Abstract
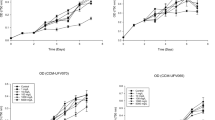
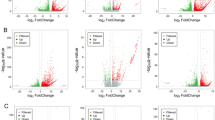
When the concentrations of ampicillin (Amp), atrazine (Atr) and cadmium chloride (Cd) reach excessive quantities, they become toxic to aquatic organisms. Due to the acceleration of the industrialization and the intensification of human activities, the incidence and concentrations of these types of pollutants in aquatic systems are increasing. The primary purpose of this study was to evaluate the short-term effects of Amp, Atr and Cd on the physiological indices and gene expression levels in Microcystis aeruginosa. These three pollutants significantly induced antioxidant activity but continuously accelerated the cellular oxidative damage in microalgae, which suggests an imbalance between the oxidant and the antioxidant systems. Amp, Atr and Cd also decreased the transcription of psaB, psbD1 and rbcL; the lowest transcription of these genes was only 38.1, 23.7 and 7% of the control, respectively. These three pollutants affected nitrogen (N) and phosphorous (P) uptake by inhibiting the transcription of N or P absorbing and transporting related genes, and they down regulated the transcription of microcystin-related genes, which caused a decrease of microcystin levels; and the lowest level of microcystin was only 42.4% of the control. Our results suggest that these pollutants may cause pleiotropic effects on algal growth and physiological and biochemical reactions, and they may even affect secondary metabolic processes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asada K, Endo T, Mano J, Miyake C (1998) Molecular mechanism for relaxation of and protection from light stress. In: Sato K, Murata N (eds) Stress responses of photosynthetic organisms. Elsevier Science Publishing, Amsterdam, pp 37–52
Capuano V, Thomas JC, de Tandeau Marssac N, Houmard J (1991) The anchor polypeptide of cyanobacterial phycobilisomes. J Biol Chem 266:7239–7247
Cood GA, Poon AM (1988) Cyanobacterial toxins. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Dai R, Liu H, Qu J, Zhao X, Ru J, Hou Y (2008) Relationship of energy charge and toxin content of Microcystis aeruginosa in nitrogen-limited or phosphorous-limited cultures. Toxicon 51:649–658
Dai R, Liu H, Qu J, Hou Y, Zhao X (2009) Effects of amino acids on microcystin production of the Microcystis aeruginosa. J Hazard Mater 161:730–736
De Lorenzo ME, Taylor LA, Lund SA, Pennington PL, Strozier ED, Fulton MH (2002) Toxicity and bioconcentration potential of the agricultural pesticide endosulfan in phytoplankton and zooplankton. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 42:173–181
Elbaz A, Wei YY, Meng Q, Zheng Q, Yang ZM (2010) Mercury induced oxidative stress and impact on antioxidant enzymes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Ecotoxicology 19:1285–1293
Geiken B, Masojídek J, Rizzuto M, Pompili ML, Giardi MT (1998) Incorporation of [35S] methionine in higher plants reveals that stimulation of D1 reaction center II protein turnover accompanies tolerance to heavy metal stress. Plant Cell Environ 21:1265–1273
Halling-Sørensen B, Nors Nielsen S, Lanzky PF, Ingerslev F, Holten Lützhøft HC, Jørgensen SE (1998) Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment-a review. Chemosphere 36:357–393
Hanikenne M (2003) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as a eukaryotic photosynthetic model for studies of heavy metal homeostasis and tolerance. New Phytol 159:331–340
Harrass MC, Kindig AC, Taub FB (1985) Response of blue-green and green algae to streptomycin in unialgal and paired culture. Aquat Toxicol 6:1–11
Herrero A, Muro-Pastor AM, Flores E (2001) Nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol 183:411–425
Holten Lützhøft HC, Halling-Sørensen B, Jørgensen SE (1999) Algal toxicity of antibacterial agents applied in Danish fish farming. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36:1–6
Hong Y, Hu H, Xie X, Akiyoshi S, Masaki S, Li F (2009) Gramine-induced growth inhibition, oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Toxicol 91:262–269
Isidori M, Lavorgna M, Nardelli A, Pascarella L, Parrella A (2005) Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci Total Environ 346:87–98
Kaebernick M, Neilan BA, Börner T, Dittmann E (2000) Light and the transcriptional response of the microcystin biosynthesis gene cluster. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3387–3392
Krupa Z, Baszynski T (1995) Some aspects of heavy metals toxicity towards photosynthetic apparatus–direct and indirect effects on light and dark reactions. Acta Physiol Plant 17:177–190
Latifi A, Ruiz M, Zhang CC (2009) Oxidative stress in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:258–278
Li X, Pan H, Xu J, Xian Q, Gao S, Yin D, Zou H (2008) Allelopathic effects of Ceratophyllum demersum and Microcystis aeruginosa in cocultivation. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 28:2243–2249
Liu XG, Zhao JJ, Wu QY (2005) Oxidative stress and metal ions effects on the cores of phycobilisomes in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. FEBS Lett 579:4571–4576
Long BM, Jones GJ, Orr PT (2001) Cellular microcystin content in N-limited Microcystis aeruginosa can be predicted from growth rate. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:278–283
Lopez-Gomollon S, Hernandez JA, Pellicer S, Angarica VE, Peleato ML, Fillat MF (2007) Cross-talk between iron, nitrogen regulatory networks in Anabaena (Nostoc) sp. PCC 7120: identification of overlapping genes in FurA and NtcA regulons. J Mol Biol 374:267–281
Lürling M, Roessink I (2006) On the way to cyanobacterial blooms: impact of the herbicide metribuzin on the competition between a green alga (Scenedesmus) and a cyanobacterium (Microcystis). Chemosphere 65:618–626
MEPPRC (2002) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 4th edition. Beijing, Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China
Palatnik JF, Carrillo N, Valle EM (1999) The role of photosynthetic electron transport in the oxidative degradation of chloroplastic glutamine synthetase. Plant Physiol 121:471–478
Pan X, Chang F, Kang L, Liu Y, Li G, Li D (2008a) Effects of gibberellin A3 on growth and microcystin production in Microcystis aeruginosa (cyanophyta). J Plant Physiol 165:1691–1697
Pan X, Deng C, Zhang D, Wang J, Mu G, Chen Y (2008b) Toxic effects of amoxicillin on the photosystem II of Synechocystis sp. characterized by a variety of in vivo chlorophyll fluorescence tests. Aquat Toxicol 89:207–213
Pan X, Zhang D, Chen X, Mu G, Li L, Bao A (2009) Effects of levofloxacin hydrochloride on photosystem II activity and heterogeneity of Synechocystis sp. Chemosphere 77:413–418
Pearson LA, Hisbergues M, Börner T, Dittmann E, Neilan BA (2004) Inactivation of an ABC transporter gene, mcyH, results in loss of microcystin production in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6370–6378
Perrona MC, Juneau P (2011) Effect of endocrine disrupters on photosystem II energy fluxes of green algae and cyanobacteria. Environ Res 11:520–529
Prado R, García R, Rioboo C, Herrero C, Abalde J, Cid A (2009) Comparison of the sensitivity of different toxicity test endpoints in a microalgae exposed to the herbicide paraquat. Environ Int 35:240–247
Qian H, Sheng GD, Liu W, Lu Y, Liu Z, Fu Z (2008) Inhibitory effects of atrazine on Chlorella vulgaris as assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:182–187
Qian H, Li J, Sun L, Chen W, Sheng GD, Liu W, Fu Z (2009) Combined effect of copper and cadmium on Chlorella vulgaris growth and photosynthesis-related gene transcription. Aquat Toxicol 94:56–61
Qian H, Li J, Pan X, Sun Z, Ye C, Jin G, Fu Z (2010) Effects of streptomycin on growth of algae Chlorella vulgaris and Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Toxicol. doi:10.1002/tox.20636
Qu JH (2004) Sensitivity of five kinds of algae to commonly used antibiotics. J Dalian Inst Light Industry 23:111–113
Rioboo C, Prado R, Herrero C, Cid A (2007) Population growth study of the rotifer Brachionus sp. fed with triazine-exposed microalgae. Aquat Toxicol 83:247–253
Sartory DP, Grobbelar JU (1986) Extraction of chlorophyll a from freshwater phytoplankton for spectrophotometric analysis. Hydrobiologia 114:177–187
Sevilla E, Martin-Luna B, Vela L, Bes MT, Fillat MF, Peleato ML (2008) Iron availability affects mcyD expression and microcystin-LR synthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Environ Microbiol 10:2476–2483
Sevilla E, Martin-Luna B, Vela L, Bes MT, Peleato ML, Fillat MF (2010) Microcystin-LR synthesis as response to nitrogen: transcriptional analysis of the mcyD gene in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Ecotoxicology 19:1167–1173
Sinha RP, Häder DP (2008) UV-protectants in cyanobacteria. Plant Sci 174:278–289
Straub C, Quillardet P, Vergalli J, de Marsac NT, Humbert JF (2011) A Day in the life of Microcystis aeruginosa strain PCC7806 as revealed by a transcriptomic analysis. PLoS ONE 6:e16208
Su Z, Olman V, Mao F, Xu Y (2005) Comparative genomics analysis of NtcA regulons in cyanobacteria: regulation of nitrogen assimilation and its coupling to photosynthesis. Nucleic Acid Res 33:5156–5171
Utkilen H, Gjolme N (1995) Iron-stimulated toxin production in Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:797–800
Vezie C, Rapala J, Vaitomaa J, Seitsonen J, Sivonen K (2002) Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus on growth of toxic and nontoxic Microcystis strains and on intracellular microcystin concentrations. Microbiol Ecol 43:443–454
Wang Y, Jin H, Deng S, Chen Y, Yu Y (2011) Effects of neodymium on growth and physiological characteristics of Microcystis aeruginosa. J Rare Earth 29:388–395
Watanabe MF, Oishi S (1985) Effects of environmental factors on toxicity of a cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa) under culture conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1342–1344
Xu J, Li M, Mak NK, Chen F, Jiang Y (2011) Triphenyltin induced growth inhibition and antioxidative responses in the green microalga Scenedesmus quadricauda. Ecotoxicology 20:73–80
Zeng J, Yang L, Wang W (2009) Acclimation to and recovery from cadmium and zinc exposure by a freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Toxicol 93:1–10
Zhang SC, Qiu CB, Zhou Y, Jin ZP, Yang H (2011) Bioaccumulation and degradation of pesticide fluroxypyr are associated with toxic tolerance in green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Ecotoxicology 20:337–347
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2010CB126100), the Natural Science Foundation of China (21077093), the Qianjiang talents project of technology office in Zhejiang province (2010R10033), and the Opening project of key laboratory of biogeography and bioresource in arid Land, Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first two authors contributed equally to the article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, H., Pan, X., Chen, J. et al. Analyses of gene expression and physiological changes in Microcystis aeruginosa reveal the phytotoxicities of three environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicology 21, 847–859 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0845-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0845-4