Abstract
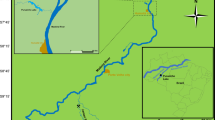
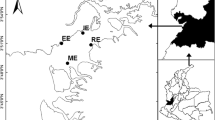
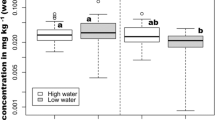
Hg accumulation in fish is influenced by several factors including seasonality. In the Amazon, ecosystems are marked by strong seasonal variation in precipitation, which leads to drastic changes in the water level of lakes and rivers. The aim of this study was to evaluate Hg levels in muscle of detritivorous, herbivorous and omnivorous fish from an Amazon lake (Madeira River Basin, Amazonas, Brazil) over four seasons (rising water, high water, falling water and low water). We hypothesized that total Hg concentration varies during the seasons. The results indicate that total Hg levels in detritivorous fish were higher in rising and low water seasons while in herbivorous and omnivorous fish the total Hg concentration was higher during the rising water season. The hypothesis was supported by the results. Additionally, the study provides evidence that Hg levels in fish with different feeding habits are influenced by the flood pulse of the Amazon region.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agência Nacional de Águas (ANA) (2019): Rede Hidrometeorológica Nacional, Sistema HIDRO - Telemetria, Estação Humaitá, Código 15630000. http://www.snirh.gov.br/gestorpcd/gerarGrafico.aspx
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (2017) U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Priority list of hazardous substances. Digital report. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/. Accessed 4 Dec 2017
Almeida R, Bernardi JVE, Oliveira RC, Carvalho DP, Manzatto AG, Lacerda LD, Bastos WR (2014) Flood pulse and spatial dynamics of Mercury in sediments in Puruzinho Lake, Brazilian Amazon. Acta Amazonica 44:99–106
Araujo-Lima CARM, Forsberg BR, Victoria R, Martinelli LA (1986) Energy sources for detritivorous fishes in the Amazon. Science 234:1256–1258
Bastos WR, Malm O, Pfeifer WC, Cleary D (1998) Establishment and analytical quality control of laboratories for Hg determination in biological and geological samples in the Amazon, Brazil. Rev. Ciên. Cult. 50:255–260
Bastos WR, Rebelo MF, Fonseca MF, Almeida R, Malm O (2008) A description of mercury in fishes from the Madeira River Basin, Amazon, Brazil. Acta Amazonica 38:431–438
Batley GE (1983) The current status of trace element speciation studies in natural waters. In: Leppard GG (Ed.) Trace element speciation in surface waters and its ecological implications. Plenum, New York, NY, pp. 17–36
Bernhoft RA (2011) Mercury toxicity and treatment: a review of literature. J Environ Public Health 2012:460508
Bosch AC, O’Neill B, Sigge GO, Kerwath SE, Hoffman LC (2016) Mercury accumulation in Yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) with regards to muscle type, muscle position and fish size. Food Chem 190:351–356
Brito BC, Forsberg BR, Kasper D, Amaral JHF, Vasconcelos MRR, Sousa OP, Cunha FAG, Bastos WR (2017) The influence of inundation and lake morphometry on the dynamics of mercury in the water and plankton in an Amazon floodplain lake. Hydrobiologia 790:35–48
Campbell LM, Balirwa J, Dixon D, Hecky R (2010) Biomagnification of mercury in fish from Thruston Bay, Napoleon Gulf, Lake Victoria (East Africa). African J Aquatic Sci 29:91–96
Carroll RWH, Memmott J, Warwick JJ, Fritsen CH, Bonzongo JC, Acharya K (2011) Temporal variation of mercury associated with different phytoplankton size fractions in Lahontan Reservoir, Nevada. Water Air Soil Pollut 217:221–232
Cella-Ribeiro A, Torrente-Vilara G, Lima-Filho JA, Doria CRC (2017) Ecologia e Biologia de peixes do Rio Madeira. EDUFRO, Porto Velho
Chen CY, Kamman N, Williams J, Bugge D, Taylor V, Jackson B, Miller E (2012) Spatial and temporal variation in mercury bioaccumulation by zooplankton in Lake Champlain (North America). Environ Pollut 161:343–349
Correa SB, Crampton WGR, Chapman LJ, Albert JS (2008) A comparison of flooded forest and floating meadow fish assemblages in an upper Amazon floodplain. J Fish Biol 72:1–16
Driscoll CT, Han YJ, Chen CY, Evers DC, Lambert KF, Holsen T, Kamman NC, Munson R (2007) Mercury contamination in remote forest and aquatic ecosystems in the Northeastern U.S.: sources, transformations and management options. Bioscience 57:17–28
Durães R, Pompeu PS, Godinho AAL (2001) Alimentação de quatro espécies de Leporinus (Characiformes, Anostomidae) durante a formação de um reservatório no sudeste do Brasil. Iheringia, Sér.Zool., Porto Alegre 90:183–191
Fadini PS, Jardim WF (2001) Is the Negro River Basin (Amazon) impacted naturally occurring mercury? Sci Total Environ 275:71–82
Forsberg BR, Araujo-Lima CARM, Martinelli LA, Victoria RL, Bonassi JA (1993) Autotrophic carbon sources for fish of the central amazona. Ecology 74:643–652
Freitas CEC, Batista VS, Inhamuns AJ (2002) Strategies of small-scale fisheries on the Central Amazon floodplain. Acta Amazonica 32:1–7
Ikingura JR, Akagi H (2003) Total mercury and methylmercury levels in fish from hydroelectric reservoirs in Tanzania. Sci Total Environ 304:355–368
INMET, Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia, 2018. http://www.inmet.gov.br. Accessed Dec 2018
Kasper D, Forsberg BR, Amaral JHF, Py-Daniel SS, Bastos WR, Malm O (2017) Methylmercury modulation in Amazon rivers linked to basin characteristics and seasonal flood-pulse. Environ Sci Technol 51:14182–14191
King JK, Saunders FM, Lee RF, Jahnke RA (1999) Coupling mercury methylation rates to sulfate reduction rates in marine sediments. Environmental Toxicology. Chemistry 18:1362–1369
Kraepiel AML, Keller K, Chin HB, Malcolm EG, Morel FMM (2003) Sources and variations of mercury in tuna. Environ Sci Technol 37:5551–5558
Lavoie RA, Jardine TD, Chumchal MM, Kidd KA, Campbell LM (2013) Biomagnification of mercury in aquatic food webs: a worldwide meta-analysis. Environ Sci Technol 47:13385–13394
Lamberti GA, Gregory SV (2007) CPOM transport, retention, and measurement. In:Hauer FR, Lamberti GA (eds.) Methods in stream ecology. 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, p. 273–289
Lopes IG, Oliveira RG, Ramos FM (2016) Perfil do consumo de peixe da população brasileira. Biota Amazônia 6:62–65
Maia PD, Maurice L, Tessier E, Amouroux D, Cossa D, Pérez M, Moreira-Turcq P, Rhéault I (2009) Mercury distribution and exchanges between the Amazon river and connected floodplain lakes. Sci Total Environ 407:6073–6084
Maia PD, Maurice L, Tessier E, Amouroux D, Cossa D, Moreira-Turcq P, Etcheber H (2018) Role of the floodplain lakes in the methylmercury distribution and exchanges with the Amazon River, Brazil. J Environ Sci 68:24–40
Malm O (1998) Gold mining as a source of mercury exposure in the Brazilian Amazon. Environ Res 77:73–78
Marçal-Simabuku MAe, Peret AC (2002) Alimentação de peixes (Osteichthyes, Characiformes) em duas Lagoas de uma Planíce de Inundação brasileira da Bacia do rio Paraná. Interciência 27:299–306
Melack J, Novo EMLM, Forsberg BR, Piedade MTF, Maurice L (2009) Floodplain ecosystem processes. In: Keller M, Bustamante M, Gash J, Silva PD (eds.). Amazonia and global change. American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C., USA, pp. 525–541
Nascimento EL, Gomes JPO, Almeida R, Bastos WR, Bernardi JVE, Miyai RK (2006) Mercurio no plâncton de um lago natural amazônico, Lago Puruzinho (Brasil). J Braz Soc Ecotoxicol 1:1–6
Northcote TG, Pick FR, Fillion DB, Salter SP (2009) Interaction of nutrients and turbidity in the control of phytoplankton in a large Western Canadian Lake prior to major watershed impoundments. Lake Reserv Manage 21:261–276
Oliveira RC, Dórea JG, Bernardi JVE, Bastos WR, Almeida R, Manzatto AG (2010) Annals Human Biol 37:629–642
Pestana IA, Almeida MG, Bastos WR, Souza CMM (2018) Total Hg and methylmercury dynamics in a river-floodplain system in the Western Amazon: influence of the seasonality, organic matter and physical and chemical parameters. Sci Total Environ 656:388–399
Pickhardt PC, Fisher NS (2007) Accumulation of inorganic and methylmercury by freshwater phyto plankton in two contrasting water bodies. Environ Sci Technol 41:125–131
Queiroz MMA, Horbe AMC, Moura CAV (2011) Mineralogia e química dos sedimentos de fundo do médio e baixo Madeira e de seus principais tributários e Amazonas e Brasil. Acta Amazonica 41:453–464
R Core Team (2018) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for statistical computing, Austria, Vienna, http://www.R-project.org/
Rezende CF, Mazzoni R (2005) Seasonal variation in the input of allochthonous matter in an Atlantic Rain Forest stream, Ilha Grande- RJ. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 17:167–175
Roulet M, Lucotte M, Saint-Aubin A, Tran S, Rhéault I, Farella N, Silva EJ, Dezencourt J, Sousa Passos CJ, Guimarães JRD, Mergler D, Amorim M (1988) The geochemistry of mercury in 43 central Amazonian soils developed on the Alter-do-Chão formation of the lower Tapajos River Valley, Para State, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 223:1–24
Roulet M, Lucotte M, Guimarães JRD, Rheault I (2000) Methylmercury in water, seston, and epiphyton of an Amazonian river and its floodplain, Tapajós River, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 261:43–59
Roulet M, Lucotte M, Canuel R, Farella N, Goch YGF, Peleja JRP, Guimarães JRD, Mergler D, Amorim M (2001) Spatio-temporal geochemistry of mercury in waters of the Tapajós and Amazon rivers, Brazil. Limnol Oceanogr 46:1141–1157
Roulet M, Maury-Brachet R (2001) Le mercure dans les organisms aquatiques amazoniens. In: Carmouse JP, Lucotte M, Boudou A (eds.) Le mercure en Amazonie. Rôle de L' homme et de L'environment, risques sanitaries. IRD editions, Paris, p. 494
Sahoo PK, Guimarães JTF, Souza-Filho PWM, Silva MS, Silva Junior RO, Pessim G, Moraes BC, Pessoa PFP, Rodrigues TM, Costa MF, Dall’Agnol R (2016) Influence of seasonal variation on the hydro-biogeochemical characteristics of two upland lakes of the southeastern Amazon, Brazil. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 88:2211–2227
Santos GM (1982) Caracterização, hábitos alimentares e reprodutivos de quatro espécies de “aracus” e considerações ecológicas sobre o grupo no lago Janaucá-AM (Osteychthyes, Characoidei, Anostomidae). Acta Amazonica 12:713–739
Santos GM, Santos ACM (2005) Sustentabilidade da pesca na Amazônia. Estudos Avançados 54:165–182
Sccuder-Eikenberry BC, Riva-Murray K, Knightes CD, Journey CA, Chasar LC, Brigham ME, Bradley PM (2015) Optimizing fish sampling for fish–mercury bioaccumulation factors. Chemosphere 135:467–473
Signa G, Mazzola A, Tramati CD, Vizzini S (2017) Diet and habitat use influence Hg and Cd transfer to fish and consequent biomagnification in a highly contaminated area: Augusta Bay (Mediterranean Sea). Environ Pollut 230:394–404
Trudel M, Rasmussen JB (1997) Modeling the elimination of mercury. Environ Sci Technol 31:1716–1722
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern Applied Statistics with S., 4th edn. Springer, New York, NY, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-21706-2
Vieira M, Bernardi JVE, Dórea JG, Rocha BCP, Ribeiro R, Zara LF (2018) Distribution and availability of mercury and methylmercury in different waters from the Rio Madeira Basin, Amazon. Environ Pollut 235:771–779
Watras CJ, Bloom NS (1992) Mercury and methylmercury in individual zooplankton: implications for bioaccumulation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37:1313–1318
Watras CJ, Morrison KA, Host J, Bloom NS (1995) Concentration of mercury species in relation to other site-specific factors in the surface waters of northern Wisconsin lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 40:556–565
Wissmar RC, Richey JE, Stallard RF, Edmond JM (1981) Plankton metabolism and carbon processes in the Amazon River, its tributaries, and floodplain waters, Peru- Brazil, May-June 1977. Ecology 62:1622–1633
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) through CNPq/CT-Universal project (Grant no. 458977/2014-4). We are grateful to IBAMA (Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis) for the fish collection license (DIFAP/IBAMA no. 091). We extend special thanks to the fisherman Raimundo Nonato dos Santos. This study was also financed in part by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoa de Nível Superior – Brazil (CAPES) – Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Fish sampling was approved by Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis (IBAMA) (license: DIFAP/IBAMA no. 091).
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azevedo, L.S., Pestana, I.A., Nery, A.F.d.C. et al. Influence of the flood pulse on mercury accumulation in detritivorous, herbivorous and omnivorous fish in Brazilian Amazonia. Ecotoxicology 28, 478–485 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02044-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02044-y