Abstract
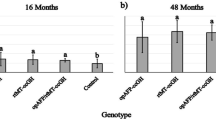
Calcareous otoliths in the inner ears of fishes are necessary for proper hearing and vestibular function. Sagittal otoliths are usually composed of the calcium carbonate polymorph aragonite but may contain the polymorph vaterite, a phenomenon called otolith crystallization. The causes of otolith crystallization are poorly understood. Thyroid hormone (TH) can influence the chemical microenvironment and structure of the inner ear, suggesting that TH may influence otolith crystallization. The present study examined the effect of exogenous TH treatment on sagittal otolith crystallization and growth in larval and juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. In the first experiment, 110–179 day-old fish raised from TH-treated oocytes had significantly fewer sagittal otoliths containing the crystalline calcium carbonate polymorph vaterite as compared to untreated fish. Vaterite-containing otoliths were significantly longer than those containing the typical polymorph aragonite, although there was no effect of TH treatment on otolith length. In the second experiment, juveniles immersed in an exogenous solution of TH for 6 weeks had slightly longer otoliths (relative to fish length) than age-matched controls, but this effect was not significant. This juvenile population had a very high percentage (88.3 %) of vaterite sagittae overall and this percentage did not change significantly with treatment, suggesting the switch from aragonite to vaterite occurred prior to inclusion of the fish in the study. These results suggest that early manipulation of TH levels may affect calcium carbonate deposition on the otolith but that later TH exposure is unable to restore typical otolith composition.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison WT, Dann SG, Veldhoen KM, Hawryshyn CW (2006) Degeneration and regeneration of ultraviolet cone photoreceptors during development in rainbow trout. J Comp Neurol 499:702–715
Bowen CA, Bronte CR, Argyle RL, Adams JV, Johnson JE (1999) Vateritic sagitta in wild and stocked lake trout: applicability to stock origin. Trans Am Fish Soc 128:929–938
Browman HI, Hawryshyn CW (1992) Thyroxine induces a precocial loss of ultraviolet sensitivity in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Teleostei). Vision Res 32:2303–2312
Browman HI, Hawryshyn CW (1994) The developmental trajectory of ultraviolet photosensitivity in rainbow trout is altered by thyroxine. Vision Res 11:1397–1406
Brown SB, MacLatchy DL, Hara TJ, Eales JG (1991) Effects of cortisol on aspects of 3,5,30-triiodo-L-thyronine metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Gen Comp Endocrinol 81:207–216
Campana SE (1999) Chemistry and composition of fish otoliths: pathways, mechanisms and applications. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 188:263–297
Forrest D, Reh TA, Rüsch H (2002) Neurodevelopmental control by thyroid hormone receptors. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:49–56
Gauldie RW (1986) Vaterite otoliths from Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). N Z J Mar Freshw Res 20:209–217
Hoar W (1988) The physiology of smelting salmonids. In: Hoar W, Randall D (eds) Fish physiology. Academic, San Diego, pp 275–343
Leak JC (1986) The relationship of standard length and otolith diameter in larval bay anchovy, Anchoa mitchilli (Val.). A shrinkage estimator. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 95:167–172
Oliveria AM, Farina M (1996) Vaterite, calcite, and aragonite in the otoliths of three species of Piranha. Naturwissenschaften 83:133–135
Oxman DS, Barnett-Johnson R, Smith ME, Coffin A, Miller DL, Josephson R, Popper AN (2007) The effect of vaterite deposition on sound reception, otolith morphology, and inner ear sensory epithelia in hatchery-reared Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytshca). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 64:1469–1478
Palmer AR (1994) Fluctuating asymmetry analyses: a primer. In: Markow TA (ed) Developmental instability: its origins and evolutionary implications. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 335–364
Raine JC, Leatherland JF (2003) Trafficking of L-triiodothyronine between ovarian fluid and oocytes of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 136:267–274
Raine JC, Cameron C, Vijayan MM, Lamarre J, Leatherland JF (2004) The effect of elevated oocyte triiodothyronine content on development of rainbow trout embryos and expression of mRNA encoding for thyroid hormone receptors. J Fish Biol 65:206–226
Raine JC, Coffin AB, Hawryshyn CW (2010) Systemic thyroid hormone is necessary and sufficient to induce ultraviolet-sensitive cone loss in the juvenile rainbow trout retina. J Exp Biol 213:493–501
Raine JC, Coffin AB, Hawryshyn CW (2011) In ovo thyroxine exposure alters later UVS cone loss in juvenile rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 214:2248–2257
Raz Y, Kelley MW (1997) Effects of retinoid and thyroid receptors during development of the inner ear. Semin Cell Dev Biol 8:257–264
Redding JM, Schreck CB, Birks EK, Ewing RD (1984) Cortisol and its effects on plasma thyroid hormone and electrolyte concentrations in fresh water and during seawater acclimation in yearling coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch. Gen Comp Endocrinol 56:146–155
Redding JM, deLuze A, Leloup-Hatey J, Leloup J (1986) Suppression of plasma thyroid hormone concentrations by cortisol in the European eel Anguilla anguilla. Comp Biochem Physiol 83:409–413
Romanek CS, Gauldie RW (1996) A predictive model of otolith growth in fish based on the chemistry of the endolymph. Comp Biochem Physiol 114A:71–79
Schreiber AM, Wang X, Tan Y, Sievers Q, Sievers B, Lee M, Burral K (2010) Thyroid hormone mediates otolith growth and development during flatfish metamorphosis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 169:130–137
Shiao J, Hwang P (2004) Thyroid hormones are necessary for teleostean otolith growth. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 278:271–278
Shiao J, Hwang P (2006) Thyroid hormones are necessary for metamorphosis of tarpon Megalops cyprinoides leptocephali. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 331:121–132
Shiao J, Wu S, Hwang Y, Wu D, Hwang P (2008) Evaluation of thyroid-mediated otolith growth of larval and juvenile tilapia. J Exp Biol 211:1919–1926
Somarakis S, Kostikas I, Peristeraki N, Tsimenides N (1997) Fluctuating asymmetry in the otoliths of larval anchovy Engraulis encrasicolus and the use of developmental instability as an indicator of condition in larval fish. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 151:191–203
Sweeting RM, Beamish RJ, Noakes DJ, Neville CM (2003) Replacement of wild coho salmon by hatchery-reared coho salmon in the Strait of Georgia over the past three decades. N Am J Fish Manag 23:492–502
Sweeting RM, Beamish RJ, Neville CM (2004) Crystalline otoliths in teleosts: comparison between hatchery and wild coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) in the Strait of Georgia. Rev Fish Biol Fish 14:361–369
Takabayashi A, Ohmura-Iwasaki T (2003) Functional asymmetry estimated by measurements of otolith in fish. Biol Sci Space 17(4):293–297
Tomás J, Geffen AJ (2003) Morphometry and composition of aragonite and vaterite otoliths of deformed laboratory reared juvenile herring from two populations. J Fish Biol 63:1383–1401
Tomás J, Allen AJ, Berges J (2004) Analysis of the soluble matrix of vaterite otoliths of juvenile herring (Clupea harengus): do crystalline otoliths have less protein? Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 139:301–308
Walpita CN, Grommen SVH, Darras VM, Van der Geyten S (2007) The influence of stress on thyroid hormone production and peripheral deiodination in the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 150:18–25
Wang X, Tan Y, Sievers Q, Lee M, Burrall K, Schreiber AM (2011) Thyroid hormone-responsive genes mediate otolith growth and development during flatfish metamorphosis. Comp Biochem Physiol A 158:163–168
Wangemann P, Nakaya K, Wu T, Maganti RJ, Itza EM, Sanneman JD, Harbidge DG, Billings S, Marcus DC (2007) Loss of cochlear HCO −3 secretion causes deafness via endolymphatic acidification and inhibition of Ca2+ reabsorption in a Pendred syndrome mouse model. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292:F1345–F1353
Acknowledgements
We thank the University of Washington Center for Statistical Consulting for analytical assistance and D. Oxman for insightful discussions on otolith growth and crystallization and for critical reading of an early draft of this manuscript. We also thank M. Burke and the Alma Aquaculture Research Station for providing the rainbow trout gametes used in this study, and two anonymous reviewers for suggestions that greatly improved the manuscript. This research was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada Discovery Grant, Canada Research Chair Program, Canada Foundation for Innovation and Ontario Innovation Trust to CWH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coffin, A.B., Raine, J.C. & Hawryshyn, C.W. Exposure to thyroid hormone in ovo affects otolith crystallization in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss . Environ Biol Fish 95, 347–354 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-012-0007-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-012-0007-4