Abstract
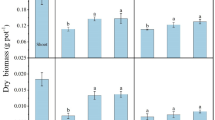
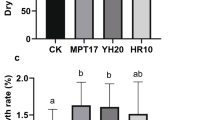
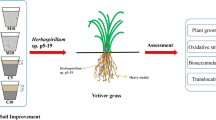
Soil contamination caused by petroleum hydrocarbons has become a worldwide environmental problem. Microorganism combined with phytoremediation appears to be more effective for removal and/or degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons from impacted soils. The current study investigated the effect of inoculated with PGPR Serratia marcescens BC-3 alone or in combination with AMF Glomus intraradices on the phytoremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. Pot experiments were conducted to analyze the effect on plant and soil for 90 days in greenhouse. The inoculation treatments showed higher plant biomass and antioxidant enzyme activities than the non inoculation control. Inoculation treatments also improved rhizosphere microbial populations in petroleum contaminated soil. The degradation rate of total petroleum hydrocarbons with PGPR and AMP co-inoculation treatment was up to 72.24 %. The results indicated that plant combined with microorganisms for remediation of petroleum hydrocarbons would be a feasible method.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Method Enzymol 105:121–126
Al-Hashem MA, Brain PF, Omar SA (2007) Effects of oil pollution at Kuwait’s greater Al-Burgan oil field on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentrations in the tissues of the desert lizard Acanthodactylus scutellatus and their ant prey. Ecotoxicology 16(8):551–555
Alkorta I, Garbisu C (2001) Phytoremediation of organic contaminants in soils. Bioresour Technol 79:273–276
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Atlas RM (1981) Microbial degradation of Petroleum hydrocarbons: an environmental perspective. Microbiol Rev 45:180–209
Bartels D, Sunkar R (2005) Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:23–58
Besalatpour A, Hajabbasi MA, Khoshgoftarmanesh AH, Dorostkar V (2011) Landfarming process effects on biochemical properties of petroleum-contaminated soils. Soil Sediment Contam 20(2):234–248
Bonello P, Bruns TD, Gardes M (1998) Genetic structure of a natural population of the ectomycorrhizal fungus Suillus pungens. New Phytol 138:533–542
Brundrett MC (2002) Coevolution of roots and mycorrhizas of land plants. New Phytol 154(2):275–304
Casida LE Jr, Klein D, Santoro T (1964) Soil dehydrogenase activity. Soil Sci 98:371–376
Charles H, Pradeeo T, John H, Cutler C, Michael J (2003) Hydrocarbons and the evolution of human culture. Nature 426:318–322
Colwell RR, Walker JD (1977) Ecological aspects of microbial degradation of petroleum in the marine environment. Crit Rev Microbiol 5(4):423–445
Escalante-Espinosa E, Gallegos-Martínez ME, Favela-Torres E, Gutiérrez-Rojas M (2005) Improvement of the hydrocarbon phytoremediation rate by Cyperus laxus Lam. inoculated with a microbial consortium in a model system. Chemosphere 59(3):405–413
Garcı′a C, Herna′ndez MT, Costa F (1997) Potential use of dehydrogenase activity as an index of microbial activity in degraded soils. Commun Soil Sci Plan 28:123–134
Glick BR, Changping L, Sibdas G, Dumbroff EB (1997) Early development of canola seedlings in the presence of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas puitda GR12–2. Soil Biol Biochem 29:1233–1239
Hii YS, Law AT, Shazili NAM, Abdul-Rashid MK (2009) Biodegradation of Tapis blended crude oil in marine sediment by a consortium of symbiotic bacteria. Int Biodeter Biodegr 23(2):142–150
Hong SH, Ryu H, Kim J, Cho KS (2011) Rhizoremediation of diesel-contaminated soil using the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Gordonia sp. S2RP-17. Biodegradation 22(3):593–601
Huang XD, El-Alawi Y, Gurska J, Glick BR, Greenberg BM (2005) A multiprocess phytoremediation system for decontamination of persistent total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPHs) from soils. Microchem J 81(1):139–147
Johnson DL, Anderson DR, McGrath SP (2005) Soil microbial response during the phytoremediation of a PAH contaminated soil. Soil Biol Biochem 37(12):2334–2336
Joner EJ, Leyval C (2003) Phytoremediation of organic pollutants using mycorrhizal plants: a new aspect of rhizosphere interactions. Agronomie 23:495–502
Joo HS, Ndegwa PM, Shoda M, Phae CG (2008) Bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil using Candida catenulata and food waste. Environ Pollut 156(3):891–896
Khan Z (2007) Endophyte assisted phytoremediation of trichloroethanol (TCE): an environmental contaminant. Comp Biochem Physiol 146:273–274
Kohler J, Caravaca F, Carrasco L, Roldan A (2007) Interactions between a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium, an AM fungus and a phosphate-solubilising fungus in the rhizosphere of Lactuca sativa. Appl Soil Ecol 35:480–487
Kozdrój J, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Krupa P (2007) Mycorrhizal fungi and ectomycorrhiza associated bacteria isolated from an industrial desert soil protect pine seedlings against Cd (II) impact. Ecotoxicology 16(6):449–456
Kumari B, Singh SN (2011) Phytoremediation of metals from fly ash through bacterial augmentation. Ecotoxicology 20(1):166–176
Liu W (2010) Do genetically modified plants impact arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi? Ecotoxicology 19(2):229–238
Liu J, Zhang X, Sun Y, Lin W (2010) Antioxidative capacity and enzyme activity in Haematococcus pluvialis cells exposed to superoxide free radicals. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 28(1):1–9
Margesin A, Walder G, Schinner F (2000) The impact of hydrocarbon remediation (diesel oil and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) on enzyme activities and microbial properties of soil. Acta Biotechnol 20:313–333
Merkl N, Schultze-Kraft R, Infante C (2005) Phytoremediation in the tropics-influence of heavy crude oil on root morphological characteristics of graminoids. Environ Pollut 138:86–91
Mishra S, Jyot J, Kuhad RC, Lal B (2001) In situ bioremediation potential of an oily sludge-degrading bacterial consortium. Curr Microbiol 43(5):328–335
Nannipieri P, Ceccanti B, Cervelli S, Matarese E (1980) Extraction of phosphatase, urease, proteases, organic carbon, and nitrogen from soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44(5):1011–1016
Park IS, Park JW (2010) A novel total petroleum hydrocarbon fractionation strategy for human health risk assessment for petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated site management. J Hazard Mater 179:1128–1135
Parrish ZD, Banks MK, Schwab AP (2005) Assessment of contaminant lability during phytoremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon impacted soil. Environ Pollut 137:189–197
Phillips LA, Greer CW, Germida JJ (2006) Culture based and culture independent assessment of the impact of mixed and single plant treatments on rhizosphere microbial communities in hydrocarbon contaminated flare pit soil. Soil Biol Biochem 38(9):2823–2833
Robertson SJ, McGill WB, Massicotte HB, Rutherford PM (2007) Petroleum hydrocarbon contamination in boreal forest soils: a mycorrhizal ecosystems perspective. Biol Rev 82:213–240
Sabljic A (2001) QSAR models for estimating properties of persistent organic pollutants required in evaluation of their environmental fate and risk. Chemosphere 43:363–375
Sarand I, Timonen S, Nurmiaho-Lassila EL, Koivula T, Haahtela K, Romantschuk M, Sen R (1998) Microbial biofilms and catabolic plasmid harbouring degradative fluorescent pseudomonads in Scots pine mycorrhizospheres developed on petroleum contaminated soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 27:115–126
Sathishkumar M, Binupriya AR, Baik SH, Yun SE (2008) Biodegradation of crude oil by individual bacterial strains and a mixed bacterial consortium isolated from hydrocarbon contaminated areas. Clean-soil Air Water 36(1):92–96
Scott SL (2003) Biodegradation and toxicity of total petroleum hydrocarbon leachate from land treatment units. California Polytechnic State University, Department of Engineering, San Luis Obispo, p 52
Serrano A, Tejada M, Gallego M, Gonzalez JL (2009) Evaluation of soil biological activity after a diesel fuel spill. Sci Total Environ 407:4056–4061
Singer AC, Crowley DE, Thompson IP (2003) Secondary plant metabolites in phytoremediation and biotransformation. Trends Bio-technol 21:123–130
Smith SS, Read DJ (1997) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 3rd edn. Academic Press, SanDiego
Sun FL, Wang YS, Sun CC, Peng YL, Deng C (2012) Effects of three different PAHs on nitrogen-fixing bacterial diversity in mangrove sediment. Ecotoxicology 21(6):1651–1660
Valdenegro M, Barea JM, Azcón R (2001) Influence of arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi, Rhizobium meliloti strains and PGPR inoculation on the growth of Medicago arborea used as model legume for re-vegetation and biological reactivation in a semi-arid mediterranean area. Plant Growth Regul 34(2):233–240
Van Hamme JD, Singh A, Ward OP (2003) Recent advances in petroleum microbiology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67(4):503–549
Vessey JK (2003) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 255:571–586
Wang J, Zhang Z, Su Y, He W, He F, Song H (2008) Phytoremediation of petroleum polluted soil. Petrol Sci 5:167–171
Wang WB, Kim YH, Lee HS, Kim KY, Deng XP, Kwak SS (2009) Analysis of antioxidant enzyme activity during germination of alfalfa under salt and drought stresses. Plant Physiol Bioch 47(7):570–577
Weissenhorn I, Mench M, Leyval C (1995) Bioavailability of heavy metals and arbuscular mycorrhizal in a sewage-sludge amended sandy soil. Soil Biol Biochem 27(3):287–296
White PM Jr, Wolf DC, Thoma GJ, Reynolds CM (2006) Phytoremediation of alkylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a crude oil-contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 169:207–220
Zhang W, Wang H, Zhang R, Yu XZ, Qian PY, Wong MH (2010) Bacterial communities in PAH contaminated soils at an electronic-waste processing center in China. Ecotoxicology 19(1):96–104
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31170479), Programs for Science and Technology Development of Heilongjiang Province, China (Grant No. GC12B304), Aid program for Science and Technology Innovative Research Team in Higher Educational Institutions of Heilongjiang Province (2010TD10), Harbin Normal University (KJTD2011-2) and the Graduate Innovation Fund of Harbin Normal University (HSDBSCX2013-04).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rui Dong and Lijing Gu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, R., Gu, L., Guo, C. et al. Effect of PGPR Serratia marcescens BC-3 and AMF Glomus intraradices on phytoremediation of petroleum contaminated soil. Ecotoxicology 23, 674–680 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1200-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1200-3