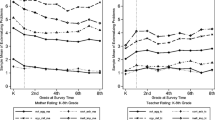
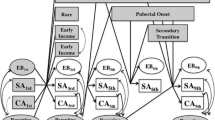
This paper will review the literature on the rate, stability, and outcomes associated with externalizing behavior problems prior to kindergarten entry. Bronfenbrenner’s (The ecology of human development. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press) ecological framework will be used to present the factors related to the onset and persistence of externalizing behavior problems in young children. Behavior problems prior to school entry are somewhat developmentally appropriate and most can be resolved within the classroom or child care setting. Intervention for children with moderate to severe behavior problems in early childhood is crucial because behavior problems are likely to persist into elementary school leading to a variety of social and academic concerns. Steps will be presented to help teachers determine whether or not a referral to a specialist is needed and locate an appropriate specialist.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Aguilar L. A. Sroufe B. Egeland E. Carlson (2000) ArticleTitleDistinguishing the early-onset/persistent and adolescence-onset antisocial behavior types from birth to 16 years Development and Psychopathology 12 109–132
Alexander, K. L., & Entwisle, D. R. (1998). Achievement in the first 2 years of school: Patterns and processes. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 53 (2, Serial No. 218).
K. L. Alexander D. R. Entwisle S. L. Dauber (1993) ArticleTitleFirst-grade classroom behavior: Its short and long-term consequences for school performance Child development 64 801–814
J. M. Barth S. T. Dunlap H. Dane J. E. Lochman K. C. Wells (2004) ArticleTitleClassroom environment influences on aggression, peer relations, and academic focus Journal of School Psychology 42 115–133
N. Bayadar J. Brooks-Gunn (1991) ArticleTitleEffects of maternal employment and child care arrangements on preschoolers’ cognitive and behavioral outcomes: Evidence from the children of the national longitudinal survey of youth Developmental Psychology 27 932–945
J. Belsky (1984) ArticleTitleThe determinants of parenting: A process model Child Development 55 83–96
U. Bronfenbrenner (1979) The ecology of human development Harvard University Press Cambrige, MA
U. Bronfenbrenner (1993) The ecology of cognitive development: Research models and fugitive findings R. H. Wozinak K. Fischer (Eds) Development in context: Acting and thinking in specific environments Erlbaum Hillsdale, NJ 3–44
M. Bubolz M. S. Sontag (1993) Human ecology theory P. Boss W. Doherty R. LarRossa W. Schumm S. Steinmetz (Eds) Sourcebook of family theories and methods: A contextual approach Plenum New York 419–448
S. B. Campbell (1994) ArticleTitleHard-to-manage preschool boys: Externalizing behavior, social competence, and family context at two-year follow-up Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 22 IssueID2 147–166
S. B. Campbell (1995) ArticleTitleBehavior problems in preschool children: A review of recent research Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 36 IssueID1 113–149
S. B. Campbell L. J. Ewing (1990) ArticleTitleFollow-up of hard-to-manage preschoolers: Adjustment at age 9 and predictors of continuing symptoms Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 31 IssueID6 871–889
S. B. Campbell C. L. March E. W. Pierce L. J. Ewing (1991) ArticleTitleHard-to-manage preschool bys: Family context and the stability of externalizing behavior Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 19 IssueID3 301–318
K. A. Clarke-Stewart D. L. Vandell K. McCartney M. T. Owen C. Booth (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of parental separation and divorce on very young children Journal of Family Psychology 14 IssueID2 304–326
A. M. Connell S. H. Goodman (2002) ArticleTitleThe association between psychopathology in fathers versus mothers and children’s internalizing and externalizing behavior problems: A meta-analysis Psychological Bulletin 128 IssueID5 746–773
K. Deater-Deckard K. A. Dodge J. E. Bates G. Pettit (1998) ArticleTitleMultiple risk factors in the development of externalizing behavior problems: Group and individual differences Development and Psychopathology 10 469–493
B. Egeland M. Heister (1995) ArticleTitleThe long-term consequences of infant day-care and mother-infant attachment Child Development 66 74–85
B. Egeland M. Kalkoske N. Gottesman M. F. Erickson (1990) ArticleTitlePreschool behavior problems: Stability and factors accounting for change Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 31 IssueID6 891–909
D. J. English D. B. Marshall A. J. Stewart (2003) ArticleTitleEffects of family violence on child behavior and health during early childhood Journal of Family Violence 18 IssueID1 43–57
J. Fantuzzo L. DaPaola L. Lambert T. Marino G. Anderson S. Sutton (1991) ArticleTitleEffects of interparental violence on the psychological adjustment and competencies of young children Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 59 IssueID2 258–265
C. George M. Main (1979) ArticleTitleSocial interactions of young abused children: Approach, avoidance, and aggression Child Development 50 306–318
R. J. Griffore L. A. Phenice (2001) The language of human ecology: A general systems perspective Kendall/Hunt Dubuque, IA
P. Harland S. A. Reijneveld E. Brugman S. P. Verloove-Vanhorick F. C. Verhulst (2002) ArticleTitleFamily factors and life events as risk factors for behavioural and emotional problems in children European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 11 176–184
R. C. Herrenkohl E. C. Herrenkohl (1981) Some antecedents and developmental consequences of child maltreatment R. Rizley D. Cicchetti (Eds) Developmental perspectives on child maltreatment Jossey-Bass San Fransisco 57–76
R. C. Herrenkohl M. J. Russo (2001) ArticleTitleAbusive early child rearing and early childhood aggression Child Maltreatment 6 IssueID1 3–16
S. H. Howell P. R. Portes J. H. Brown (1997) ArticleTitleGender and age differences in child adjustment to parental separation Journal of Divorce and Remarriage 27 141–158
C. Howes (2000) ArticleTitleSocio-emotional climate in child care, teacher–child relationships and children’s second grade peer relations Social Development 9 191–203
C. Howes E. Smith (1995) ArticleTitleChildren and their child care teachers: Profiles of relationships Social Development 4 44–61
L. R. Huessman L. D. Eron P. W. Yarmel (1987) ArticleTitleIntellectual functioning and aggression Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 52 232–240
P. G. Jaffe M. Suderman D. Reitzel (1992) Child witnesses of marital violence R. T. Ammerman M. Hersen (Eds) Assessment of family violence: A clinical and legal sourcebook Wiley New York 313–331
E. N. Jouriles A. M. Farris R. McDonald (1991) Marital functioning and child behavior: Measuring specific aspects of the marital relationship J. Vincent (Eds) Advances in family intervention, assessment and theory (Vol. 5) JAI Greenwich, CT 25–40
S. G. Kellam L. Xiange R. Mersica C. H. Brown N. Ialongo (1998) ArticleTitleThe effect of the level of aggression in the first grade classroom on the course and malleability of aggressive behavior into middle school Development and Psychopathology 10 165–185
S. Lawrence-Lightfoot (2003) The essential conversation: What parents and teachers can learn from each other Random House New York
A. Loukas H.E. Fitzgerald R.A. Zucker A. Eye Particlevon (2001) ArticleTitleParental alcoholism and co-occuring antisocial behavior: Prospective relationships to externalizing behavior problems in their young sons Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 29 IssueID2 91–106
A. Loukas R. A. Zucker H. E. Fitzgerald J. L. Krull (2003) ArticleTitleDevelopmental trajectories of disruptive behavior problems among sons of alcoholics: Effects of parent psychopathology, family conflict, and child undercontrol Journal of Abnormal Psychology 112 IssueID1 119–131
M. C. Lovejoy (1996) ArticleTitleSocial inferences regarding inattentive-overactive and aggressive child behavior and their effects on teacher reports of discipline Journal of Clinical Child Psychology 25 33–42
K. Lyons-Ruth A. Easterbrooks C. Cibelli (1997) ArticleTitleInfant attachment strategies, infant mental lag, and maternal depressive symptoms: Predictors of internalizing and externalizing problems at age 7 Development and Psychopathology 3 377–396 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0954579400007586
A. Mahoney W. O. Donnelly T. Lewis C. Maynard (2000) ArticleTitleMother and father self-reports of corporal punishment and severe physical aggression toward clinic-referred youth Journal of Clinical Child Psychology 29 266–281
S. McLanahan J. Teitler (1999) The consequences of father absence M. E. Lamb (Eds) Parenting and child development in “nontraditional” families Erlbaum Mahwah, NJ 83–102
V. McLoyd (1998) ArticleTitleSocioeconomic disadvantage and child development American Psychologist 53 185–204
J. Mesman I. L. Bongers H. M. Koot (2001) ArticleTitlePreschool developmental pathways to preadolescent internalizing and externalizing problems Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 42 IssueID5 679–695
D. Nagin R. E. Tremblay (1999) ArticleTitleTrajectories of boys’ physical aggression, opposition, and hyperactivity on the path to physically violent and nonviolent juvenile delinquency Child Development 70 IssueID5 1181–1196
National Clearinghouse on child Abuse and Neglect Information (2000). What is Child Maltreatment? Retrieved March 12, 2002. Available from http://www.calib.com/nccanch/pubs/factsheets/childmal.cfm.
InstitutionalAuthorNameNational Institute of Child Health and Human Development Early Child Care Research Network (2003) ArticleTitleDoes amount of time spent in child care predict socioemotional adjustment during the transition to kindergarten Child Development 7 IssueID4 976–1005
L. Pagani B. Boulerice R. E. Tremblay F. Vitaro (1997) ArticleTitleBehavioural development in children of divorce and remarriage Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines 38 769–781
G. R. Patterson D. Capaldi L. Bank (1992) An early starter model for predicting delinquency D. J. Pepler K. H. Rubin (Eds) The development and treatment of childhood aggression Erlbaum Hillsdale, NJ 139–188
G. Patterson B. DeBaryshe E. Ramsey (1989) ArticleTitleA developmental perspective on antisocial behavior American Psychologist 44 329–335
Peth-Pierce, R. (2001). A good beginning: Sending America’s children to school with the social and emotional competence they need to succeed. [Electronic Version] http: www.nimh.nih.gov/childhp/monograph.pdf.
R. C. Pianta C. B. Caldwell (1990) ArticleTitleStability of externalizing symptoms from kindergarten to first grade and factors related to instability Development and Psychopathology 2 247–258 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0954579400000754
R. C. Pianta S. L. Nimetz E. Bennett (1997) ArticleTitleMother–child relationships, teacher–child relationships, and school outcomes in preschool and kindergarten Early Childhood Research Quarterly 12 263–280
B. Renken B. Egeland D. Marvinney S. Mangelsdorf L. A. Sroufe (1989) ArticleTitleEarly childhood antecedents of aggression and passive withdrawal in early elementary school Journal of Personality 57 257–281
S. E. Rimm-Kaufman R. C. Pianta M. J. Cox (2000) ArticleTitleTeachers’ judgments of problems in the transition to kindergarten Early Childhood Research Quarterly 15 IssueID2 147–166
Rubin, K. H., Bukowski, W., & Parker, J. (1998). Peer interactions, relationships, and groups. In W. Damon (Series Ed.) & N. Eisenbers (Vol. Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Vol. 3. social, emotional, and personality development (5th ed., pp. 619–700). New York: Wiley.
A. Sameroff R. Seifer T. Bartko (1997) Environmental perspectives on adaptation during childhood and adolescence S. S. Luthar J. A. Burack D. Cicchetti J. R. Weisz (Eds) Developmental psychopathology: Perspectives on adjustment, risk, and disorder Cambridge University Press New York 507–526
D. S. Shaw E. B. Winslow E. B. Owens N. Hood (1998) ArticleTitleYoung children’s adjustment to chronic family adversity: A longitudinal study of low-income families Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 37 IssueID5 545–553
J. Solomon C. George A. DeJong (1995) ArticleTitleChildren classified as controlling at age six: Evidence of disorganized representational strategies and aggression at home and at school Development and Psychopathology 2 32–46
M. A. Straus D. A. Donnelly (1994) Beating the devil out of them: Corporal punishment in American families Lexington Books New York
J. Squires D. Bricker E. Twombly (2002) Ages and stages questionnaires: Social-emotional: A parent-completed, child monitoring system for social-emotional behaviors Brookes Baltimore, MD
R. E. Tremblay R. O. Pihl F. Vitaro P. L. Dobkin (1994) ArticleTitlePredicting early onset of male antisocial behavior from preschool behavior Archives of General Psychiatry 15 732–739
J. S. Wallerstein S. Blakeslee (1989) Second chances: Men, women and children a decade after divorce Basic Books New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stacks, A.M. Using an Ecological Framework for Understanding and Treating Externalizing Behavior in Early Childhood. Early Childhood Educ J 32, 269–278 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-004-0754-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-004-0754-8