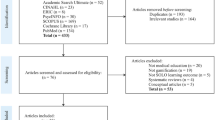
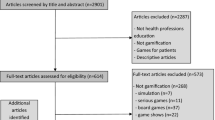
Abstract
Engaging activities are increasingly a staple in higher education. Professional programs, including business, engineering, and healthcare, rely on engaging activities to better prepare students for their future careers. Experiential learning can be achieved through a wide variety of approaches that can generally be classified as hands-on activities, such as internships, practicums, and medical practice models, or as high-tech tools, such as simulations, games, and exercises delivered via an electronic medium. It is unlikely that all activities produce equally valuable outcomes under all course settings and disciplines. The purpose of this study is to specifically compare a computer-based simulation to hands-on based activities. An empirical structural equation model has been estimated developing pathways between dimensions of gamification, measures of satisfaction, scales of student attitudes, and measures of student loyalty. The model was estimated using undergraduate hospitality students as part of business coursework in a large U.S. public university. Findings validate significant paths. Based on the findings, this study proposes theoretical and pedagogical implications for faculty in higher education.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar-Castillo, L., Clavijo-Rodriguez, A., Hernández-López, L., De Saa-Pérez, P., & Pérez-Jiménez, R. (2020). Gamification and deep learning approaches in higher education. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 29, 100290.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179–211
Aleksic-Maslac, K., Sinkovic, B., & Vranesic, P. (2017). Influence of gamification on student engagement in education. International Journal of Education and Learning Systems, 2, 76–82.
Anderson, J. C., & Gerbing, D. W. (1992). Assumptions and comparative strengths of the two-step approach: Comment on Fornell and Yi. Sociological Methods & Research, 20(3), 321–333
Annamdevula, S., & Bellamkonda, R. S. (2016). The effects of service quality on student loyalty: The mediating role of student satisfaction. Journal of Modelling in Management, 11(2), 446–462
Astalini, A., Kurniawan, D. A., Kurniawan, N., & Anggraini, L. (2019). Evaluation of student’s attitude toward science in Indonesia. Open Journal for Educational Research, 3(1), 1–12
Aylesworth, A. B., & MacKenzie, S. B. (1998). Context is key: The effect of program-induced mood on thoughts about the ad. Journal of Advertising, 27(2), 17–31
Bagozzi, R. P., & Yi, Y. (1990). Assessing method variance in multitrait-multimethod matrices: The case of self-reported affect and perceptions at work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 75(5), 547–560
Bai, S., Hew, K. F., & Huang, B. (2020). Does gamification improve student learning outcome? Evidence from a meta-analysis and synthesis of qualitative data in educational contexts. Educational Research Review, 30, 100322
Chandra, T., Ng, M., Chandra, S., & Priyono, I. (2018). The effect of service quality on student satisfaction and student loyalty: An empirical study. Journal of Social Studies Education Research, 9(3), 109–131
Eppmann, R., Bekk, M., & Klein, K. (2018). Gameful experience in gamification: Construction and validation of a gameful experience scale [GAMEX]. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 43, 98–115
Fabian, K., Topping, K. J., & Barron, I. G. (2018). Using mobile technologies for mathematics: Effects on student attitudes and achievement. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(5), 1119–1139
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50
Francis, P. (2021). One year later: Are higher ed pandemic tech investments here to stay? Forbes, Mar 7, 2021.
Fuad, M., Deb, D., Etim, J., & Gloster, C. (2018). Mobile response system: A novel approach to interactive and hands-on activity in the classroom. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(2), 493–514
Fu, X., Kang, J., & Tasci, A. (2017). Self-congruity and flow as antecedents of attitude and loyalty towards a theme park brand. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 34(9), 1261–1273
Gao, B. W., Jiang, J., & Tang, Y. (2020). The effect of blended learning platform and engagement on students’ satisfaction——the case from the tourism management teaching. Journal of Hospitality Leisure Sport & Tourism Education, 27, 100272
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (1998). Multivariate data analysis. Prentice Hall
Hofacker, C. F., De Ruyter, K., Lurie, N. H., Manchanda, P., & Donaldson, J. (2016). Gamification and mobile marketing effectiveness. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 34, 25–36
Holbeck, R., & Hartman, J. (2018). Efficient strategies for maximizing online student satisfaction: Applying technologies to increase cognitive presence, social presence, and teaching presence. Journal of Educators Online, 15(3), n3
Huang, B., & Hew, K. F. (2018). Implementing a theory-driven gamification model in higher education flipped courses: Effects on out-of-class activity completion and quality of artifacts. Computers & Education, 125, 254–272
Hung, A. C. Y. (2017). A critique and defense of gamification. Journal of Interactive Online Learning, 15(1), 57–72
Huotari, K., & Hamari, J. (2017). A definition for gamification: Anchoring gamification in the service marketing literature. Electronic Markets, 27(1), 21–31
Hwang, J., & Choi, L. (2020). Having fun while receiving rewards?: Exploration of gamification in loyalty programs for consumer loyalty. Journal of Business Research, 106, 365–376
Inoue, Y., Funk, D. C., & McDonald, H. (2017). Predicting behavioral loyalty through corporate social responsibility: The mediating role of involvement and commitment. Journal of Business Research, 75, 46–56
Iordanova, E. (2017). Tourism destination image as an antecedent of destination loyalty: The case of Linz, Austria. European Journal of Tourism Research, 16, 214–232
Isabelle, D. A. (2020). Gamification of entrepreneurship education. Decision Sciences Journal of Innovative Education, 18(2), 203–223
James, L. T., & Casidy, R. (2018). Authentic assessment in business education: Its effects on student satisfaction and promoting behaviour. Studies in Higher Education, 43(3), 401–415
Jayawickreme, E., Tsukayama, E., & Kashdan, T. B. (2017). Examining the effect of affect on life satisfaction judgments: A within-person perspective. Journal of Research in Personality, 68, 32–37
Jennett, C., Cox, A. L., Cairns, P., Dhoparee, S., Epps, A., Tijs, T., & Walton, A. (2008). Measuring and defining the experience of immersion in games. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 66(9), 641–661
Jöreskog, K. G., & Sörbom, D. (1993). LISREL 8: Structural equation modeling with the SIMPLIS command language. Scientific Software International.
Kaushal, V., & Ali, N. (2020). University reputation, brand attachment and brand personality as antecedents of student loyalty: A study in higher education context. Corporate Reputation Review, 23(4), 254–266.
Kim, M., Koo, D. W., Shin, D. J., & Lee, S. M. (2017). From servicescape to loyalty in the medical tourism industry: A medical clinic’s service perspective. Inquiry: The Journal of Health Care Organization Provision and Financing, 54, 1–16
Kim, M. S., & Stepchenkova, S. (2018). Examining the impact of experiential value on emotions, self-connective attachment, and brand loyalty in Korean family restaurants. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 19(3), 298–321
Kotler, P. (2003). Marketing insights from A to Z: 80 concepts every manager needs to know. Wiley
Ladhari, R., Souiden, N., & Dufour, B. (2017). The role of emotions in utilitarian service settings: The effects of emotional satisfaction on product perception and behavioral intentions. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 34, 10–18
Leclercq, T., Poncin, I., & Hammedi, W. (2020). Opening the black box of gameful experience: Implications for gamification process design. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 52, 101882
Lee, K. M. (2004). Presence, explicated. Communication Theory, 14(1), 27–50
Lee, M. J. M., Lee, P. C., Dopson, L. R., & Yoon, S. (2020). What dimensions of career expos have the most impact on student satisfaction? Journal of Hospitality Leisure Sport & Tourism Education, 27, 100263
Nunnally, J., & Bernstein, I. (1994). Psychometric theory. McGraw Hill
Oliver, R. L. (1980). A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. Journal of Marketing Research, 17(4), 460–469
Panigyrakis, G., Panopoulos, A., & Koronaki, E. (2020). Looking for luxury CSR practices that make more sense: The role of corporate identity and consumer attitude. Journal of Marketing Communications, 26(6), 666–684
Pechenkina, E., Laurence, D., Oates, G., Eldridge, D., & Hunter, D. (2017). Using a gamified mobile app to increase student engagement, retention and academic achievement. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 14(1), 1–12
Pham, L., Limbu, Y. B., Bui, T. K., Nguyen, H. T., & Pham, H. T. (2019). Does e-learning service quality influence e-learning student satisfaction and loyalty? Evidence from Vietnam. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16(1), 1–26
Plass, J. L., Homer, B. D., & Kinzer, C. K. (2015). Foundations of game-based learning. Educational Psychologist, 50(4), 258–283
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2012). Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annual Review of Psychology, 63, 539–569
Podsakoff, P. M., & Organ, D. W. (1986). Self-reports in organizational research: Problems and prospects. Journal of Management, 12(4), 531–544
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2008). Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behavior Research Methods, 40(3), 879–891
Purgina, M., Mozgovoy, M., & Blake, J. (2020). WordBricks: Mobile technology and visual grammar formalism for gamification of natural language grammar acquisition. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 58(1), 126–159
Rachels, J. R., & Rockinson-Szapkiw, A. J. (2018). The effects of a mobile gamification app on elementary students’ Spanish achievement and self-efficacy. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 31(1–2), 72–89
Sanchez, D. R., Langer, M., & Kaur, R. (2020). Gamification in the classroom: Examining the impact of gamified quizzes on student learning. Computers & Education, 144, 103666
Snijders, I., Wijnia, L., Rikers, R. M., & Loyens, S. M. (2020). Building bridges in higher education: Student-faculty relationship quality, student engagement, and student loyalty. International Journal of Educational Research, 100, 101538
Su, C. H., & Cheng, C. H. (2015). A mobile gamification learning system for improving the learning motivation and achievements. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 31(3), 268–286
Taghizadeh, M., & Hajhosseini, F. (2021). Investigating a blended learning environment: Contribution of Attitude, interaction, and quality of teaching to satisfaction of graduate students of TEFL. The Asia-Pacific EducationResearcher, 30(5), 459–469.
Tan, A. L., & Wong, H. M. (2012). ‘Didn’t get expected answer, rectify it.’: Teaching science content in an elementary science classroom using hands-on activities. International Journal of Science Education, 34(2), 197–222
Tyrrell, J. T. (1989). Tourism development simulation model: The game. University of Rhode Island, Department of Resource Economics, Office of Travel, Tourism and Recreation
van Roy, R., & Zaman, B. (2018). Need-supporting gamification in education: An assessment of motivational effects over time. Computers & Education, 127, 283–297
van Roy, R., & Zaman, B. (2019). Unravelling the ambivalent motivational power of gamification: A basic psychological needs perspective. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 127, 38–50
Wagner, M. (2011). Corporate performance implications of extended stakeholder management: New insights on mediation and moderation effects. Ecological Economics, 70(5), 942–950
Weli, W. (2019). Student satisfaction and continuance model of enterprise resource planning (ERP) system usage. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 14(1), 71–83
Xi, N., & Hamari, J. (2019). Does gamification satisfy needs? A study on the relationship between gamification features and intrinsic need satisfaction. International Journal of Information Management, 46, 210–221
Yao, T., Qiu, Q., & Wei, Y. (2019). Retaining hotel employees as internal customers: Effect of organizational commitment on attitudinal and behavioral loyalty of employees. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 76, 1–8
Zhang, H., Fu, X., Cai, L. A., & Lu, L. (2014). Destination image and tourist loyalty: A meta-analysis. Tourism Management, 40, 213–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M., Knotts, T.L. & Albers, N.D. Hands-on activity vs. high-tech tools in the higher education classroom to improve student satisfaction and loyalty in professional programs. Educ Inf Technol 27, 12147–12177 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11124-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11124-2