng J, Chen Y, Tou F, Garner E, Xu J, Liu M, Hochella MF (2018) Biofilms as a sink for antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the Yangtze Estuary. Water Res 129(1):277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.11.029
Headley JV, Gandrass J, Kuballa J, Peru KM, Gong Y (1998) Rates of sorption and partitioning of contaminants in river biofilm. Environ Sci Technol 32:3968–3973. https://doi.org/10.1021/es980499l
Huerta B, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Nannou C, Nakis L, Ruhí A, Acuña V, Sabater S, Barcelo D (2016) Determination of a broad spectrum of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in biofilm from a waste water treatment plant-impacted river. Sci Total Environ 540:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.049
Kaeseberg T, Schubert S, Oertel R, Zhang J, Berendonk TU, Krebs P (2018) Hot spots of antibiotic tolerant and resistant bacterial subpopulations in natural freshwater biofilm communities due to inevitable urban drainage system overflows. Environ Pollut 242:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.081.
Karickhoff S, Brown D, Scott T (1979) Sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments. Water Res 13:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(79)90201-X
Keller N, Bruchmann J, Sollich T et al. (2019) Study of biofilm growth on slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces made from Fluoropor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:4480–4487. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b12542
Kim Tiam S, Fauvelle V, Morin S, Mazzella N (2016) Improving toxicity assessment of pesticide mixtures: the use of polar passive sampling devices extracts in microalgae toxicity tests. Front Microbiol 7:1388. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01388
Konhauser KO, Fyfe WS, Schultze-Lam S, Ferris FG, Beveridge TJ (1994) Iron phosphate precipitation by epilithic microbial biofilms in Arctic Canada. Can J Earth Sci 31(8):1320–1324. https://doi.org/10.1139/e94-114
Laurent E (2013) Evaluation de l’état de contamination des bassins versants par les résidus de médicaments: Utilisation des biofilms épilithiques comme marqueur d’imprégnation du milieu. Thesis, Université de Poitiers, Poitiers (FR)
Lawrence JR, Kopf G, Headley JV, Neu TR (2001) Sorption and metabolism of selected herbicides in river biofilm communities. Can J Microbiol 47:634–641. https://doi.org/10.1139/w01-061
Lear G, Anderson MJ, Smith JP, Boxen K, Lewis GD (2008) Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of the bacterial communities in stream epilithic biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 65(3):463–473. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00548.x
Lear G, Lewis GD (2009) Impact of catchment land use on bacterial communities within stream biofilms. Ecol Indic 9(5):848–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2008.10.001
Li W, Shi Y, Gao L et al. (2012) Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 89:1307–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.079
Livermore DM (2003) Bacterial resistance: origins, epidemiology, and impact bacterial resistance. Clin Infect Dis 36(1):11–23. https://doi.org/10.1086/344654
Martins AF, Mallmann CA, Arsand DR et al. (2011) Occurrence of the antimicrobials sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in hospital effluent and study of their degradation products after electrocoagulation. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water 39:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201000126
Mcdougald D, Rice SA, Barraud N, Steinberg PD, Kjelleberg S (2012) Should we stay or should we go: mechanisms and ecological consequences for biofilm dispersal. Nat Rev Microbiol 10(1):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2695
Meylan S, Behra R, Sigg L (2003) Accumulation of copper and zinc in periphyton in response to dynamic variations of metal speciation in freshwater. Environ Sci Technol 37:5204–5212. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034566+
Miguel ALCSF (2007) Aplicação da técnica de PCR na pesquisa de bactérias patogénicas em biofilmes de condutas e reservatórios de água do sistema de distribuição da EPAL. Dissertação, Instituto Superior Técnico da Universidade Técnica de Lisboa
Mokh S, EL Khatib M, Koubar M et al. (2017) Innovative SPE-LC-MS/MS technique for the assessment of 63 pharmaceuticals and the detection of antibiotic-resistant-bacteria: a case study natural water sources in Lebanon. Sci Total Environ 609:830–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.230
Mori N, Sugitani K, Yamamoto M, Tomioka R, Sato M, Harada N (2018) Major and minor elemental compositions of streambed biofilms andits implications of riverine biogeochemical cycles. Environ Pollut 243:308–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.007
Morin S, Duong TT, Dabrin A, Coynel A, Herlory O, Baudrimont M, Delmas F, Durrieu G, Schäfer J, Winterton P, Blanc G, Coste M (2008) Long-term survey of heavy-metal pollution, biofilm contamination and diatom community structure in the Riou Mort watershed, South-West France. Environ Pollut 151:532–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.04.023
Moyaert H, Morrissey I, De Jong A, El Garch F, Klein U, Ludwig C, Thiry J, Youala M (2017) Antimicrobial susceptibility monitoring of bacterial pathogens isolated from urinary tract infections in dogs and cats across Europe: com Path results. Microb Drug Resist 23:391–403. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2016.0110
O’Neill J (2014) Antimicrobial résistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. Wellcome Trust, London, p 20
Papageorgiou M, Kosma C, Lambropoulou D (2016) Seasonal occurrence, removal, mass loading and environmental risk assessment of 55 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Central Greece. Sci Total Environ 543:547–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.047
Paule A, Roubeix V, Lauga B, Duran R, Delmas F, Paul E, Rols JL (2013) Changes in tolerance to herbicide toxicity throughout development stages of phototrophic biofilms. Aquat Toxicol 144-145:310–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.09.024
Pesce S, Bouchez A, Montuelle B (2011) Effects of organic herbicides on phototrophic microbial communities in freshwater ecosystems. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 214:87–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-0668-6.
Proia L, Osorio V, Soley S, Köck-Schulmeyer M, Pérez S, Barceló D, Romaní AM, Sabater S (2013) Effects of pesticides and pharmaceuticals on biofilms in a highly impacted river. Environ Pollut 178:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.02.022
Proia L, Von Schiller D, Sànchez-Melsió A, Sabater S, Borrego CM, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Balcázar JL (2016) Occurrence and persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in river biofilms after wastewater inputs in small rivers. Environ Pollut 210:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.035
Pyl’nik SV, Dueck JH, Min’kov LL (2007) Equilibrium thickness of a biofilm. Theor Found Chem Eng 41:430–435. https://doi.org/10.1134/S004057950704015X
Rabiet M, Margoum C, Gouy V, Carluer N, Coquery M (2010) Assessing pesticide concentrations and fluxes in the stream of a small vineyard catchment e effect of sampling frequency. Environ Pollut 158:737–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.10.014
Rheinheimer DS, de Castro Lima JAM, de Vargas JPR et al. (2020) Pesticide Bioaccumulation in Epilithic Biofilms as Biomarkers of agricultural activities in a representative watershed. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08264-8
Rinta-Kanto JM, Lehtola MJ, Vartiainen T, Martikainen PJ (2004) Rapid enumeration of virus-like particles in drinking water samples using SYBR green I-staining. Water Res 38:2614–2618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.03.008
Romaní AM, Amalfitano S, Artigas J, Fazi S, Sabater S, Timoner X, Ylla I, Zoppini I (2017) Microbial biofilm structure and organic matter use in mediterranean streams. Hydrobiologia 719:43–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1302-y
Romaní AM, Fund K, Artigas J, Schwartz T, Sabater S, Obst U (2008) Relevance of polymeric matrix enzymes during biofilm formation. Microb Ecol 56:427–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-007-9361-8
Rosi EJ, Bechtold HA, Snow D, Rojas M, Reisinger AJ, Kelly JJ (2018) Urban stream microbial communities show resistance to pharmaceutical exposure. Ecosphere 9(1):e02041. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.2041
Ruhí A, Acuña V, Barceló D et al. (2016) Bioaccumulation and trophic magnification of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in a Mediterranean river food web. Sci Total Environ 540:250–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.009
Sabater S, Guasch H, Ricart M, Romaní A, Vidal G, Klunder C, Schmitt-Jansen M (2007) Monitoring the effect of chemicals on biological communities. The biofilm as an interface. Anal Bioanal Chem 387(4):1425–1434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-1051-8
Sabater S, Timoner X, Borrego C, Acuña V (2016) Stream biofilm responses to flow intermittency: from cells to ecosystems. Front Environ Sci 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2016.00014
Santos M, Peixoto S, Pereira JL, Luís AT, Henriques I, Gonçalves FJM, … Vidal T (2019) Using flow cytometry for bacterioplankton community analysis as a complementary tool to Water Framework Directive to signal putatively impacted sites. Sci Total Environ 133754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133754
Schorer M, Eisele M (1997) Accumulation of inorganic and organic pollutants by biofilms in the aquatic environment. Water Air Soil Pollut 99:651–659. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018384616442
Serra-Compte A, Corcoll N, Huerta B, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Sabater S, Barceló D, Álvarez-Muñoz D (2018) Fluvial biofilms exposed to desiccation and pharmaceutical pollution: new insights using metabolomics. Sci Total Environ 15:1382–1388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.258
Biggs BJF (1996) Patterns in benthic algae of streams, Chapter 2, pp. 31–56. In: Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (eds), Algal ecology: freshwater benthic ecosystems. Academic Press, San Diego, California, p 753
Stoodley P, Sauer K, Davies DG, Costerton JW (2002) Biofilms as complex differentiated communities. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:187–209. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160705
Sutherland IW (1984) Microbial exopolysaccarides—their role in microbial adhesion in aqueous systems. Crit Rev Microbiol 10(2):173–201. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408418209113562
Teunis P, Rutjes S, Westrell T, De Roda Husman A (2009) Characterization of drinking water treatment for virus risk assessment. Water Res 43:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.10.049
Tien C-J, Chen CS (2013) Patterns of metal accumulation by natural river biofilms during their growth and seasonal succession. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 64:605–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9856-2
Tlili A, Dorigo U, Montuelle B, Margoum C, Carluer N, Gouy V, Bouchez A, Bérard A (2008) Responses of chronically contaminated biofilms to short pulses of diuron. An experimental study simulating flooding events in a small river. Aquat Toxicol 87:252–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.02.004
Tlili A, Montuelle B, Berard A, Bouchez A (2011) Impact of chronic and acute pesticide exposures on periphyton communities. Sc Total Environ 409:2102–2113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.01.056
Tortora GJ, Funke BR, Case CL (2017) Microbiologia, 12th edn. Artmed, Porto Alegre, p 9390
Vercraene-Eairmal M, Lauga B, Saint Laurent S, Mazella N, Boutry S, Simon M, Solange K, Delmas F, Duran R (2010) Diuron biotransformation and its effects on biofilm bacterial community structure. Chemosphere 81:837–843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.08.014
Vert M, Doi Y, Hellwich K, Hess M, Hodge P, Kubisa P, Rinaudo M, Schué F (2012) Terminology for biorelated polymers and applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012). Pure Appl Chem 84(2):377–410. https://doi.org/10.1351/PAC-REC-10-12-04
Vidal JM, Miranda CD, De la Fuente M et al. (2020) Formation of biofilms of the salmon pathogen Flavobacterium psychrophilum in differents surfaces using the CDC biofilm reactor. Aquaculture 514:734459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734459
Villeneuve A, Montuelle B, Bouchez A (2011) Effects of flow regime and pesticides on periphytic communities: evolution and role of biodiversity. Aquat Toxicol 102:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.01.004
Wannmacher L (2004) Uso indiscriminado de antibióticos e resistência microbiana: Uma guerra perdida? Organção Pan-Am da Saúde 1(4):1–6
Wang J, Li G, Yin H, An T (2020) Bacterial response mechanism during biofilm growth on different metal material substrates: EPS characteristics, oxidative stress and molecular regulatory network analysis. Environ Res 185:109451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109451
Williams DL, Smith SR, Peterson BR et al. (2019) Growth substrate may influence biofilm susceptibility to antibiotics. PLoS ONE 14:e0206774. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206774
Writer JH, Barber LB, Ryan JN, Bradley PM (2011) Biodegradation and attenuation of steroidal hormones and alkylphenols by stream biofilms and sediments. Environ Sci Technol 45:4370–4376. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2000134
Yin J, Shao B, Zhang J, Li K (2010) A preliminary study on the occurrence of cytostatic drugs in hospital effluents in Beijing, China. Bull Environ Contamination Toxicol 84:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9884-4
Zacheus OM, Lehtola MJ, Korhonen LK, Martikainen PJ (2001) Soft deposits, the key site for microbial growth in drinking water distribution networks. Water Res 35:1757–1765. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(00)00431-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandes, G., Bastos, M.C., de Vargas, J.P.R. et al. The use of epilithic biofilms as bioaccumulators of pesticides and pharmaceuticals in aquatic environments. Ecotoxicology 29, 1293–1305 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02259-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-020-02259-4