Abstract
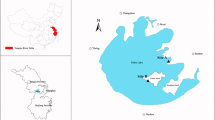
The marine shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei were used as an active biomonitoring organism to assess the bioavailability and impact of metal contaminants in seven study sites along the Maluan Bay of China. Metal concentrations in the hepatopancreas of shrimps were determined in conjunction with four biomarkers responses after a 7 day in situ cage exposures. The results showed that contaminant tissue burdens at the deployment sites were greater than those of the reference site, and antioxidant enzyme activities were strongly inhibited compared to those of reference organisms. Variations in these biomarker responses were correlated significantly (p < 0.05 or p < 0.01) with the specific metal pollutants at the study sites, but no significant correlations existed between catalase activity responses and the metal contaminants. This suggests the presence of undetermined contaminants or other exposure routes that may be responsible for the decreased catalase activity. Multivariate analysis revealed a causal relationship between contaminants at each deployment site and the biochemical “response” of the caged shrimps at these sites and demonstrated the presence of two contaminant “hot” spots. This investigation suggested that the incorporation of chemical data on trace metal concentrations with the analysis of antioxidant enzymatic activities in caged shrimps can be a useful tool for the identification of causal toxic contaminants in complex mixtures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1974) Methods of enzymatic analysis. In: Bergmayer HU (ed) Catalase. Academic Press, London, pp 671–684
Barata C, Lekumberri I, Vila-Escale M, Prat N, Porte C (2005) Trace metal concentration, antioxidant enzyme activities and susceptibility to oxidative stress in the tricoptera larvae Hydropsyche exocellata from the Llobregat river basin (NE Spain). Aquat Toxicol 74:3–19
Bervoets L, Voets J, Covaci A, Chu SG, Qadah D, Smolders R, Schepens P, Blust R (2005) Use of transplanted zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) to assess the bioavailbility of microcontaminants in Flemish surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 39:1492–1505
Bocchetti R, Fattorini D, Gambi MC, Regoli F (2004) Trace metal concentrations and susceptibility to oxidative stress in the polychaete Sabella spallanzanii (Gmelin) (Sabellidae): potential role of antioxidants in revealing stressful environmental conditions in the Mediterranean. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:353–361
Bradford MM (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Burton GA, Greenberg MS, Rowland CD, Irvine CA, Lavoie DR, Brooker JA, Moore L, Raymer DFN, McWilliam RA (2005) In situ exposures using caged organisms: a multi-compartment approach to detect aquatic toxicity and bioaccumulation. Environ Pollut 134:133–144
CMEP-SOA (China Ministry of Environmental Protection, State Oceanic Administration) (1998) The People’s Republic of China National Standards GB 3097-97 marine seawater quality. China Ministry of Environmental Protection and State Oceanic Administration, Beijing
Comrey AL (1973) A first course in factor analysis. Academic Press, New York
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, American Waterworks Association, Water Environment Federation, Washington
Faria M, Carrasco L, Diez S, Riva MC, Bayona JM, Barata C (2009) Multi-biomarker responses in the freshwater mussel Dreissena polymorpha exposed to polychlorobiphenyls and metals. Comp Biochem Physiol C 149:281–288
Galloway TS, Sanger RC, Smith KL, Filimann G, Readman JW, Ford TE, Depledge MH (2002) Rapid assessment of marine pollution using multiple biomarkers and chemical immunoassays. Environ Sci Technol 36:2219–2226
Giarratano E, Comoglio L, Amin O (2007) Heavy metal toxicity in Exosphaeroma gigas (Crustacea, Isopoda) from the coastal zone of Beagle Channel. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 68:451–462
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hagger JA, Galloway TS, Langston WJ, Jones MB (2009) Application of biomarkers to assess the condition of European marine sites. Environ Pollut 157:2003–2010
Keating J, Delaney M, Meehan-meola D, Warren W, Alcivar A, Alcivar-warren A (2007) Histological fidings, cadmium bioaccumulation, and isolation of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) in cadmium-exposed, specific pathogen-free shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei postlarvae. J Shellfish Res 26:1225–1237
Livingstone DR (2001) Contaminated-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar Pollut Bull 42:857–864
Livingstone DR, Lips F, Martinez PG, Pipe RK (1992) Antioxidant enzymes in the digestive gland of the common mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar Biol 112:265–276
Maria VL, Santos MA, Bebianno MJ (2009) Biomarkers of damage and protection in Mytilus galloprovincialis cross transplanted in Ria Formosa Lagoon (Portugal). Ecotoxicology 18:1018–1028
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase: an enzymatic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Neff JM (2002) Bioaccumulation in marine organisms. Elsevier, Oxford
Paez-Osuna F, Tron-Mayen L (1996) Concentration and distribution of heavy metals in tissues of wild and farmed shrimp Penaeus vannamei from the northwest coast of Mexico. Environ Int 22:443–450
Tabachnick BG, Fidell LS (1996) Using multivariate statistics, 3rd edn. Harper Collins, New York
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:178–189
Wang ZS, Yan CZ, Zhang X (2009) Acute and chronic cadmium toxicity to a saltwater cladoceran Moina monogolica Daday and its relative importance. Ecotoxicology 18:47–54
Wang ZS, Yan CZ, Hyne RV (2010) Effects of dietary cadmium exposure on reproduction of saltwater cladoceran Moina monogolica Daday: implications in water quality criteria. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:365–372
Wang ZS, Yan CZ, Pan QK, Yan YJ (2011) Concentrations of some heavy metals in water, suspended solids, and biota species from Maluan Bay, China and their environmental significance. Environ Monit Assess 175:239–249
Wu JP, Chen HC, Huang DJ (2008) Histopathological and biochemical evidence of hepatopancreatic toxicity caused by cadmium and zinc in the white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Chemosphere 73:1019–1026
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the project of NSFC (National Scientific Foundation of China) in “Research of ecotoxicity effects and assessment methods based on in situ tests” (Grant No. 20807034/B070704 to Zaosheng Wang). Dr Zaosheng Wang was also supported by the KC Wong Education Foundation, Hong Kong. The authors would be very grateful for the help by Dr Yue Lin in the fishery research institute of Xiamen, who provided sufficient quantities of shrimps for field experiments. The manuscript benefited greatly from the helpful comments of three anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Yan, C., Yan, Y. et al. Integrated assessment of biomarker responses in caged shrimps (Litopenaeus vannamei) exposed to complex contaminants from the Maluan Bay of China. Ecotoxicology 21, 869–881 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0849-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0849-0