Abstract
Diet studies are critical for ecosystem-level understanding of fish populations and a move toward ecosystem-based management of marine resources. European hake, Merluccius merluccius, a demersal mesopredator species, is one of the most important commercial fish in the Mediterranean, and as a predatory species it controls the food web. Here, we characterize the diet of M. merluccius with two different analytical methods, visual assessment of stomach contents and DNA metabarcoding. Seasonal and size-based differences in fish prey composition were investigated. Both methods produced complementary results with regard to fish prey contribution of European hake diet. The visual assessment approach showed significant differences between adult and juvenile hakes, while the metabarcoding approach indicated high seasonality in fish prey contribution and richness in its diet. An increase in fish prey diversity was found for both adult and juvenile hakes during the summer. Trachurus sp. was detected as the dominant fish prey in both methods. A broader range of fish prey species was detected by metabarcoding due to its ability to identify highly digested items from the stomach. Combining visual assessment with a novel metabarcoding approach has the potential to improve our understanding of trophic ecology, which can be useful for ecosystem-based management.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The NCBI BioProject database was used to store all of the DNA metabarcoding reads of prey species collected from the stomach contents, with the BioProject ID PRJNA807866.
References
Abella AJ, Caddy JF, Serena F (1997) Do natural mortality and availability decline with age? An alternative yield paradigm for juvenile fisheries illustrated by the hake Merluccius merluccius fishery in the Mediterranean. Aquat Living Resour 10:257–269. https://doi.org/10.1051/alr:1997029
Aldebert Y, Recasens L (1996) Comparison of methods for stock assessment of European hake Merluccius merluccius in the Gulf of Lions (Northwestern Mediterranean). Aquat Living Resour 9:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1051/ALR:1996003
Alonso H, Granadeiro JP, Waap S, Xavier J, Symondson WO, Ramos JA, Catry P (2014) An holistic ecological analysis of the diet of Cory’s shearwaters using prey morphological characters and DNA barcoding. Mol Ecol 23(15):3719–3733
Amundsen P-A, Sánchez-Hernández J (2019) Feeding studies take guts—critical review and recommendations of methods for stomach contents analysis in fish. J Fish Biol 95:1364–1373. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.14151
Andrews S (2010) FastQC: A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/
Arancibia H, Pitcher T, Livingston M (2015) An overview of hake and hoki fisheries: analysis of biological, fishery and economic indicator. In: Aranciaba E (ed), Hakes: Biology and exploitation. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp 324–340
Aritomi A, Andou E, Yonezawa T, Kume G (2017) Monthly occurrence and feeding habits of larval and juvenile Ryukyu-ayu Plecoglossus altivelis ryukyuensis in an estuarine lake and coastal area of the Kawauchi River, Amami-oshima Island, southern Japan. Ichthyol Res 64(2):159–168
Bachiller E, Albo-Puigserver M, Giménez J, Pennino MG, Marí-Mena N, Esteban A, Coll M (2020) A trophic latitudinal gradient revealed in anchovy and sardine from the Western Mediterranean Sea using a multi-proxy approach. Sci Rep 10:17598
Bachiller E, Giménez J, Albo-Puigserver M, Pennino MG, Marí-Mena N, Esteban A, Coll M (2021) Trophic niche overlap between round sardinella (Sardinella aurita) and sympatric pelagic fish species in the Western Mediterranean. Ecol Evol 11(22):16126–16142
Bensch A, Gianni M, Gréboval D, Sanders J, Hjort A (2009) Worldwide review of bottom fisheries in the high seas. FAO, Rome, p 156
Berry O, Bulman C, Bunce M, Coghlan M, Murray DC, Ward RD (2015) Comparison of morphological and DNA metabarcoding analyses of diets in exploited marine fishes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 540:167–181. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps11524
Bilecenoğlu M, Kaya M, Cihangir B, Çiçek E (2014) An updated checklist of the marine fishes of Turkey. Turk J Zool 38(6):901–929. https://doi.org/10.3906/zoo-1405-60
Boyer F, Mercier C, Bonin A, Le Bras Y, Taberlet P, Coissac E (2016) Obitools: a unix-inspired software package for DNA metabarcoding. Mol Ecol Resour 16(1):176–182
Bozzano A, Recasens L, Sartor P (1997) Diet of the European hake Merluccius merluccius (Pisces: Merlucciidae) in the western Mediterranean (Gulf of Lions). Sci Mar 61:1–8
Buckland A, Baker R, Loneragan N, Sheaves M (2017) Standardising fish stomach content analysis: the importance of prey condition. Fish Res 196:126–140
Burgar JM, Murray DC, Craig MD, Haile J, Houston J, Stokes V, Bunce M (2014) Who’s for dinner? High-throughput sequencing reveals bat dietary differentiation in a biodiversity hotspot where prey taxonomy is largely undescribed. Mol Ecol 23(15):3605–3617
Caddy JF (2015) Criteria for sustainable fisheries on juveniles illustrated for Mediterranean hake: control the juvenile harvest, and safeguard spawning refugia to rebuild population fecundity. Sci Mar 79:287–299. https://doi.org/10.3989/scimar0426909A
Carpentieri P, Colloca F, Cardinale M, Belluscio A, Ardizzone GD (2005) Feeding habits of European hake (Merluccius merluccius) in the central Mediterranean Sea. Fish Bull 103(2):411–416
Carreon-Martinez L, Johnson TB, Ludsin SA, Heath DD (2011) Utilization of stomach content DNA to determine diet diversity in piscivorous fishes. J Fish Biol 78(4):1170–1182
Carrozzi V, Di Lorenzo M, Massi D, Titone A, Ardizzone G, Colloca F (2019) Prey preferences and ontogenetic diet shift of European hake Merluccius merluccius (Linnaeus, 1758) in the central Mediterranean Sea. Reg Stud Mar Sci 25:100440. https://doi.org/10.1016/jrsma2018100440
Casey JM, Meyer CP, Morat F, Brandl SJ, Planes S, Parravicini V (2019) Reconstructing hyperdiverse food webs: gut content metabarcoding as a tool to disentangle trophic interactions on coral reefs. Methods Ecol Evol 10(8):1157–1170. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X13206
Cinar ME, Bilecenoğlu M, Yokeş MB, Güçlüsoy H (2021) Pinna nobilis in the South Marmara Islands (Sea of Marmara); It still remains uninfected by the epidemic and acts as egg laying substratum for an alien invader. Medit Mar Sci 22(1):161–168. https://doi.org/10.12681/Mms.25289
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) Primer. PRIMER-e, Plymouth
Cortés E (1997) A critical review of methods of studying fish feeding based on analysis of stomach contents: application to elasmobranch fishes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 54(3):726–738. https://doi.org/10.1139/f96-316
Deagle BE, Jarman SN, Coissac E, Pompanon F, Taberlet P (2014) DNA metabarcoding and the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I marker: Not a perfect match. Biol Lett 10:20140562. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl20140562
Demirel N, Zengin M, Ulman A (2020) First large-scale Eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea stock assessment reveals a dramatic decline. Front Mar Sci 7:103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.00103
Druon JN, Fiorentino F, Murenu M, Knittweis L, Colloca F, Osio C, Mérigot BH, Garofalo G, Mannini A, Jadaud AH, Sbrana MH, Scarcella G, Tserpes G, Peristeraki PH, Carlucci R, Heikkonen J (2015) Modelling of European hake nurseries in the Mediterranean Sea: an ecological niche approach. Prog Oceanogr 130:188–204
D’lglio C, Porcino N, Savoca S, Profeta A, Perdichizzi A, Armeli E, Davide M, Francesco S, Rinelli P, Giordano D (2022) Ontogenetic shift and feeding habits of the European hake (Merluccius merluccius L., 1758) in Central and Southern Tyrrhenian Sea (Western Mediterranean Sea): A comparison between past and present data. Ecol Evol 12:e8634. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.8634
Fanelli E, Rumolo P, Barra M, Basilone G, Genovese S, Bonanno A (2018) Mesoscale variability in the trophic ecology of the European hake Merluccius merluccius in the Strait of Sicily. Hydrobiologia 821:57–72
Ferraton F, Harmelin-Vivien M, Mellon-Duval C, Souplet A (2007) Spatio-temporal variation in diet may affect condition and abundance of juvenile European hake in the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean). Mar Ecol Progr Ser 337:197–208. https://doi.org/10.3354/MEPS337197
Froese R, Pauly D (2022) Editors FishBase World Wide Web electronic publication. www.fishbase.org (05/2022)
Gehri RR, Larson WA, Gruenthal K, Sard NM, Shi Y (2021) eDNA metabarcoding outperforms traditional fisheries sampling and reveals fine-scale heterogeneity in a temperate freshwater lake. Environ DNA 3(5):912–929
Gerking SD (1994) Feeding ecology of fish. Elsevier, eBook ISBN: 9781483288529, 416.
Gerovasileiou V, Akel EK, Akyol O, Alongi G, Azevedo F, Babali N (2017) Zenetos A (2017) New Mediterranean biodiversity records (July, 2017). Med Mar Sci 18(2):355–384. https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.13771
Goldberg CS, Sepulveda A, Ray A, Baumgardt J, Waits LP (2013) Environmental DNA as a new method for early detection of New Zealand mudsnails (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). Freshw Sci 32:792e800
Gucu AC, Bingel F (2011) Hake, Merluccius merluccius L, in the northeastern Mediterranean Sea: a case of disappearance. J Appl Ichthyol 27:1001–1012. https://doi.org/10.1111/J1439-0426201101765X
Gül G, Demirel N (2022) Ontogenetic shift in diet and trophic role of Raja clavata inferred by stable isotopes and stomach content analysis in the Sea of Marmara. J Fish Biol 101:560–572. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.15123
Hajibabaei M, Singer GA, Hebert PD, Hickey DA (2007) DNA barcoding: how it complements taxonomy, Molecular phylogenetics and population genetics. Trends Genet 23:167–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/jtig200702001
Hyslop EJ (1980) Stomach contents analysis—a review of methods and their application. J Fish Biol 17:411–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/j1095-86491980tb02775x
Jakubavičiūtė E, Bergström U, Eklöf JS, Haenel Q, Bourlat SJ (2017) DNA metabarcoding reveals diverse diet of the three-spined stickleback in a coastal ecosystem. PLoS ONE 12(10):e0186929
Kahraman AE, Yıldız T, Uzer U, Karakulak FS (2017) Sexual maturity and reproductive patterns of European Hake Merluccius merluccius (Linneaus, 1758) (Actinopterygii: Merlucciidae) from the Sea of Marmara, Turkey. Acta Zool Bulg 49:2–3s
Kemp BM, Smith DG (2005) Use of bleach to eliminate contaminating DNA from the surface of bones and teeth. Forensic Sci Int 154(1):53–61
Khoukh M, Maynou F (2018) Spatial management of the European hake Merluccius merluccius fishery in the Catalan Mediterranean: simulation of management alternatives with the InVEST model. Sci Mar 82:175–188
Lazic T, Pierri C, Corriero G, Balech B, Cardone F, Deflorio M, Gristina M (2021) Evaluating the efficiency of DNA metabarcoding to analyze the diet of Hippocampus guttulatus (Teleostea: Syngnathidae). Life 11(10):998. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11100998
Leray M, Yang JY, Meyer CP, Mills SC, Agudelo N, Ranwez V, Boehm JT, Machida RJ (2013) A new versatile primer set targeting a short fragment of the mitochondrial COI region for metabarcoding metazoan diversity: application for characterizing coral reef fish gut contents. Front Zool 10:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-9994-10-34
Ley G, Saltzgiver MJ, Dowling TE, Karam AP, Kesner BR, Marsh PC (2014) Use of a molecular assay to detect predation of an endangered fish species. Trans Am Fish Soc 143:49–54
Lloret-Lloret E, Navarro J, Giménez J, López N, Albo-Puigserver M, Pennino MG, Coll M (2020) The seasonal distribution of a highly commercial fish is related to ontogenetic changes in its feeding strategy. Front Mar Sci 7:1068
Martínez-Baños P, Ramírez JG, Demestre M, Maynou F (2018) European hake (Merluccius merluccius) assessment based on size frequencies and basic biological parameters in the SW Mediterranean. Fish Res 205:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/jfishres201804003
Mellon-Duval C, Harmelin-Vivien M, Métral L, Loizeau V, Mortreux S, Roos D, Fromentin JM (2017) Trophic ecology of the European hake in the Gulf of Lions, northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Sci Mar. 81(1):7–18
Miya M, Sato Y, Fukunaga T, Sado T, Poulsen JY, Sato K, Iwasaki W (2015) MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R Soc Open Sci 2(7):150088
Modica L, Bozzano A, Velasco F, Albertelli G, Olaso I (2011) Predation, feeding strategy and food daily ration in juvenile European hake. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 440:177–189. https://doi.org/10.3354/MEPS09341
Morato T, Afonso P, Lourinho P, Nash RDM, Santos RS (2003) Reproductive biology and recruitment of the white sea bream in the Azores. J Fish Biol 63(1):59–72. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1095-8649.2003.00129.x
Murua H (2010) The biology and fisheries of European hake, Merluccius merluccius, in the north-east Atlantic. Adv Mar Biol 58:97–154
Newman SP, Handy RD, Gruber SH (2010) Diet and prey preference of juvenile lemon sharks Negaprion brevirostris. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 398:221–234
Nguyen NP, Warnow T, Pop M, White B (2016) A perspective on 16S rRNA operational taxonomic unit clustering using sequence similarity. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2:16004. https://doi.org/10.1038/npjbiofilms.2016.4
Piroddi C, Colloca F, Tsikliras AC (2020) The living marine resources in the Mediterranean Sea Large Marine Ecosystem. Environ Develop 36:100555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2020.100555
Rätz HJ, Charef A, Abella AJ, Colloca F, Ligas A, Mannini A, Lloret J (2013) A medium-term, stochastic forecast model to support sustainable, mixed fisheries management in the Mediterranean Sea. J Fish Biol 83:921–938. https://doi.org/10.1111/JFB12236
Riccioni G, Stagioni M, Piccinetti C, Libralato S (2018) Metabarcoding approach for the feeding habits of European hake in the Adriatic Sea. Ecol Evol 8:10435–10447. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece34500
Rueda L, Valls M, Hidalgo M, Guijarro B, Esteban A, Massutí E (2019) From trophic ecology to fish condition: contrasting pathways for European hake in the western Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 623:131–143
Saygu İ, Akoglu E, Gül G, Bedikoğlu D, Demirel N (2023) Fisheries impact on the Sea of Marmara ecosystem structure and functioning during the last three decades. Front Mar Sci 9:1076399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.1076399
Sepulveda AJ, Hutchins PR, Forstchen M, Mckeefry MN, Swigris AM (2020) The elephant in the lab (and field): contamination in aquatic environmental DNA studies. Front Ecol Evol 8:609973
Sinopoli M, Fanelli E, D’Anna G, Badalamenti F, Pipitone C (2012) Assessing the effects of a trawling ban on diet and trophic level of hake Merluccius merluccius in the southern Tyrrhenian Sea. Sci Mar 76(4):677–690
Stagioni M, Montanini S, Vallisneri M (2011) Feeding habits of European hake, Merluccius merluccius (Actinopterygii: Gadiformes: Merlucciidae), from the northeastern Mediterranean Sea. Acta Ichthyol Piscat 41(4):277–284. https://doi.org/10.3750/aip2011.41.4.03
Symondson WOC (2002) Molecular identification of prey in predator diets. Mol Ecol 11:627–641. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.2002.01471.x
Symondson WOC, Harwood JD (2014) Special issue on molecular detection of trophic interactions: unpicking the tangled bank. Mol Ecol 23:3601–3604
Taberlet P, Griffin S, Goossens B, Questiau S, Manceau V, Escaravage N, Waits LP, Bouvet J (1996) Reliable genotyping of samples with very low DNA quantities using PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 24:3189e3194
Taberlet P, Bonin A, Zinger L, Coissac E (2018) Environmental DNA for biodiversity research and monitoring. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Tserpes G, Nikolioudakis N, Maravelias C, Carvalho N, Merino G (2016) Viability and management targets of Mediterranean demersal fisheries: the case of the Aegean Sea. PloS One 11:e0168694
Yamamoto S, Masuda R, Sato Y, Sado T, Araki H, Kondoh M, Minamoto M, Miya M (2017) Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals local fish communities in a species-rich coastal sea. Sci Rep 7:40368
Yu DW, Ji Y, Emerson BC, Wang X, Ye C, Yang C, Ding Z (2012) Biodiversity soup: metabarcoding of arthropods for rapid biodiversity assessment and biomonitoring. Methods Ecol Evol 3:613–623. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-210X.2012.00198.x
Zengin M, Polat H, Kutlu S, Dinçer C, Güngör H, Aksoy M, Özgündüz C, Karaarslan E, Firidin S (2004) An investigation on development of deep rose shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris, Lucas, 1846) fishery in the Sea of Marmara. Central Fisheries Research Institute, Trabzon, p 149
Zorica B, Ezgeta-Balić D, Vidjak O, Vuletin V, Šestanović M, Isajlović I, Harro C (2021) Diet composition and isotopic analysis of nine important fisheries resources in the Eastern Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean). Front Mar Sci 8:183. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.609432
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dalida Bedikoğlu, Özkan Çamurcu, Fuat Dursun, Engin Erol, and the crew of Şükriye Ana 2 for their great help during research.
Funding
This study was funded by Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Istanbul University, Turkey [Project number: FBA-2018–30845 and MBA-2021-37457].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GG, EK, and ND: data curation, visualization, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, and writing—reviewing and editing. ND: supervision, funding acquisition, and conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
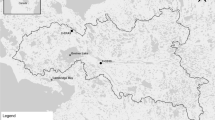
Fish samples in this study were collected through commercial shrimp fisheries in the Sea of Marmara. All fishes were retained and used as per international guidelines for the care and use of animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gül, G., Keskin, E. & Demirel, N. Comparison of fish prey contribution in the diet of European hake by visual assessment of stomach contents and DNA metabarcoding. Environ Biol Fish 106, 613–625 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-023-01398-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-023-01398-x