Abstract
The aim of this study was to determine if the cytotoxic and genotoxic responses of Allium cepa are effective biomarkers of harmful effects caused by polluted river water and if changes in the responses reflect seasonality in the harmful effects. Samples were collected in the dry season (August 2011 and 2012) and rainy season (February 2012 and 2013) at sampling points on the Jaguari River and the Ribeirão Lavapés, in Brazil. Allium cepa bulbs were exposed to the samples, to positive controls (15 µg/L methyl methanesulfonate), and to negative controls (tap water). Three root tips from each bulb were then stained using the Feulgen reaction, then the micronucleus frequency, the mitotic index, and mitotic anomalies were measured. The total number of anomalies (stickiness, c-mitosis, multipolarity, chromosome bridges, and unidentified anomalies) in the rainy season (8.61 ± 3.65) and dry season (7.07 ± 2.96) were significantly different (U = 11.31, p = 0.04). Toxicity, indicated by the formation of micronuclei and the mitotic index, was higher in the February 2012 samples than in the August 2012 samples. The mean manganese concentration (0.13 mg/L) in the rainy season samples was higher than the maximum concentration permitted by the Brazilian National Environmental Council (<0.1 mg/L) and the manganese concentrations positively correlated with chromosomal aberration induction (p = 0.01, r = 0.69). In conclusion, the rainy season samples were more toxic than the dry season samples. This was probably related to rain water carrying compounds with potentially negative impacts into the rivers. These findings highlight the importance of biomonitoring studies and of treating wastewater in urban areas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achary VMM, Jena S, Panda KK, Panda BB (2008) Aluminium induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in root cells of Allium cepa L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 70:300–310. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.10.022
Almeida MAB, Schwarzbold A (2003) Avaliação Sazonal da Qualidade do Arroio da Cria Montenegro, RS com Aplicação de um Índice de Qualidade da Água (IQA). Revista brasileira de recursos hídricos 8(1):81–97
Amaral AM, Barbério A, Voltolini JC, Barros L (2007) Avaliação preliminar da citotoxicidade e genotoxicidade da água da bacia do rio Tapanhon (SP-Brasil) através do teste Allium (Allium cepa). Braz J Toxicol 20(1/2):65–71
Aschner M, Erikson KM, Herrero Hernández E, Tjalkens RB (2009) Manganese and its role in Parkinson’s disease: from transport to neuropathology. Neuromol Med 11(4):252–266. doi:10.1007/s12017-009-8083-0
Bagatini MD, Silva ACF, Tedesco SB (2007) Uso do sistema teste de Allium cepa como bioindicadora de genotoxicidade de infusões de plantas medicinais. Brazil J Pharmacogn 17(3):444–447. doi:10.1590/S0102-695X2007000300019
Banta RG, Markesbery WR (1977) Elevated manganese levels associated with dementia and extrapyramidal signs. Neurology 27:213–216
Barbério A (2013) Bioassays with plants in the monitoring of water quality. In: Elshorbagy W and Chowdhury RK (eds) Water treatment, 1rd edn. Rijeka, Croatia, pp 317–334. doi:10.5772/50546
Barbério A, Barros L, Voltolini JC, Mello MLS (2009) Evaluation of the cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of water from the River Paraíba do Sul, in Brazil, with the Allium cepa L. test. Braz. J Biol 69(3):837–842. doi:10.1590/S1519-69842009000400010
Barbério A, Voltolini JC, Mello MLS (2011) Standardization of bulb and root sample sizes for the Allium cepa test. Ecotoxicology 20(4):320–325. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0602-8
Barbosa JS, Cabral TM, Ferreira DN, Agnez-lima LF, Medeiros SRB (2010) Genotoxicity assessment in aquatic environment impacted by the presence of heavy metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:320–325. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.10.008
Barcellos CC, Fernandes HM, Azevedo HLP (1988) The role of the Arroio Pavuna river in the transport of particulate heavy metals to Jacarepaguá lagoon, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 75:211–223. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(88)90034-4
Caritá R, Marin-Morales MA (2008) Induction of chromosome aberrations in the Allium cepa test system caused by the exposure of seeds to industrial effluents contaminated with azo dyes. Chemosphere 72:722–725. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.03.056
Carruyo I, Fernandez Y, Marcano L, Montiel X, Torrealba Z (2008) Correlation of toxicity with lead content in root tip cells (Allium cepa L.). Biol Trace Elem Res 125:276–285. doi:10.1007/s12011-008-8175-y
CETESB—Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental (BR) (2011) Relatório de qualidade das águas interiores do estado de São Paulo 2011. Governo do Estado de São Paulo: Secretária do Meio Ambiente. http://www.cetesb.sp.gov.br/userfiles/file/agua/aguas-superficiais/relatorio-aguas-superficiais-2011.zip. Accessed 18 March 2013.
CETESB—Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental (BR) (2012) Relatório de qualidade das águas interiores do estado de São Paulo 2012. Governo do Estado de São Paulo: Secretária do Meio Ambiente. http://www.cetesb.sp.gov.br/userfiles/file/agua/aguas-superficiais/relatorio-aguas-superficiais-2012-substituido-em-060513.zip. Accessed 1 July 2013.
CETESB—Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental (BR) (2013) Relatório de qualidade das águas interiores do estado de São Paulo 2013. Governo do Estado de São Paulo: Secretária do Meio Ambiente. http://www.cetesb.sp.gov.br/agua/aguas-superficiais/35-publicacoes-/-relatorios. Accessed 2 July 2014.
Chandra SV, Srivastava RS, Shukla GS (1979) Regional distribution of metals and biogenic amines in the brain of monkeys exposed to manganese. Toxicol Lett 4:189–192
Chandra S, Chauhan LKS, Murthy RC, Saxena PN, Pande PN, Gupta SK (2005) Comparative biomonitoring of leachates from hazardous solid waste of two industries using Allium cepa. Sci Total Environ 347:46–52. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.002
Confalonieri U, Heller L, Azevedo S (2010) Água e Saúde: aspectos Globais e Nacionais. In Tundisi JG (ed) Águas do Brasil: Análises estratégicas, pp 27–38. http://www.abc.org.br/IMG/pdf/doc-808.pdf. Accessed 30 Mar 2013.
Costa M, Salnikow K, Sutherland JE, Broday L, Peng W, Zhang Q, Kluz T (2002) The role of oxidative stress in nickel and chromate genotoxicity. Mol Cell Biochem 235:265–275. doi:10.1023/A:1015909127833
Curriero FC, Jonathan AP, Rose JB, Lele S (2001) The association between extreme precipitation and waterborne disease outbreaks in the United States, 1948–1994. Am J Public Health 91(8):1194–1199
Donaldson J (1987) The physiopathological significance of manganese in brain—its relation to schizophrenia and neurodegenerative disorders. Neurotoxicol 8:451–462
Egito LCM, Medeiros MG, Medeiros SRB, Agnez-Lima LF (2007) Cytotoxic and genotoxic potential of surface water from Pitimbu river, northeastern/RN Brazil. Genet Mol Biol 30(2):435–441. doi: 10.1590/S1415-47572007000300023
Fatima RA, Ahmad M (2006) Genotoxicity of industrial wastewaters obtained from two different pollution sources in northern India: a comparison of three bioassays. Mutat Res 609:81–91. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.06.023
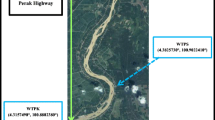
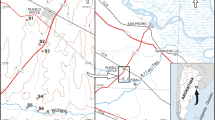
Ferreira GM, Faria MHA, Toledo MCB, César ACG (2012) Biomonitoramento nas águas do rio Jaguari e ribeirão Lavapés na região bragantina. In The 4th International Congress on University Industry Cooperation. Taubate, SP. http://www.unitau.br/unindu/artigos/pdf517.pdf. Accessed 9 Oct 2013.
Fiskesjö G (1985) The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas 102:99–112. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1985tb00471.x
Fiskesjö G (1989) INVITTOX Protocol no 8—Allium test. Russel and Burch House, Nottingham
Gajalakshmi K, Ruban P (2014) Evaluation of physic chemical parameters and cytotoxic effect of Orathupalayam dam in Tirupur District. Int J Agric Pol Res 2(5):191–197
Glińska S, Bartczak M, Oleksiaka S, Wolska A, Gabara B, Posmyk M, Janas K (2007) Effects of anthocyanin-rich extract from red cabbage leaves on meristematic cells of Allium cepa L. roots treated with heavy metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 68:343–350. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.02.004
Grover IS, Kaur S (1999) Genotoxicity of wastewater samples from sewage and industrial effluent detected by the Allium root anaphase aberration and micronucleus assays. Mutat Res 426:183–188. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(99)00065-2
Guilarte TR (2010) Manganese and Parkinson’s disease: a critical review and new findings. Environ Health Perspect 118:1071–1080
Hafeman D, Factor-Litvak P, Cheng ZQ, van Geen A, Ahsan H (2007) Association between manganese exposure through drinking water and infant mortality in Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 115:1107–1112. doi:10.1289/ehp.10051
Health Ministry (2011). Ordinance no 2.914, de 12 de dezembro de 2011. Dispõe sobre os procedimentos de controle e de vigilância da qualidade da água para consumo humano e seu padrão de potabilidade. Diário Oficial União. Brasília, BR. 14 dez 2011.
Helma C, Eckl P, Gottmann E, Kassie F, Rodinger W, Steinkellner H, Windpassinger C, Schule-Hermann R, Knasmüller S (1998) Genotoxic and ecotoxic effects of groundwaters and their relation to routinely measured chemical parameters. Environ Sci Technol 32:1799–1805. doi:10.1021/es971049g
Hernández RB (2009) Manganês: O papel do fracionamento químico e da especiação como determinantes de seu comportamento geoquímico e neurotóxico nos organismos em desenvolvimento. (Tese) Instituto de Química, Universidade de São Paulo.
IBGE. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (BR). (2010) http://www.ibge.gov.br/cidadesat/topwindow.htm?1. 07 Apr 2013.
Kaur G, Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2014) Pb-inhibited mitotic activity in onion roots involves DNA damage and disruption of oxidative metabolism. Ecotoxicol 23:1292–1304. doi:10.1007/s10646-014-1272-0
Khanna N, Sharma S (2013) Allium cepa root chromosomal aberration assay: a review. Indian J Pharm Biol Res 1(3):105–119
Knasmuller S, Gottmann E, Steinkellner H, Fomin A, Pickl C, Paschke A, God R, Kundi M (1998) Detection of genotoxic effects of heavy metal contaminated soils with plant bioassays. Mutat Res 420:37–48. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(98)00145-4
Leme DM, Marin-Morales MA (2008) Chromosome aberration and micronucleus frequencies in Allium cepa cells exposed to petroleum polluted water—a case study. Mutat Res 650:80–86. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2007.10.006
Lemos CT, Erdtmann B (2000) Cytogenetic evaluation of aquatic genotoxicity in human cultured lymphocytes. Mutat Res 467:1–9. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(00)00009-7
Levan A (1938) The effect of colchicine on root mitoses in Allium. Hereditas 24:471–486
Liu D, Wusheng J, Chunli W (1996) Effects of Zn2+ on root growth, cell division, and nucleoli of Allium cepa L. J Environ Sci 8(1):21–27
Majer BJ, Grummt T, Uhl M, Knasmüller S (2005) Use of plant bioassays for the detection of genotoxins in the aquatic environment. Acta Hydrochim Hidrobiol 33(1):45–55. doi:10.1002/aheh.200300557
Mannarino CF, Moreira JC, Ferreira JA, Arias ARL (2013) Avaliação de impactos do efluente do tratamento combinado de lixiviado de aterro de resíduos sólidos urbanos e esgoto doméstico sobre a biota aquática. Cien Saude Colet 18(11):3235–3243. doi:10.1590/S1413-81232013001100014
Marcano L, Bracho M, Montiel X, Carruyo I, Atencio L (1998) Efecto mitotóxico y genotóxico del cadmio em poblaciones meristemáticas de Allium cepa L. (cebolla). Ciencia 6:93–99
Martini LFD, Caldas SS, Bolzan CM, Bundt ADC, Primel EG, Avila LA (2012) Risco de contaminação das águas de superfície e subterrâneas por agrotóxicos recomendados para a cultura de arroz irrigado. Cienc Rural 42(10):1715–1721. doi:10.1590/S0103-84782012001000001
Mello MLS (1997) Cytochemistry of DNA, RNA and nuclear proteins. Braz J Genet 20:257–264
Moraes DSL, Jordão BQ (2002) Degradação de recursos hídricos e seus efeitos sobre a saúde humana. Rev Saude Publica 36(3):370–374. doi:10.1590/S0034-89102002000300018
Nielsen MH, Rank J (1994) Screening of toxicity and genotoxicity in wastewater by the use of the Allium test. Hereditas 121:249–254
Ohe T, Watanabe T, Wakabayashi K (2004) Mutagens in surface waters: a review. Mutat Res 567:109–149. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2004.08.003
Oliveira LM, Voltolini JC, Barbério A (2011) Potencial mutagênico dos poluentes na água do rio Paraíba do Sul em Tremembé, SP, Brasil, utilizando o teste Allium cepa. Ambi-Agua 6(1):90–103. doi:10.4136/ambi-agua.176
Palacio SM, Espinoza-Quiñones FR, Galante RM, Zenatti DC, Seolatto AA, Lorenz EK, Zacarkim CE, Rossi N, Rizzutto MA, Tabacniks MH (2005) Correlation between heavy metal ions (copper, zinc, lead) concentration and root length of Allium cepa L. in polluted river water. Braz Arch Biol Technol 48:191–196
PMSB (2010) Plano Municipal de Saneamento Básico de Bragança Paulista - SP: Sistemas de Abastecimento de Água e Esgotamento Sanitário. Prefeitura do Município de Bragança Paulista, SP
Prathumratana L, Sthiannopkao S, Kim KW (2008) The relationship of climatic and hydrological parameters to surface water quality in the lower Mekong River. Environ Intern 34:860–866. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.10.011
Radić S, Stipaničev D, Vujčić V, Rajčić MM, Širac S, Pevalek-Kozlina B (2010) The evaluation of surface and wastewater genotoxicity using Allium cepa test. Sci Total Environ 408:1228–1233. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.11.055
Rank J (2003) The method of Allium anaphase-telophase chromosome aberration assay. Ekologija 1:38–42
Rank J, Nielsen MH (1998) Genotoxicity testing of wastewater sludge using Allium cepa anaphase-telophase chromosome aberration assay. Mutat Res 418:113–119. doi:10.10.16/S1383-5718(98)00118-1
Rodrigues GS, Ma TH, Pimentel D, Weinstein LH, Ichikawa S (1997) Tradescantia bioassays as monitoring systems for environmental mutagenesis: a review. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16(4):325–359. doi:10.1080/07352689709701953
Rogers HR (1996) Sources, behavior and fate of organic contaminants during sewage treatment and in sewage sludges. Sci Total Environ 185:3–26. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(96)05039-5
Seth CS, Misra V, Chauhan LKS, Singh RR (2008) Genotoxicity of cadmium on root meristem cells of Allium cepa: cytogenetic and comet assay approach. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:711–716. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.02.003
Singh SP, Kashyap AK (1978) Manganese toxicity and mutagenesis in two blue-green algae. Environ Exp Bot 18:47–53. doi:10.16/0098-8472(78)90020-5
Staykova TA, Ivanova EM, Velcheva IG (2005) Cytogenetic effect of heavy-metal and cyanide in contaminated waters from the region of southwest Bulgaria. J Cell Mol Biol 4:41–46
Vujošević M, Andelković S, Savić G, Blagojević J (2008) Geotoxicity screening of the river Rasina in Serbia using the Allium anaphase-telophase test. Environ Monit Assess 147:75–81. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-0099-z
Wang X, Zang S (2014) Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of toxic heavy metals and metalloid in surface water of lakes in Daqing Heilongjiang Province, China. Ecotoxicol 23:609–617. doi:10.1007/s10646-014-1177-y
World Health Organization (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn. WHO, Geneva
Wu Q, Xia X, Mou X, Zhu B, Zhao P, Dong H (2014) Effects of seasonal climatic variability on several toxic contaminants in urban lakes: Implications for the impacts of climate change. J Environ Sci 26(12):2369–2378. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2014.04.001
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. We thank Mônica Huguenin Araújo Faria and Tiago Minoru Taguchi for technical assistance, and Dagmar Frisch for editing the English language. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation) for providing financial support and the Instituto Federal de Educação, Ciência e Tecnologia de São Paulo (São Paulo Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology) for collaborating with us executing this work.
Funding
Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP). Grant Number: 2015/21253-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salles, F.J., de Toledo, M.C.B., César, A.C.G. et al. Cytotoxic and genotoxic assessment of surface water from São Paulo State, Brazil, during the rainy and dry seasons. Ecotoxicology 25, 633–645 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1622-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1622-1