Abstract
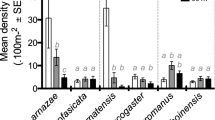
For coral reef fish with an obligate relationship to their habitat, like Pomacentrid damselfish, choosing a suitable home amongst the reef structure is key to survival. A surprisingly small number of studies have examined patterns in adult damselfish distributions compared to other ontogenetic phases. The aim of this study was to determine which reef and coral colony characteristics explained adult damselfish distribution patterns in a Red Sea reef. The characteristics investigated were reef type (continuous or patchy), coral species (seven species of Acropora), and coral morphology (coral size and branching density). The focal damselfish species were Dascyllus aruanus, D. marginatus, Chromis viridis, and C. flavaxilla. Occupancy (presence or absence of resident damselfish), group size and fish species richness were not significantly different between the seven Acropora species. However, within each coral species, damselfish were more likely to occupy larger coral colonies than smaller coral colonies. Occupancy rates were also higher in patchy reef habitats than in continuous sections of the reef, probably because average coral colony size was greater in patchy reef type. Fish group size increased significantly with coral colony volume and with larger branch spacing. Multi-species groups of fish commonly occurred and were increasingly likely with reduced branching density and increased coral size.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ault TR, Johnson CR (1998a) Spatially and temporally predictable fish communities on coral reefs. Ecol Monogr 68:25–50
Ault TR, Johnson CR (1998b) Relationships between habitat and recruitment of three species of damselfish (Pomacentridae) at Heron Reef, Great Barrier Reef. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 223:145–166
Bates D, Maechler M (2011) lme4: Linear mixed effects models using S4 classes. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lme4/
Bay LK, Jones GP, McCormick MI (2001) Habitat selection and aggression as determinants of spatial segregation among damselfish on a coral reef. Coral Reefs 20:289–298
Belmaker J, Ziv Y, Shashar N (2009) Habitat patchiness and predation modify the distribution of a coral-dwelling damselfish. Mar Biol 156:447–454
Belmaker J, Ziv Y, Shashar N (2011) The influence of connectivity on richness and temporal variation of reef fishes. Landsc Ecol 26:587–597
Ben-Tzvi O, Abelson A, Polak O, Kiflawi M (2008) Habitat selection and the colonization of new territories by Chromis viridis. J Fish Biol 73:1005–1018
Ben-Tzvi O, Kiflawi M, Polak O, Abelson A (2009) The effect of adult aggression on habitat selection by settlers of two coral-dwelling damselfishes. PLoS One 4:e5511
Bergman KC, Ohman MC, Svensson S (2000) Influence of habitat structure on Pomacentrus sulfureus, a western Indian Ocean reef fish. Environ Biol Fish 59:243–252
Berumen ML, Hoey AS, Bass WH, Bouwmeester J, Catania D, Cochran JEM, Khalil MT, Miyake S, Mughal MR, Spaet JLY, Saenz-Agudelo P (2013) The status of coral reef ecology research in the Red Sea. Coral Reefs 32:737–748
Bolker B, R Development Core Team (2012) bbmle: Tools for general maximum likelihood estimation. URL http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=bbmle. Accessed 5 April 2012
Bonin MC (2012) Specializing on vulnerable habitat: Acropora selectivity among damselfish recruits and the risk of bleaching-induced habitat loss. Coral Reefs 31:287–297
Booth DJ (1992) Larval settlement patterns and preferences by domino damselfish Dascyllus albisella Gill. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 155:85–104
Booth DJ (1995) Juvenile groups in a coral-reef damselfish: density-dependent effects on individual fitness and population demography. Ecology 76:91–106
Booth DJ (2002) Distribution changes after settlement in six species of damselfish (Pomacentridae) in One Tree Island lagoon, Great Barrier Reef. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 226:157–164
Booth DJ, Wellington G (1998) Settlement preferences in coral-reef fishes: effects on patterns of adult and juvenile distributions, individual fitness and population structure. Aust J Ecol 23:274–279
Chamberlain JA, Graus RR (1975) Water flow and hydromechanical adaptations of branched reef corals. Bull Mar Sci 25:112–125
Chang S, Elkins C, Alley M, Eaton J, Monismith S (2009) Flow inside a coral colony measured using magnetic resonance velocimetry. Limnol Oceanogr 54:1819–1827
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
Coker DJ, Pratchett MS, Munday PL (2009) Coral bleaching and habitat degradation increase susceptibility to predation for coral-dwelling fishes. Behav Ecol 20:1204–1210
Coker DJ, Pratchett MS, Munday PL (2012) Influence of coral bleaching, coral mortality and conspecific aggression on movement and distribution of coral-dwelling fish. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 414–415:62–68
Fishelson L, Popper D, Avidor A (1974) Biosociology and ecology of pomacentrid fishes around the Sinai peninsula (northern Red Sea). J Fish Biol 6:119–133
Frederick JL (1997) Post-settlement movement of coral reef fishes and bias in survival estimates. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 150:65–74
Goldshmid R, Holzman R, Weihs D, Genin A (2004) Aeration of corals by sleep-swimming fish. Limnol Oceanogr 49:1832–1839
Griffith KA, Newberry AT (2008) Effect of flow regime on the morphology of a colonial cnidarian. Invert Bio 127:259–264
Hixon MA, Beets JP (1989) Shelter characteristics and Caribbean fish assemblages: experiments with artificial reefs. Bull Mar Sci 44:666–680
Hixon MA, Beets JP (1993) Predation, prey refuges, and the structure of coral-reef fish assemblages. Ecol Monogr 63:77–101
Holbrook SJ, Forrester GE, Schmitt RJ (2000) Spatial patterns in abundance of a damselfish reflect availability of suitable habitat. Oecologia 122:109–120
Holbrook S, Brooks A, Schmitt R, Stewart H (2008) Effects of sheltering fish on growth of their host corals. Mar Biol 155:521–530
Holbrook SJ, Schmitt RJ, Brooks AJ (2011) Indirect effects of species interactions on habitat provisioning. Oecologia 166:739–749
Kent R, Holzman R, Genin A (2006) Preliminary evidence on group-size dependent feeding success in the damselfish Dascyllus marginatus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 323:299–303
Liberman T, Genin A, Loya Y (1995) Effects on growth and reproduction of the coral Stylophora pistillata by the mutualistic damselfish Dascyllus marginatus. Mar Biol 121:741–746
Lieske E, Myers RF (2004) Coral reef guide red sea. HarperCollins, London
Lowe RJ, Koseff JR, Monismith SG (2005) Oscillatory flow through submerged canopies: 2. Canopy mass transfer. J Geophys Res 11, C10017
Martinez FA, Marschall EA (1999) A dynamic model of group-size choice in the coral reef fish Dascyllus albisella. Behav Ecol 10:572–577
Mass T, Genin A (2008) Environmental versus intrinsic determination of colony symmetry in the coral Pocillopora verrucosa. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 369:131–137
Monismith SG, Genin A (2004) Tides and sea level in the Gulf of Aqaba (Eilat). J Geophys Res 109, C04015
Nanami A, Nishihira M (2001) Survival rates of juvenile coral reef fishes differ between patchy and continuous habitats. Bull Mar Sci 69:1209–1221
Nanami A, Nishihira M (2002) The structures and dynamics of fish communities in an Okinawan coral reef: effects of coral-based habitat structures at sites with rocky and sandy sea bottoms. Environ Biol Fish 63:353–372
Nanami A, Nishihira M (2003) Effects of habitat connectivity on the abundance and species richness of coral reef fishes: comparison of an experimental habitat established at a rocky reef flat and at a sandy sea bottom. Environ Biol Fish 68:183–196
Nanami A, Nishihira M (2005) Species-specific habitat distribution of coral reef fish assemblages in relation to habitat characteristic in an Okinawan coral reef. Environ Biol Fish 72:55–65
Nemeth RS (1998) The effect of natural variation in substrate architecture on the survival of juvenile bicolor damselfish. Environ Biol Fish 53:129–141
Nemeth RS (2007) Spatial patterns of bicolor damselfish populations in Jamaica and St. Croix are determined by similar post-settlement processes. Proc 8th Int Coral Reef Sym 1:1017–1022
Noonan SHC, Jones GP, Pratchett MS (2012) Coral size, health and structural complexity: effects on the ecology of a coral reef damselfish. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 456:127–237
Ormond RFG, Roberts JM, Jan R-Q (1996) Behavioural differences in microhabitat use by damselfishes (Pomacentridae): implications for reef fish biodiversity. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 202:85–95
Pereira PHC, Feitosa JLL, Mederos DV, Ferreira BP (2013) Reef fishes foraging facilitation behavior: increasing the access to a food resource. Acta Ethol 15:53–56
Pinnegar JK, Polunin NVC (2006) Planktivorous damselfish support significant nitrogen and phosphorus fluxes to Mediterranean reefs. Mar Biol 148:1089–1099
R Development Core Team (2012) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, ISBN 3-900051-07-0. Available at http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 5 April 2012
Reidenbach MA, Koseff JR, Monismith SG, Steinbuck JV, Genin A (2006) The effects of waves and morphology on mass transfer within branches reef corals. Limnol Oceanogr 51:1134–1141
Robertson DR (1996) Interspecific competition controls abundance and habitat use of territorial Caribbean damselfishes. Ecology 77:885–899
Sackley PG, Kaufman LS (1996) Effect of predation on foraging height in a planktivorous coral reef fish, Chromis nitida. Copeia 1996:726–729
Sale PF (1971) Extremely limited home range in a coral reef fish, Dascyllus aruanus (Pisces: Pomacentridae). Copeia 1971:324–327
Sale PF (1972a) Influence of corals in the dispersion of Pomacentrid fish, Dascyllus aruanus. Ecology 53:741–744
Sale PF (1972b) Effects of cover on agonistic behavior of a reef fish: a possible spacing mechanism. Ecology 53:753–758
Sale PF (1991) Reef fish communities: Open nonequilibrial systems. In: Sale PF (ed) The ecology of fishes on coral reefs. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 564–598
Shpigel M (1982) Niche overlap among two species of coral dwelling fishes of the genus Dascyllus (Pomacentridae). Environ Biol Fish 7:65–68
Shpigel M, Fishelson L (1986) Behavior and physiology of coexistence in two species of Dascyllus (Pomacentridae, Teleostei). Environ Biol Fish 17:253–265
Shulman MJ (1984) Resource limitation and recruitment patterns in a coral reef fish assemblage. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 74:85–109
Simpson SD, Jeffs A, Montgomery JC, McCauley RD, Meekan MG (2008) Nocturnal relocation of adult and juvenile coral reef fishes in response to reef noise. Coral Reefs 27:97–104
Tolimieri N (1998) Contrasting effects of microhabitat use on large-scale adult abundance in two families of Caribbean reef fishes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 167:227–239
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern applied statistics with S, 4th edn. Springer, New York. ISBN 0-387-95457-0
Weber JN, Woodhead PMJ (1970) Ecological studies of the coral predator Acanthaster planci in the South Pacific. Mar Biol 6:12–17
Wilson SK, Burgess SC, Cheal AJ, Emslie M, Fisher R, Miller I, Polunin NVC, Sweatman HPA (2008) Habitat utilization by coral reef fish: implications for specialists vs. generalists in a changing environment. J Anim Ecol 77:220–228
Wyatt ASJ, Waite AM, Humphries S (2012) Stable isotope analysis reveals community-level variation in fish trophodynamics across a fringing coral reef. Coral Reefs 31:1029–1044
Acknowledgments
We thank K. Dunlop, M. Dirnwoeber, R. Nager, D. Haydon, and the staff at the Dahab Marine Research Center and DiveIn Center (in particular K. Jentsch, A. Tischer, H. Lange, T. von Arx, M. Gold, Ibraham, and Salem) for their generous assistance. Funding for this study was provided by the University of Glasgow, Glasgow Natural History Society, Royal Geographical Society (with IBG), and the Gilchrist Trust. This work was carried out under a permit from the Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadler, L.E., McNeill, D.C., Alwany, M.A. et al. Effect of habitat characteristics on the distribution and abundance of damselfish within a Red Sea reef. Environ Biol Fish 97, 1265–1277 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-013-0212-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-013-0212-9